ADC internal principle AN2834
6/49 DocID15067 Rev 3
1 ADC internal principle
1.1 SAR ADC internal structure
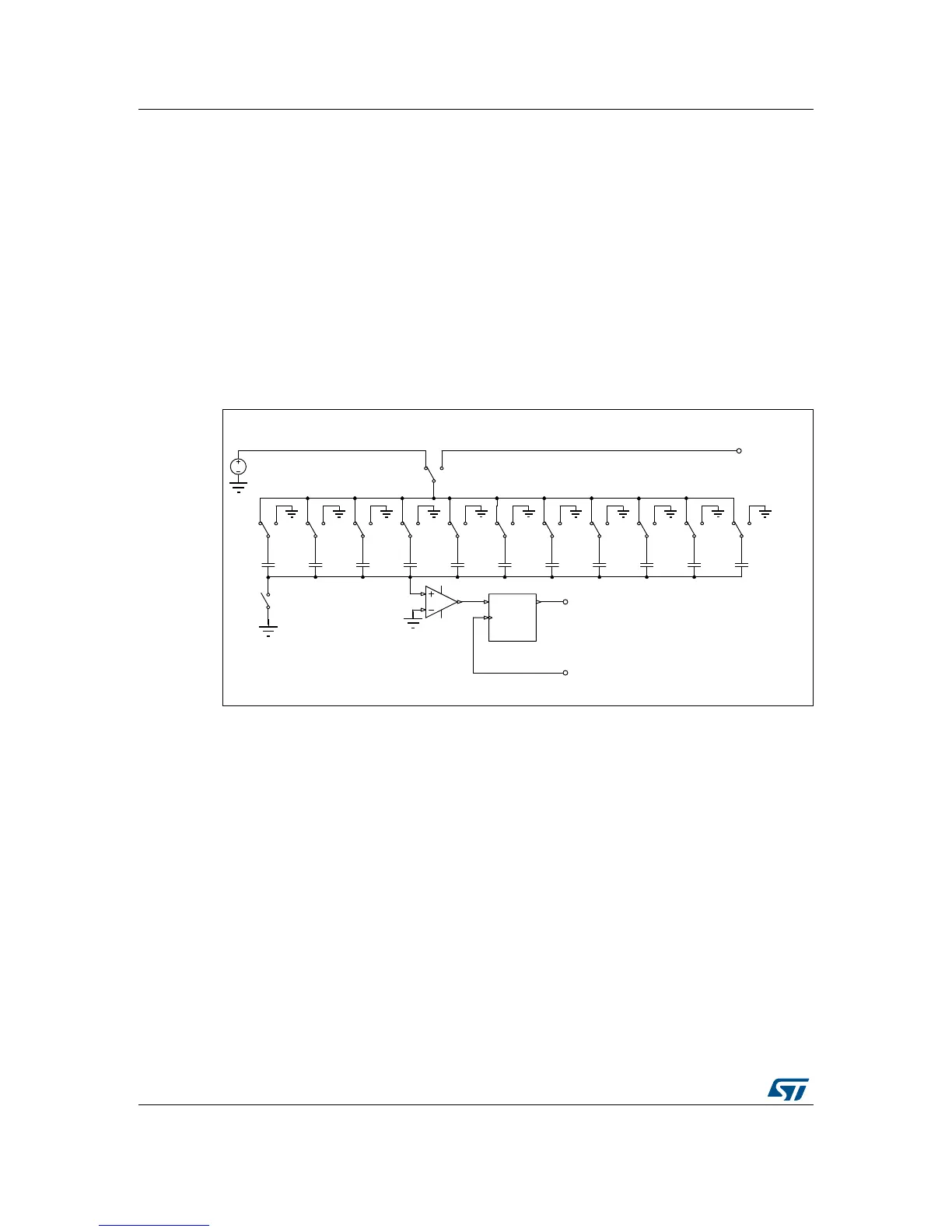
The ADC embedded in STM32 microcontrollers uses the SAR (successive approximation
register) principle, by which the conversion is performed in several steps. The number of
conversion steps is equal to the number of bits in the ADC converter. Each step is driven by
the ADC clock. Each ADC clock produces one bit from result to output. The ADC internal
design is based on the switched-capacitor technique.
The following figures (Figure 1 to Figure 6) explain the principle of
ADC operation. The
example given below shows only the first steps of approximation but the process continues
till the LSB is reached.
Figure 1. Basic schematic of SAR switched-capacitor ADC (example of 10-bit ADC)
1. Basic ADC schematic with digital output.
 Loading...
Loading...