Accompanying gas (concentration 100vol.%) Zero point deviation in
vol.%O
2
absolute
Water H
2
O -0.03
Hydrogen H
2
+0.26
Since the zero point deviations are linear, it is easy to convert to lower interfering gas
concentrations.
In the case of interfering gases with a constant concentration, an interfering gas correction
with constant zero point oset can be carried out in the gas to be measured. If the
concentration of the accompanying gases changes during the oxygen measurement, a
variable interfering gas correction has to be carried out. An external concentration must
be determined for each interfering gas with a considerable zero point deviation. Its result is
fed as interfering gas concentration into the OXYMAT7 analyzer module and the correction
value is calculated constantly.
Information on interference gas correction is available in the following operating manuals:
• Operating with the Local User Interface Table A-2 References1-Operating ManualsLUI
(Page179)
• Operation with SIMATIC PDM Table A-3 References2-Operating ManualsPDM (Page179)
See also
References (Page179)
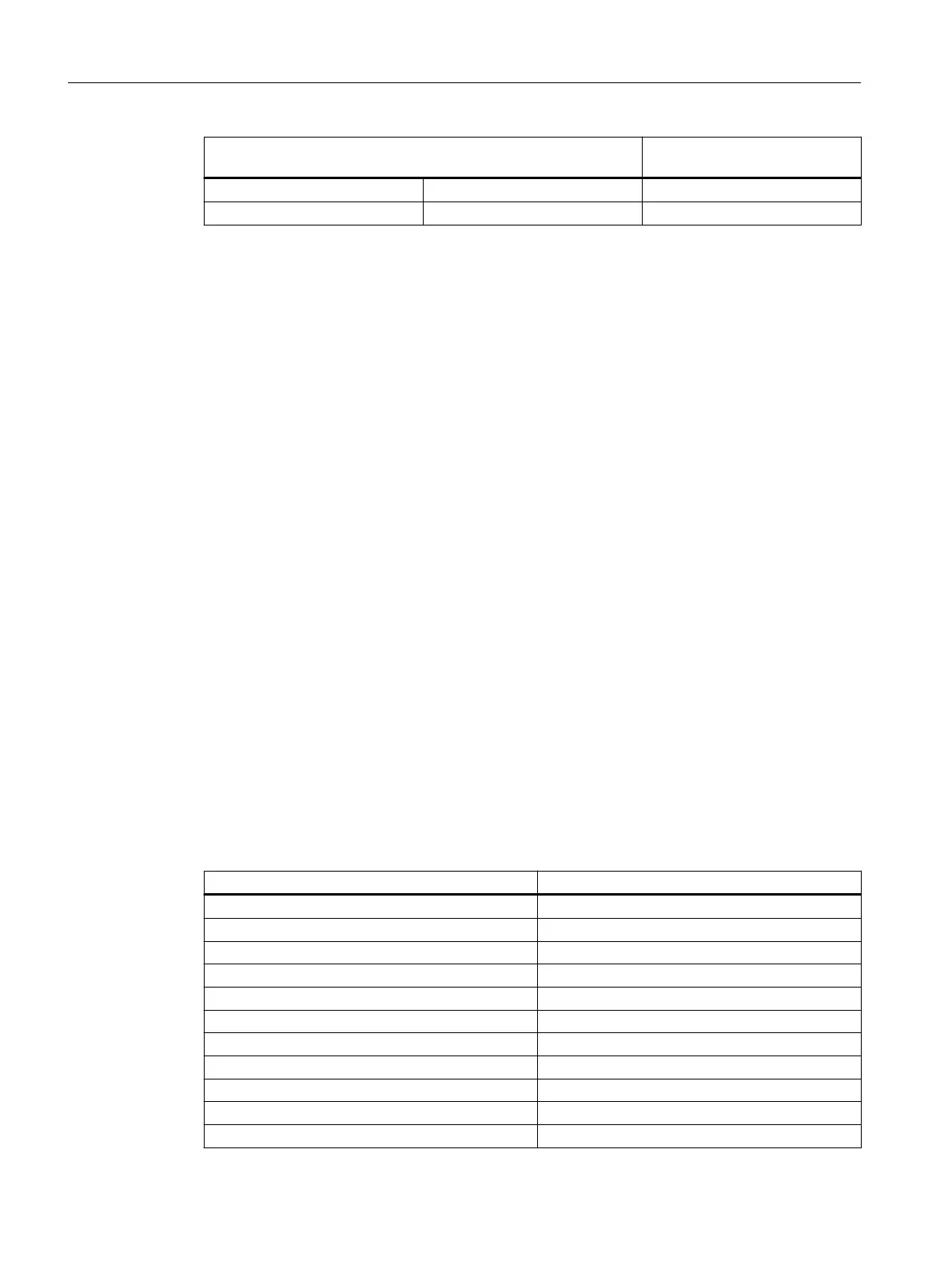
9.5.2 CALOMAT 7
Overview
To determine the cross-interferences of accompanying gases with several interference gas
components, you must know the sample gas composition. The following table contains the zero
osets for the carrier gas N
2
as H
2
equivalent values with 10% interference gas
Table 9-6 Zero oset in the system H
2
in N
2
Interference gas H
2
equivalent values with 10% inference gas
CH
4
1.77%
C
2
H
6
0.47%
C
3
H
8
-0.28%
CO -0.10%
CO
2
-0.84%
O
2
0.19%
N
2
O -0.83%
NH
3
1.45%
Ar -1.22%
He 6.32%
SF
6
-2.15%
Commissioning
9.5Zero point error
Wall-mounted device
132 Operating Instructions, 07/2023, A5E31930403-AB

 Loading...
Loading...











