Functions
2.7 Motor Protection (Motor Starting Protection 48, Motor Restart Inhibit 66, Load Jam Protection)
SIPROTEC, 7SK80, Manual
E50417-G1140-C344-A4, Release date 08.2010
121
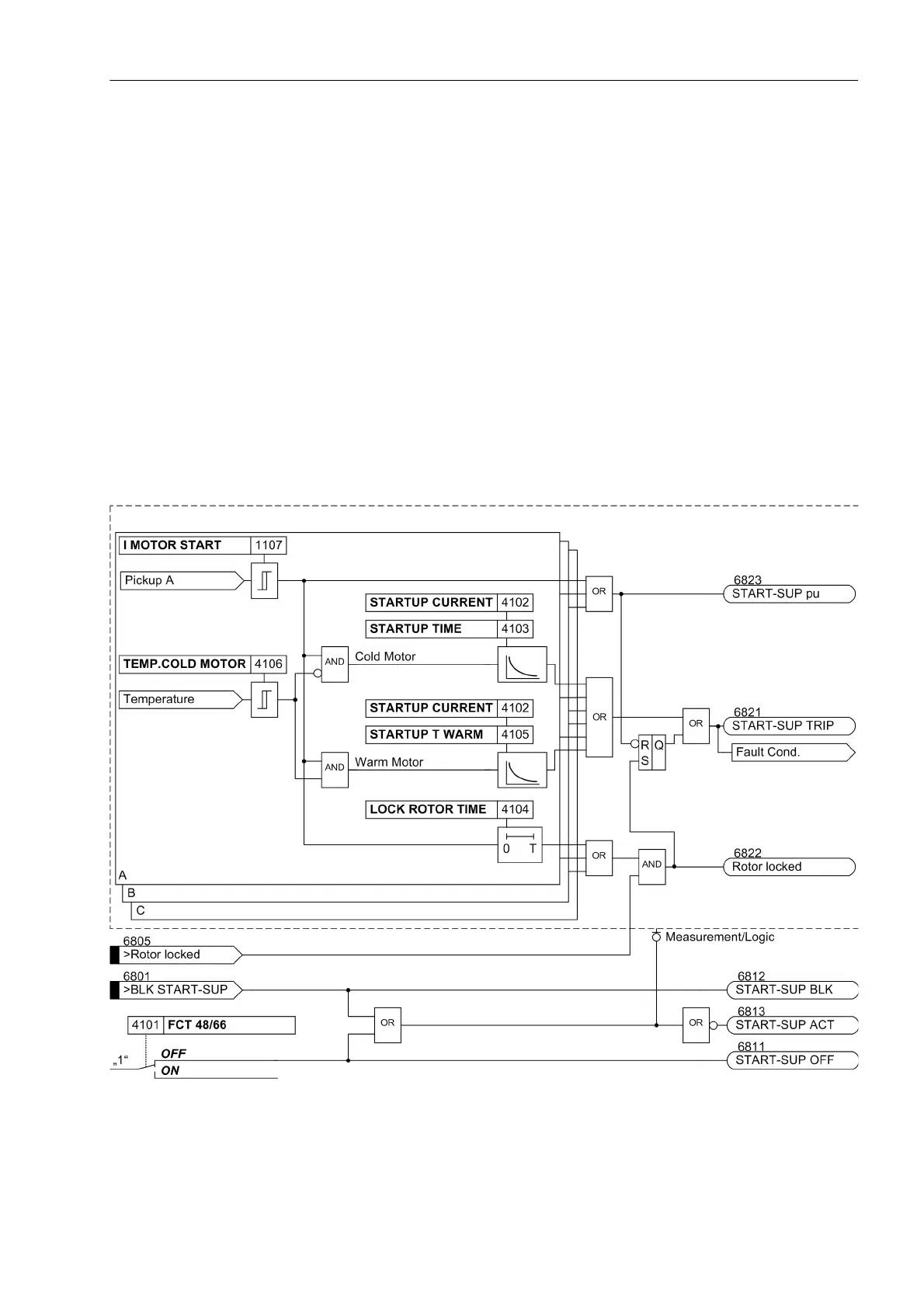
Definite Time Overcurrent Tripping Characteristic (Locked Rotor Time)
Tripping must be executed when the actual motor starting time exceeds the maximum allowable locked rotor
time if the rotor is locked. The device can be informed about the locked rotor condition via the binary input
(„>48 Rot. locked“), e.g. from an external r.p.m. monitor. The motor startup condition is assumed when
the current in any phase exceeds the current threshold I MOTOR START. At this instant, the timer LOCK
ROTOR TIME is started.
The locked rotor delay time (LOCK ROTOR TIME) is linked to a binary input „>48 Rot. locked“ via an AND
gate. If the binary input is picked up after the set locked rotor time has expired, immediate tripping will take
place regardless of whether the locked rotor condition occurred before, during or after the timeout.
Logic
Motor starting protection may be switched on or off. In addition, motor starting protection may be blocked via a
binary input which will reset timers and pickup annunciations. The following figure illustrates the logic of motor
starting protection. A pickup does not create messages in the trip log buffer. Fault recording is not started until
a trip command has been issued. When the function drops out, all timers are reset. The annunciations disap-
pear and a trip log is terminated should it have been created.
Figure 2-34 Logic diagram of the Motor Starting Protection

 Loading...
Loading...











