208
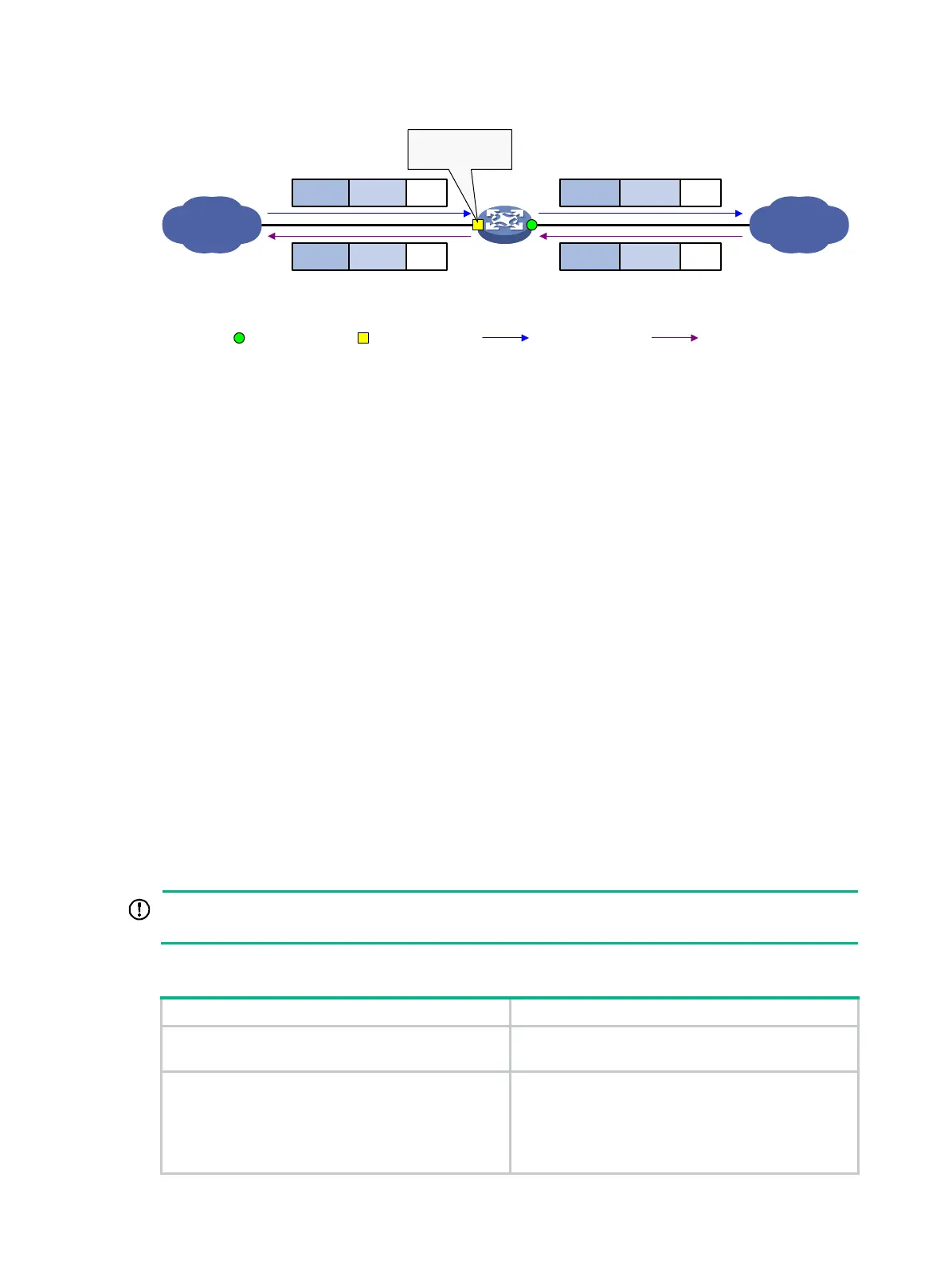
Figure 65 Two-to-two VLAN mapping implementation
General configuration restrictions and guidelines
When you configure VLAN mapping, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
• When you configure one-to-two VLAN mapping on a QinQ-enabled port, the switch operates as
follows:
{ If a packet matches the one-to-two VLAN mapping, the switch tags the packet with the
SVLAN that is specified in the VLAN mapping.
{ If a packet does not match the one-to-two VLAN mapping, the switch tags the packet with
the PVID.
• When you configure one-to-one or many-to-one VLAN mapping on a QinQ-enabled port, the
switch operates as follows:
{ If a packet matches the one-to-one or many-to-one VLAN mapping, the switch replaces the
CVLAN tag with the SVLAN tag specified in the VLAN mapping.
{ If a packet does not match the one-to-one or many-to-one VLAN mapping, the switch tags
the packet with the PVID.
For more information about QinQ, see "Configuring QinQ."
• Y
ou can configure both VLAN mapping and a QoS policy for VLAN tagging. The QoS policy
takes effect if a configuration conflict occurs. For information about QoS policies, see ACL and
QoS Configuration Guide.
VLAN mapping configuration task list
IMPORTANT:
Use the appropriate VLAN mapping methods for the devices in the network.
To configure VLAN mapping:
Tasks at a glance Remarks
Configuring one-to-one VLAN mapping
Configure one-to-one VLAN mapping on the
wiring-closet switch, as shown in Figure 59.
Configuring many-to-one VLAN mapping
• Configuring many-to-one VLAN mapping in a
net
work with dynamic IP address assignment
• Configuring many-to-one VLAN mapping in a
net
work with static IP address assignment
Configure many-to-one VLAN mapping on the
campus switch, as shown in Figure 59.
Compl
ete one of the tasks based on the IP address
assignment method.
Network-side port Customer-side port
Uplink traffic Downlink traffic
Customer
network
SP network
SVLAN DataCVLAN
SVLAN DataCVLAN
Two-to-two VLAN
mapping
DataCVLAN’SVLAN’
DataCVLAN’SVLAN’

 Loading...
Loading...











