Functions
2.14 Reverse-Power Protection Application with Flexible Protection Function
SIPROTEC, 7SK80, Manual
E50417-G1140-C344-A4, Release date 08.2010
222
Functional Logic
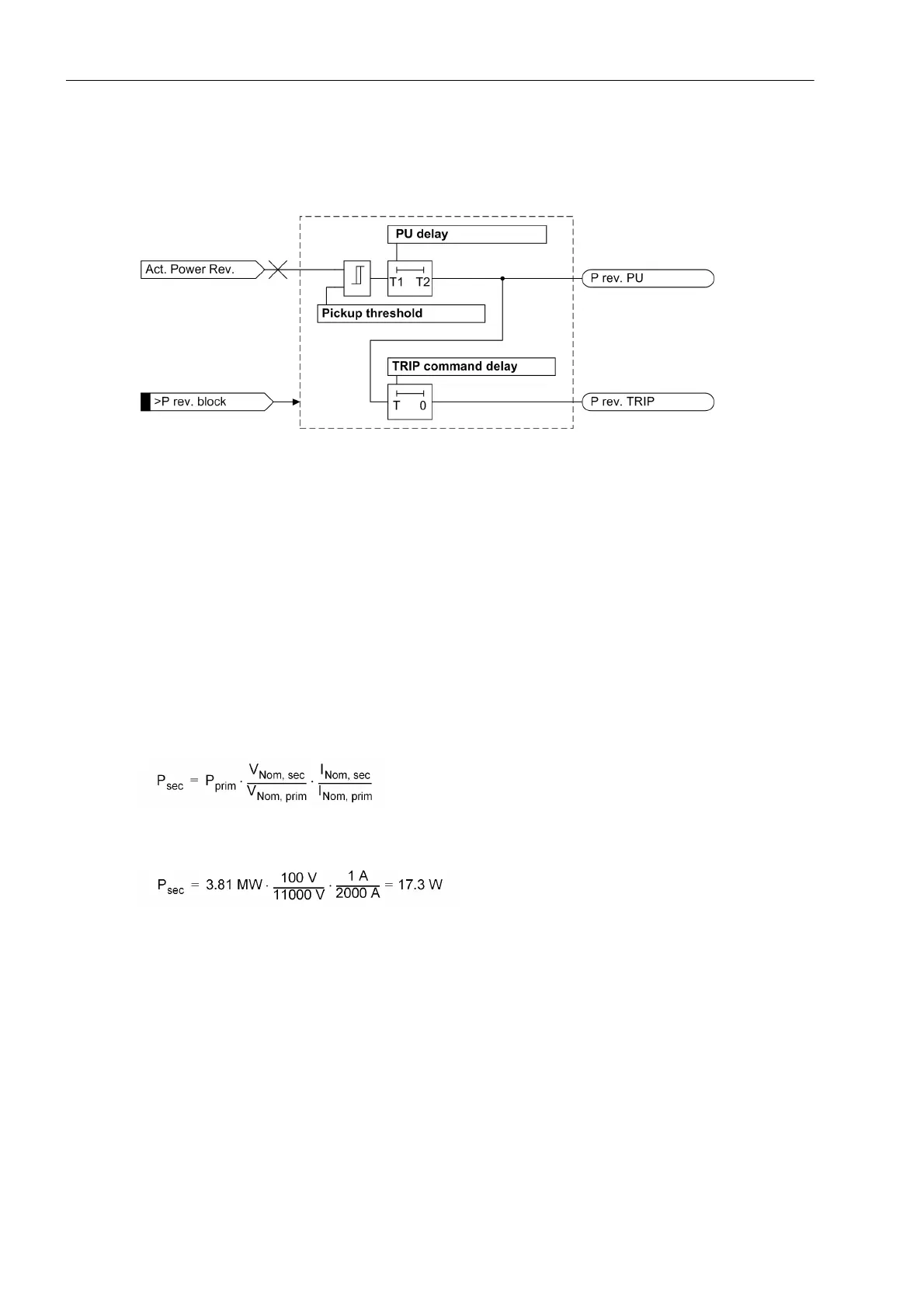
The following logic diagram depicts the functional logic of the reverse power protection.
Figure 2-80 Logic diagram of the reverse power determination with flexible protection function
The reverse power protection picks up once the configured pickup threshold has been exceeded. If the pickup
condition persists during the equally settable pickup delay, the pickup message P. rev. PU is generated and
starts the trip delay time. If the pickup condition does not drop out while the trip delay time is counting down,
the trip indication P. rev. TRIP and the timeout indication P. rev. timeout (not shown) are generated. The picked
up element drops out when the value falls below the dropout threshold. The blocking input >P rev. block blocks
the entire function, i.e. pickup, trip and running times are reset. After the blocking has been released, the
reverse power must exceed the pickup threshold and both times must run out before the protection function
trips.
Pickup Value, Dropout Ratio
The pickup value of the reverse power protection is set to 10% of the nominal generator output. In this example,
the setting value is configured as secondary power in watts. The following relationship exists between the
primary and the secondary power:
On the basis of the indicated data, the pickup values are calculated considering P
prim
= 3.81 MW (10% of 38.1
MW) on the primary level to
on the secondary level. The dropout ratio is set to 0.9. This yields a secondary dropout threshold of P
sec, dropout
= 15.6 W. If the pickup threshold is reduced to a value near the lower setting limit of 0.5 W, the dropout ratio
should equally be reduced to approximately 0.7.
Delay for Pickup, Dropout and Trip
The reverse power protection does not require short tripping times as protection from undesired power feed-
back. In the present example, it is useful to delay pickup and dropout by about 0.5 s and the trip by approx. 1
s. Delaying the pickup will minimize the number of fault logs which are opened when the reverse power oscil-
lates around the threshold.
When using the reverse power protection to disconnect the substation quickly from the power supply compa-
ny's system if faults occur, it is useful to select a larger pickup value (e.g. 50% of nominal power) and shorter
time delays.

 Loading...
Loading...











