Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively
Using QoS Classifiers To Configure QoS for Outbound Traffic
b. Configure the switch to mark a specific type of inbound traffic with
that DSCP (and thus create a policy for that traffic type).
c. Configure the internal switches in your LAN to honor the policy.
(For example, you could configure an edge switch to assign a codepoint
of 000001 to all packets received from a specific VLAN, and then handle
all traffic with that codepoint at high priority.)
For a codepoint listing and the commands for displaying and changing the
DSCP Policy table, refer to “Differentiated Services Codepoint (DSCP)
Mapping” on page 6-58.
Notes On switches covered in this guide, “mixing” ToS DSCP policies and 802.1p
priorities is not recommended. Refer to the Note on page 6-10.
■ Precedence Bits: This element is a subset of the DSCP and is comprised
of the upper three bits of the ToS byte. When configured to do so, the
switch uses the precedence bits to determine a priority for handling the
associated packet. (The switch does not change the setting of the prece-
dence bits.) Using the ToS Precedence bits to prioritize IPv4 packets relies
on priorities set in upstream devices and applications.
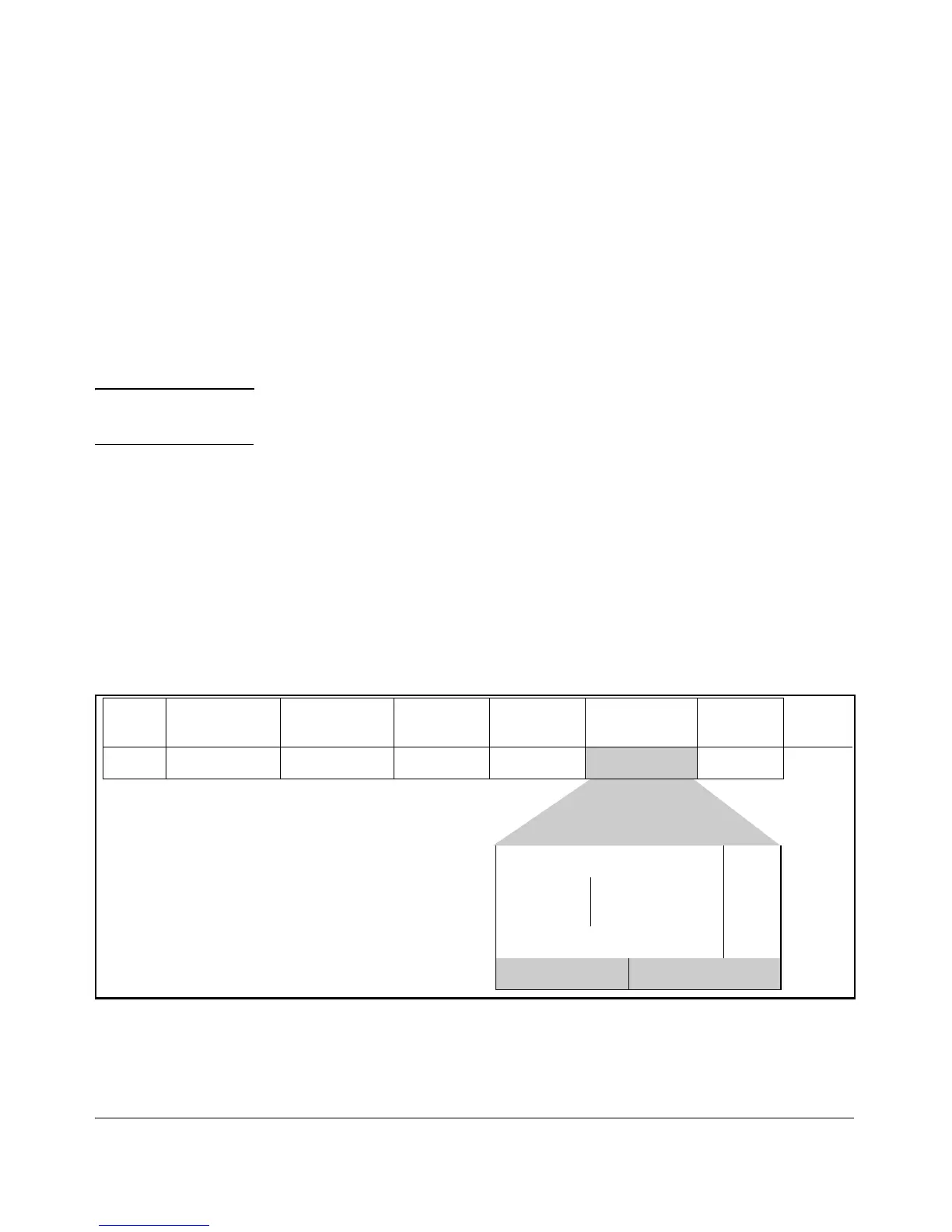
Figure 6-21 shows an example of the ToS byte in the header for an IPv4 packet,
and illustrates the diffserv bits and precedence bits in the ToS byte. (Note that
the Precedence bits are a subset of the Differentiated Services bits.)
Field: Destination
MAC Address
Source MAC
Address
802.1Q Field Type &
Version
ToS Byte …
Packet: FF FF FF FF FF FF 08 00 09 00 00 16 08 00 45
E 0 ...
Differentiated Services Codepoint
Rsvd.
Precedence
Bits
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
E 0
Figure 6-21. The ToS Codepoint and Precedence Bits
6-44
 Loading...
Loading...











