OPERATION
3.12.5 MODES OF OPERATION
There are two modes of operation possible with this talker: Synchronous (burst), and
asynchronous (demand/response). The synchronous mode provides a time message at regular
intervals selected by the user. The asynchronous mode outputs a time message upon receipt of a
predefined character. The 8 bit image of the demand character is set by the user by means of an
8 bit DIP switch.
Note: The selection of Mode, Rate, BAUD Rate, Parity, Stop Bits, Format etc. are all
made using DIP switches. The factory default for these switches is ASCII, 9600 BAUD,
8 Bits, no Parity, 1 Stop bit, and a message output (Rate) once every second. The
operation of an individual switch is:
When a switch (in this example Switch 1) is set to the “ON” position, the voltage for that
selected line is low, or 0 volts. This equates to a binary “0”.
ON
1
When a switch (in this example Switch 1) is set to the “OFF” position, the voltage for
that selected line is high, or +5 volts. This equates to a binary “1”.
ON
1
A. SYNCHRONOUS MODE (Switch S4)
This unit is capable of providing time messages at five different rates:
a. Ten messages per second.
b. One message per second.
c. One message per ten seconds.
d. One message per one-hundred seconds.
e. One message per 1000 seconds.
Note: Although the Mode is selected by Switch S4, the actual message rate is
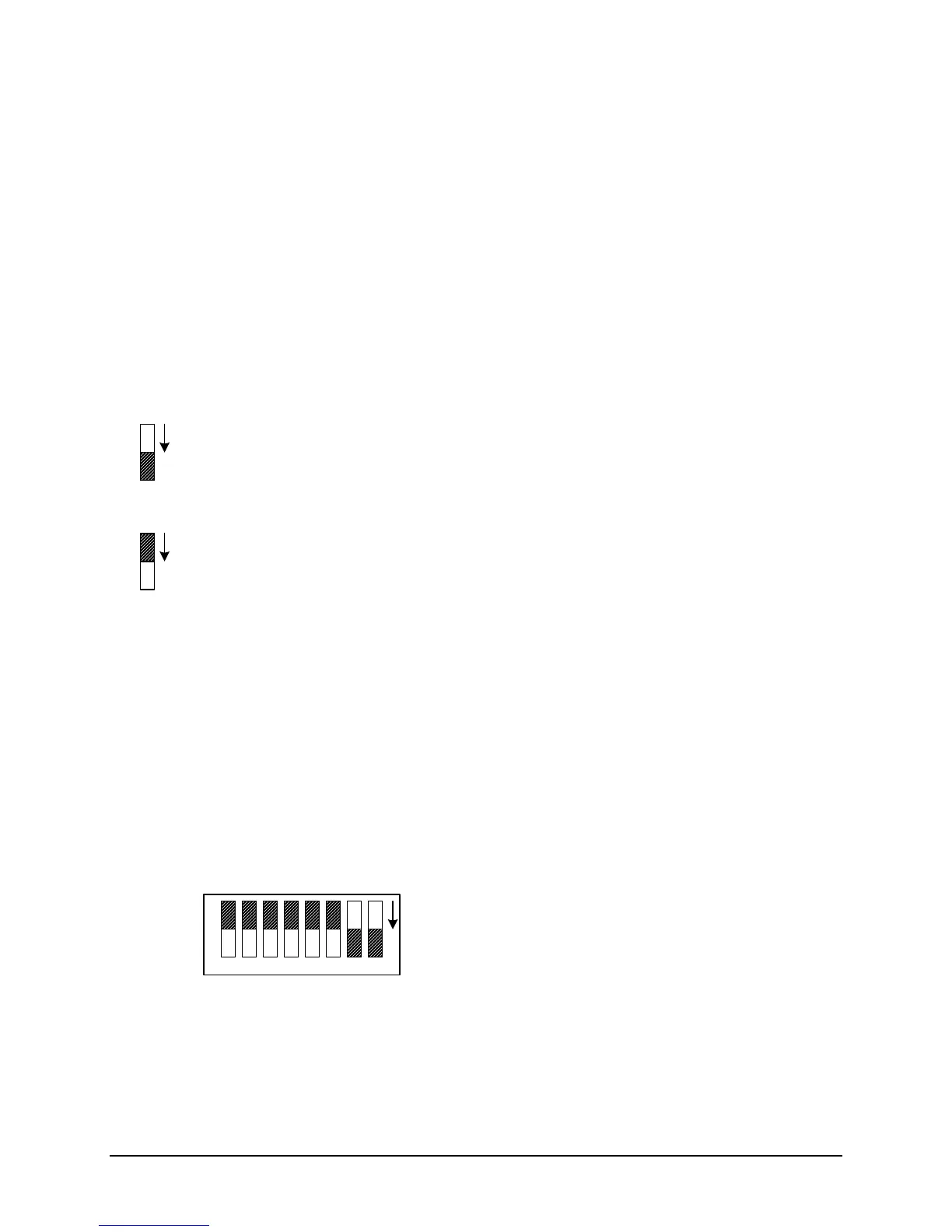
selected by Switch S1 as follows:
ON
87654321
S1
Symmetricom, Inc. TM7000 TymMachine TCG/T (Rev D) 3-43

 Loading...
Loading...