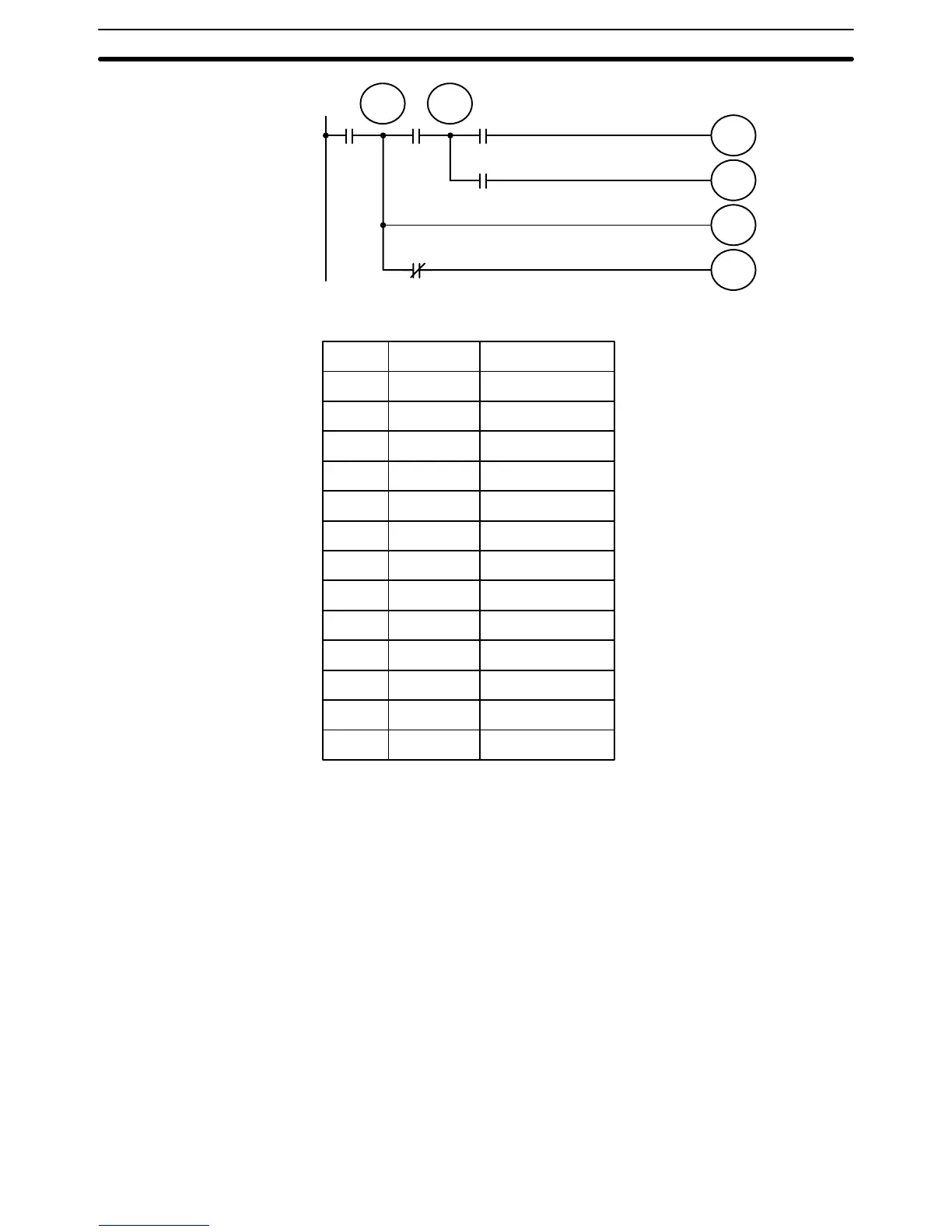
120
0000 0001 0002
0003
0005
0500
0501
0502
0503
TR
0
TR
1
Address Instruction Data
0000 LD 0000
0001 OUT TR 0
0002 AND 0001
0003 OUT TR 1
0004 AND 0002
0005 OUT 0500
0006 LD TR 1
0007 AND 0003
0008 OUT 0501
0009 LD TR 0
0010 OUT 0502
0011 AND NOT 0005
0012 OUT 0503
When coding IL(02) and ILC(03), the mnemonic code will be the same re-
gardless of whether the instruction is drawn as branching instruction lines or
whether IL(02) is placed on its own instruction line. If drawn as branching
instruction lines, each branch line is coded as if it were connected to the bus
bar, i.e., the first condition on each branch line corresponds to a LD or LD
NOT instruction.
Interlocks
Converting to Mnemonic Code Section 7–2
 Loading...
Loading...











