4 Function description
BU 0210 en-3117 55
Pos: 19 2 /Anlei tung en/El ektr onik/P OSICON /4. Funkti onsbes chr eibung/ Gleic hlauf /Fli egen de Säge_04_Diagonalsäge @ 14\mod_1478850117652_388.docx @ 2303085 @ 4 @ 1
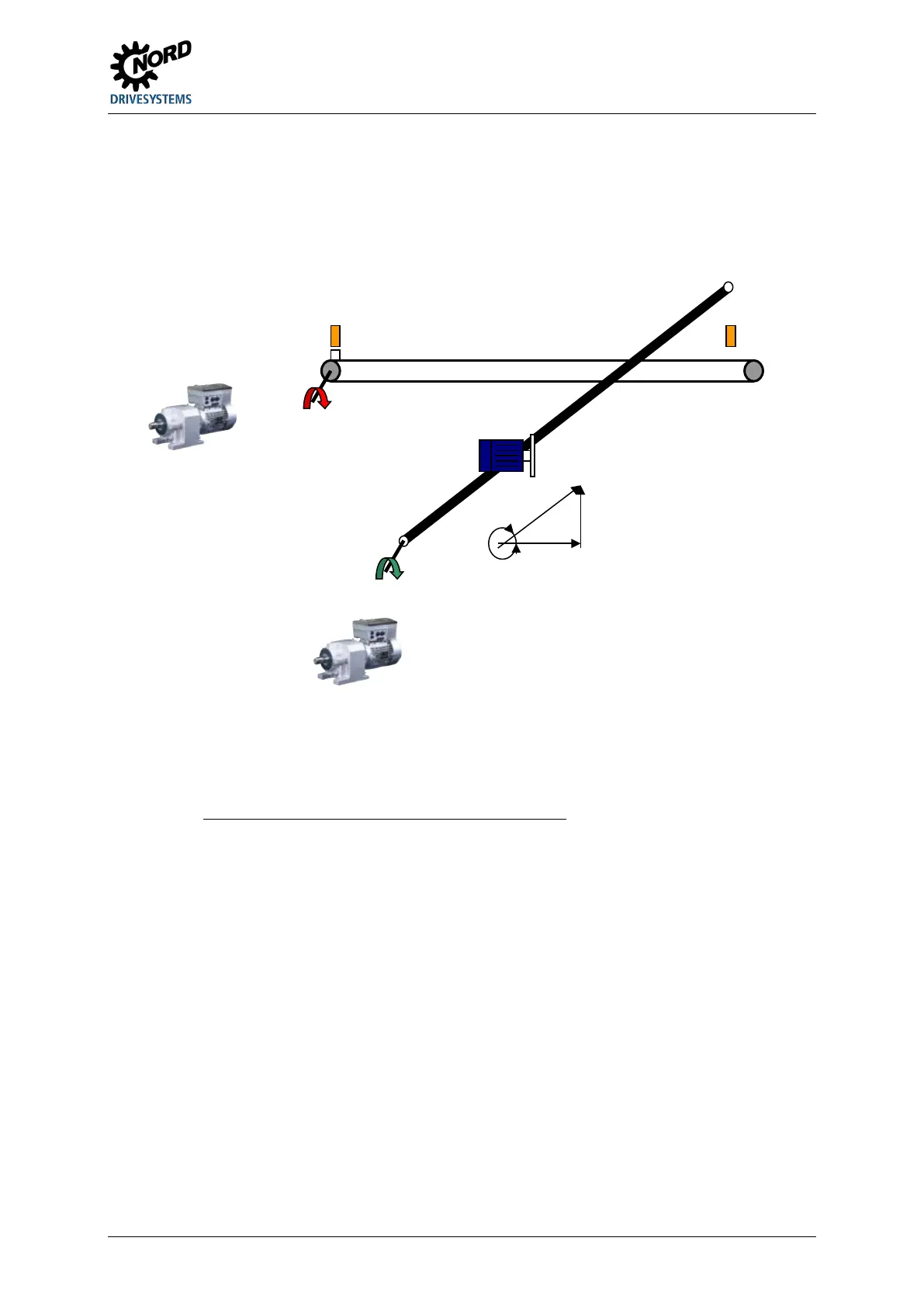
4.9.8.2 Diagonal saw
The diagonal saw is a special case of the "flying saw". Here, no differentiation is made between the
slave and the processing axis. The axis to be synchronised moves at a defined angle (e.g. 30°)
transversely to the direction of the material. The movement therefore comprises the vectors of a
longitudinal and a transverse direction. Because of this, the angle must also be taken into account for
the speed ratio between the master and the slave.
Figure 5: Flying saw - Diagonal saw
Calculation of the speed ratio for a diagonal saw
Gear Unit Slave
Master
Gear Unit Master
Slave
Slave angle – Direction of motion relative to the direction of motion of the master [°]
Diameter of gear unit output
For the diagonal saw, the advance movement of the saw is therefore proportional to the belt speed.
Therefore, the advance movement of the saw and the belt speed cannot selected independently (as
long as the angle is kept constant). For the "normal" flying saw, the advance movement of the saw is
controlled via a separate axis, independently from the speed of the belt or travel.
Regardless of the setting in parameter P600, the technology function "flying saw" is always executed
with linear ramps and a speed of movement with maximum frequency. Therefore: the return
movement of the saw is always performed with the set maximum frequency, which in general also
corresponds to the maximum speed during synchronous movement.
Pos: 19 3 /Allgemein/Allgemeingültige Module/---------Seiten umbr uch ko mpakt --------- @ 13\mod_1476369695906_0.docx @ 2265495 @ @ 1
Master drive
Slave drive
α
V
x
= V
slave
* cos(α)
V
y
= V
slave
*
sin(α)
V
slave

 Loading...
Loading...











