Process interfacing via an automation system (PLC, PC)
9.3 Control with Ident profile
SIMATIC MV500
110 Operating Instructions, 06/2018, C79000-G8976-C494-01
During initialization (INIT), the Ident profile automatically executes the "WRITE-CONFIG"
command. The parameter values of the "WRITE-CONFIG" command depend on whether the
Ident profile is used with or without a communications module.
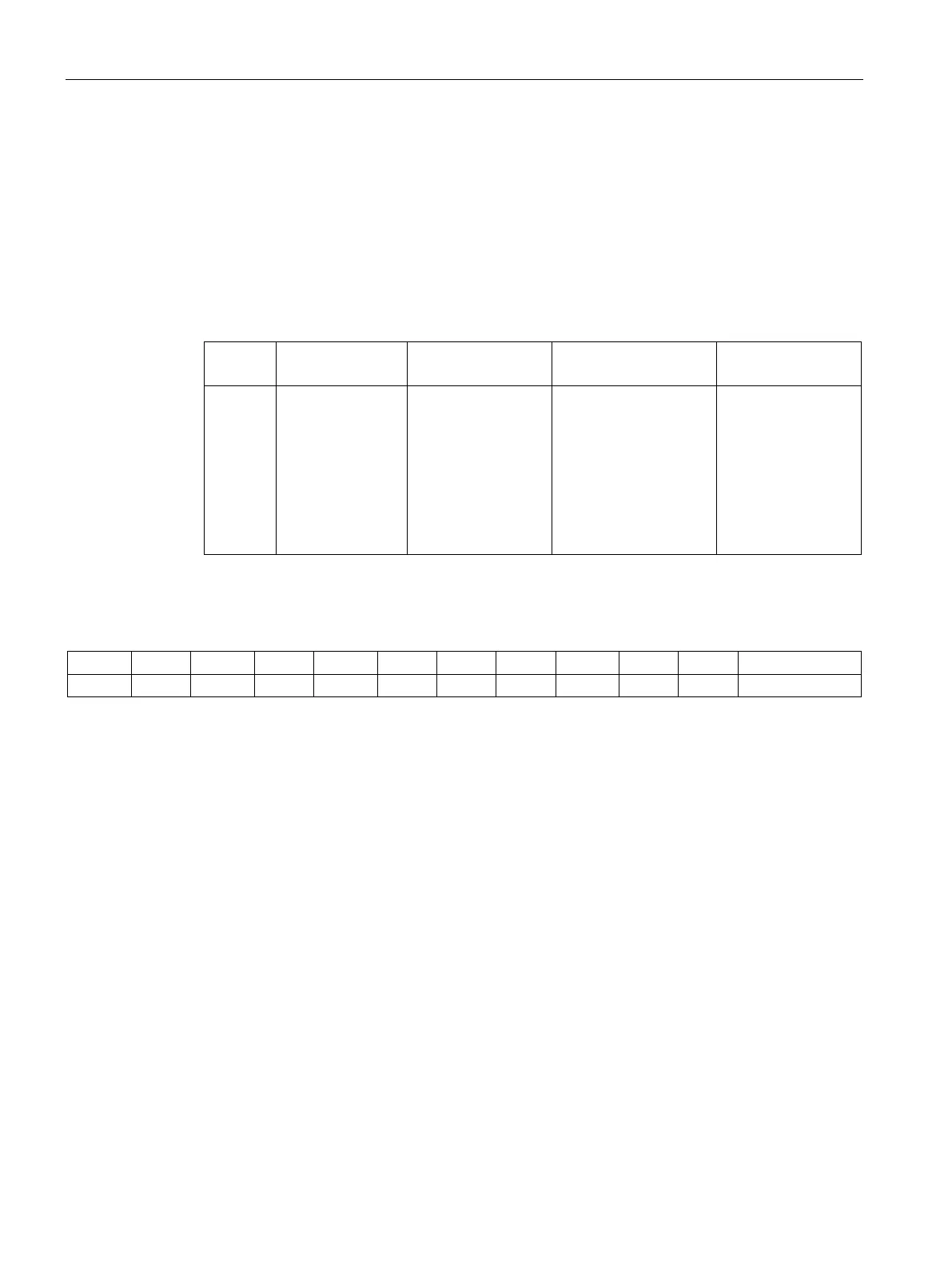
Table 9- 5 WRITE-CONFIG
0x78 Offset in the
"TXREF" send
buffer
Length of the pa-
rameter data
• 0x01 ≙ communica-
tion reset, no con-
figuration data
(LEN_DATA = 0)
• 0x03 ≙ communica-
tion reset, configu-
ration data to be
sent
Configuration data
to be sent
Structure of the configuration data attachment of WRITE-CONFIG
Table 9- 6 MV400 when CONFIG = 0x03; LEN_DATA = 0x10
1)
0x00: "INIT" without program selection
0x01 ... 0x0F: Number of the program to be started ("INIT" with program selection)
Control with MV commands via Ident profile
The optical reader is controlled by the "PHYSICAL WRITE" and "PHYSICAL READ"
commands. Chaining of commands is not supported.
An RFID system typically has a linear memory area for each transponder from which data
can be read or to which data can be written. The address space (in this case purely virtual) is
used in an optical reader to map certain MV commands (machine vision commands). In
addition, the data that is "written" to a specific address, for example, has a defined semantic
meaning.
This section explains which address space must be written to or which address must be read
from in order to cause specific behavior of the optical reader. The semantic meaning of the
read data or data to be written is also explained.

 Loading...
Loading...











