Pos: 219 /100 Sigm a/100 BA Ze ntrifugen Sigma ( Standardmo dule)/110 Anhang/ 110-0030 Beschleunigu ngs- und Bremsk urven Spinco ntrol L @ 28\mo d_140532070 7842_68.docx @ 195167 @ 2 @ 1
→
11.3 Acceleration and deceleration curves
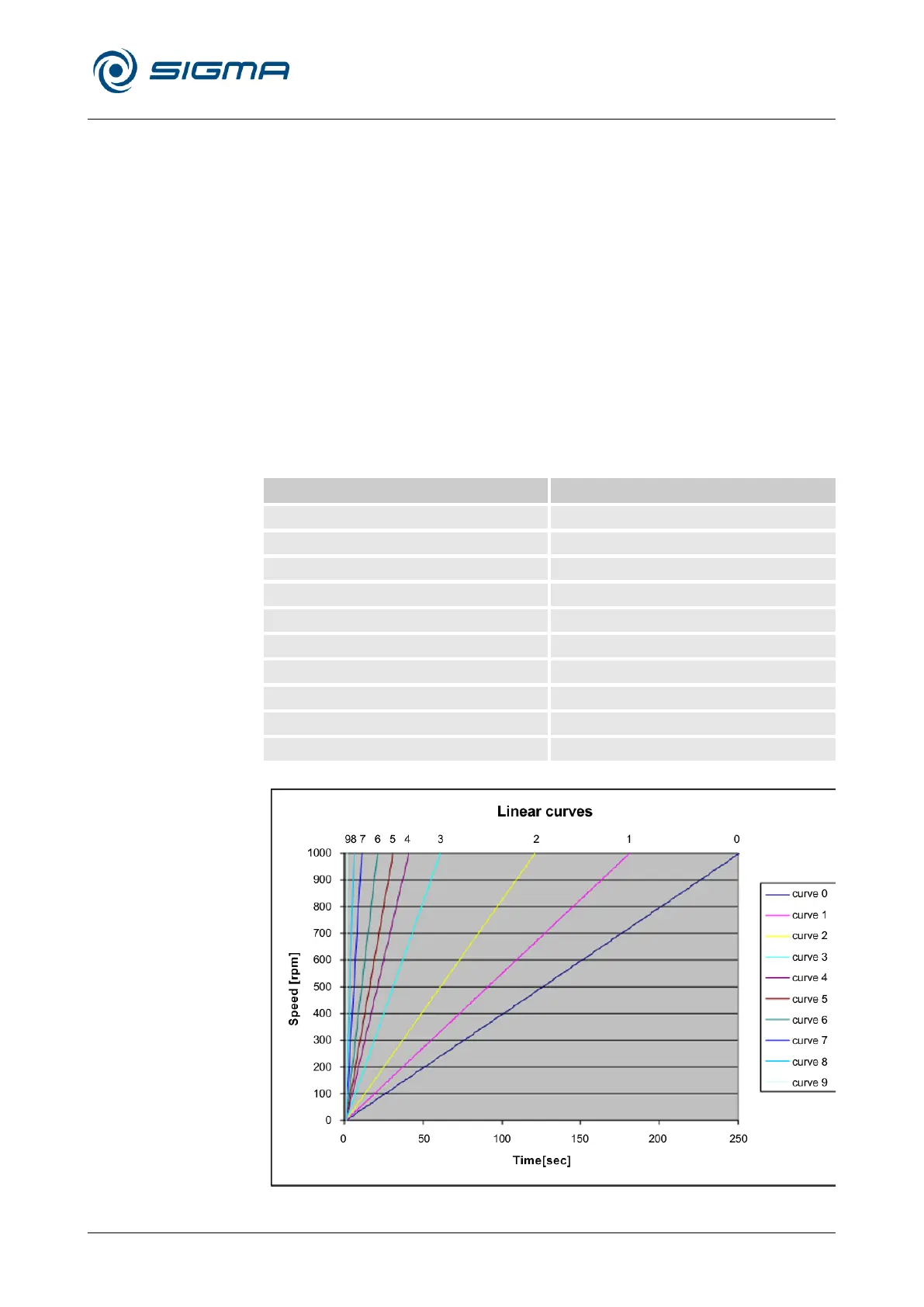
Linear curves are numbered in the direction of increasing acceleration
(from right to left).
The deceleration curves are inverted images of the acceleration curves and
are assigned the same numbers. An exception is curve 0. It decelerates
brakeless (spin-out).
In general, the runtime, until the set speed is reached, depends on the
moment of inertia of the rotor.
Linear curves
The slope of the fixed acceleration curves defines the time that is required
to accelerate the rotor by 1,000 rpm.
Curve 9 is a special case compared to the other curves. The centrifuge
accelerates with maximum power. The runtime, until the set speed is
reached, depends solely on the moment of inertia of the rotor.
Fig. 37: Diagram of linear curves
Pos: 220 /010 Univ ersalmodule/ Seitenwechs el @ 0\mo d_120211624 4312_0.docx @ 105 @ @ 1
 Loading...
Loading...