87
• Configure the same region name, revision level and VLAN-to-instance mappings on the two devices,
assigning them to the same region.
Configuring the no agreement check function
To make the no agreement check feature take effect, enable it on the root port.
To configure no agreement check:
To do... Use the command... Remarks
1. Enter system view
system-view —
Enter Ethernet interface
view or Layer 2
aggregate interface
view
interface interface-type
interface-number
2. Enter
interface or
port group
view
Enter port group view
port-group manual port-group-
name
Required.
Use either command.
3. Enable no agreement check
stp no-agreement-check
Required.
Disabled by default.
No agreement check configuration example
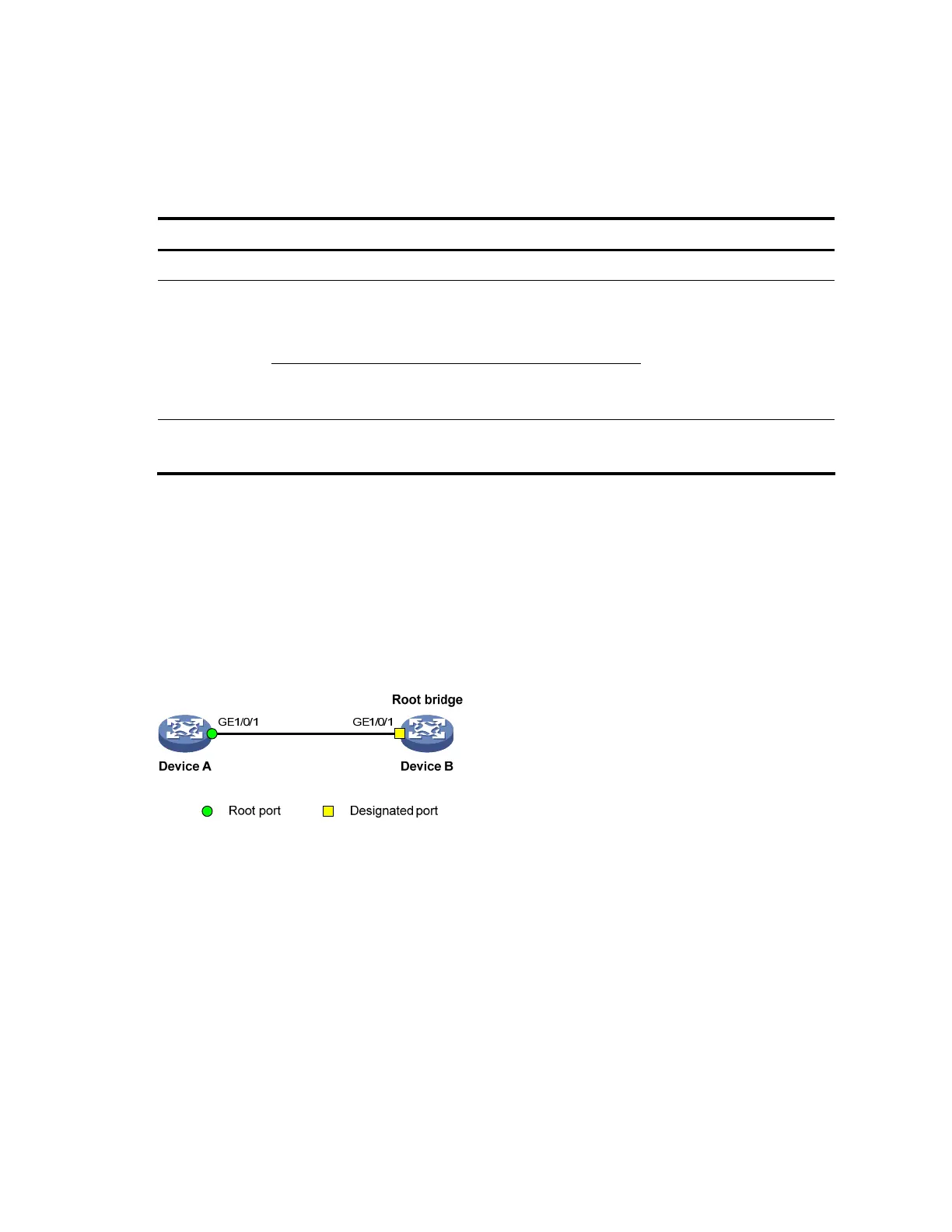
1. Network requirements
As shown in Figure 26:
• D
evice A connects to Device B, a third-party device that has different MSTP implementation. Both
devices are in the same region.
• Device B is the regional root bridge, and Device A is the downstream device.
Figure 26 No agreement check configuration
2. Configuration procedure
# Enable no agreement check on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp no-agreement-check
Configuring TC snooping
Figure 27 shows a TC snooping application scenario. Device A and Device B are both IRF-enabled
switches and form an IRF virtual device; they operate at the distribution layer and do not have STP
enabled. The IRF virtual device formed by Device A and Device B connect to multiple access-layer
customer networks, such as Customer 1 and Customer 2. Device C, Device D, and Device E in customer
network Customer 1 are all enabled with STP. Customer 1 is dual-uplinked to the IRF virtual device for

 Loading...
Loading...