179
5-18 Binary Calculations
The binary calculation instructions - ADB(50), SBB(51), MLB(52) and
DVB(53) - all perform arithmetic operations on hexadecimal data.
The addition and subtraction instructions include CY in the calculation as well
as in the result. Be sure to clear CY if its previous status is not required in the
calculation, and to use the result placed in CY, if required, before it is
changed by the execution of any other instruction. STC(40) and CLC(41) can
be used to control CY. Refer to 5-17 BCD Calculations.
5-18-1 BINARY ADD – ADB(50)
Au: Augend word (binary)
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
Ad: Addend word (binary)
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
Ladder Symbols
Operand Data Areas
R: Result word
IR, AR, DM, HR, LR
ADB(50)
Au
Ad
R
@ADB(50)
Au
Ad
R
When the execution condition is OFF, ADB(50) is not executed. When the
execution condition is ON, ADB(50) adds the contents of Au, Ad, and CY,
and places the result in R. CY will be set if the result is greater than FFFF.
Au + Ad + CY CY R
Flags ER: Indirectly addressed DM word is non-existent. (Content of *DM word
is not BCD, or the DM area boundary has been exceeded.)
CY: ON when the result is greater than FFFF.
EQ: ON when the result is 0.
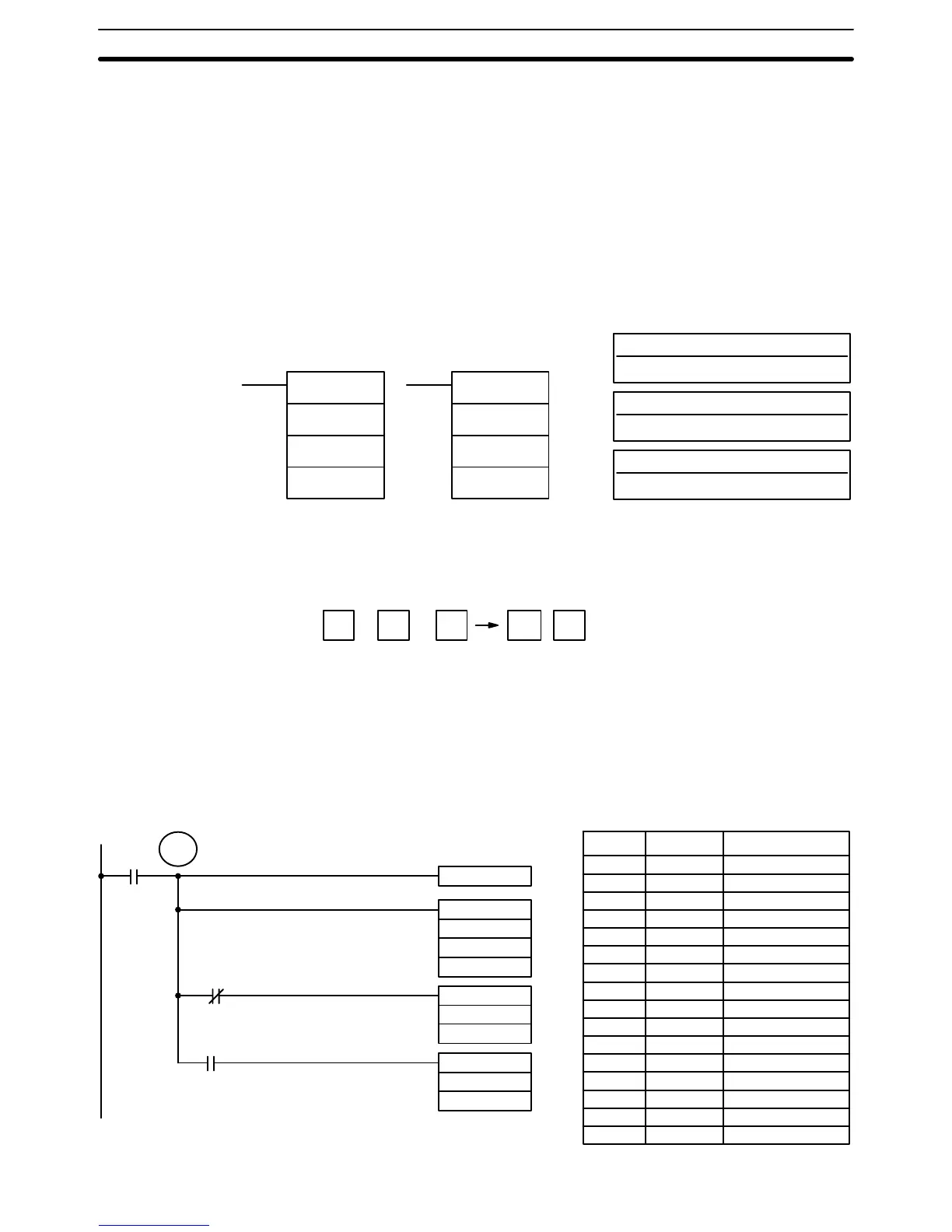
Examples The following example shows a four-digit addition with CY used to place ei-
ther #0000 or #0001 into R+1 to ensure that any carry is preserved.
CLC(41)
00000
ADB(50)
010
DM 0100
HR 10
MOV(21)
#0000
HR 11
MOV(21)
#0001
HR 11
TR 0
25504
25504
= R
= R+1
= R+1
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 OUT TR 0
00002 CLC(41)
00003 ADB(50)
010
DM 0100
HR 10
00004 AND NOT 25504
00005 MOV(21)
# 0000
HR 11
00006 LD TR 0
00007 AND 25504
00008 MOV(21)
# 00001
HR 11
Description
Binary Calculations Section 5-18
 Loading...
Loading...











