6 — CANopen COMMUNICATIONS
pg. 47
Return to TOC Curtis Model 3401T – August 2022
MESSAGE COB-IDS
CAN messages are identified by 11-bit COB-IDs. The device does not support 29-bit COB-IDs.
EXPEDITED SDOS
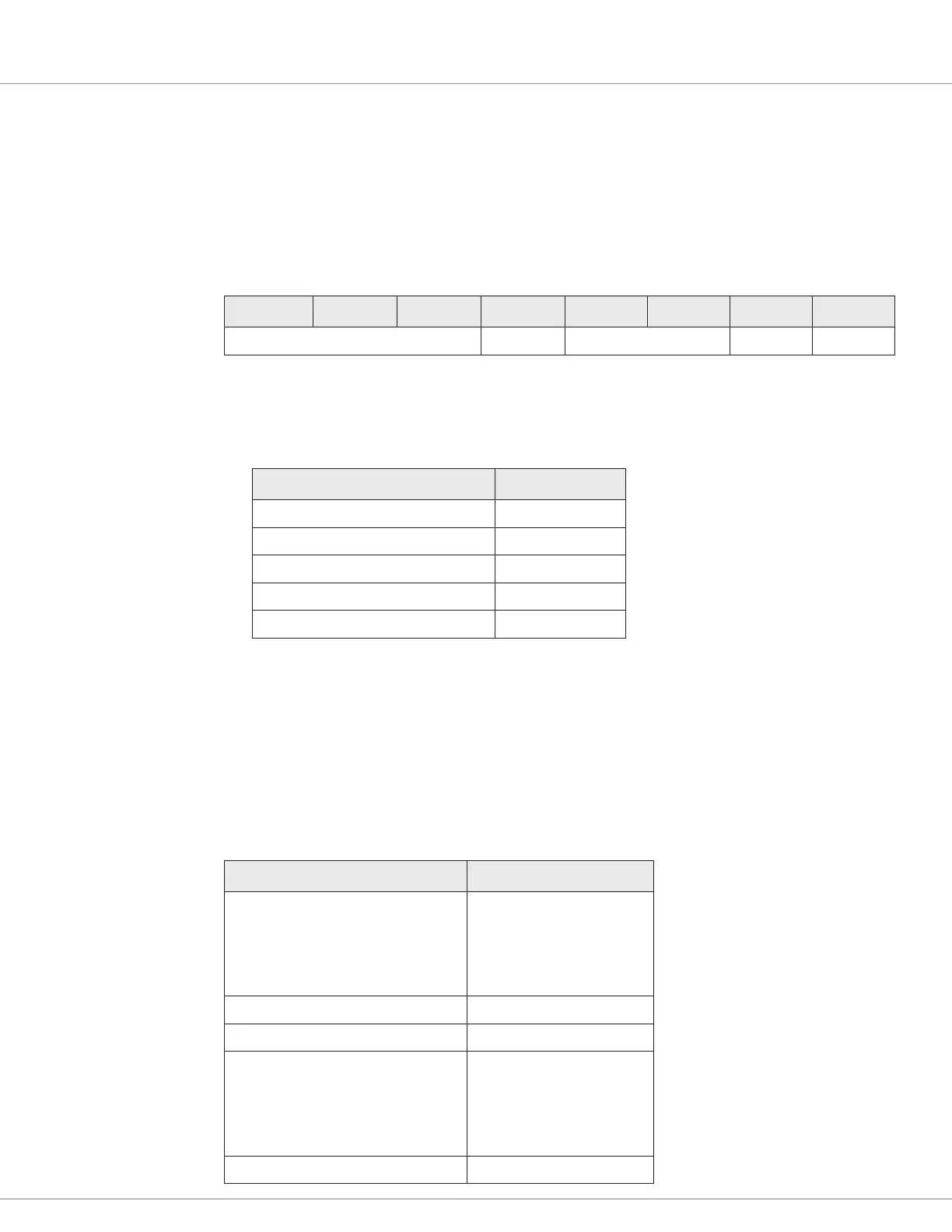
e least signicant byte of an expedited SDO is known as the control byte. e following table
describes the control byte elds:
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Command Specifier 0b n e s
e following list describes the control byte:
• e Command Specier eld indicates the SDO’s transfer type, which is described in the
following table:
Transfer Type Value
Write data to a device 001b
Conrm a write 011b
Request data from a device 010b
Device responds with requested data 010b
Abort SDO 100b
• Bit 4 is always 0b.
• e values of bits 0–3 depend upon whether the SDO transfers data. If the SDO does not
transfer data, these bits are always 0b. If the SDO transfers data, the bit values are as follows:
– n indicates the number of unused data bytes.
– e = 1b, which indicates the message contains data.
– s = 1b, which indicates that the n eld species the number of unused data bytes.
e following table lists the control byte values for the various transfer types:
Transfer Type Control Byte
Write data to a device Depends upon the data size:
• 1 byte = 2Fh
• 2 bytes = 2Bh
• 3 bytes = 27h
• 4 bytes = 23h
Conrm a write 60h
Request data from a device 40h
Device responds with requested data Depends upon the data size:
• 1 byte = 4Fh
• 2 bytes = 4Bh
• 3 bytes = 47h
• 4 bytes = 43h
Abort SDO 80h

 Loading...
Loading...