USER’S MANUAL__________________________________________________________________
44 __________________________________________________________________ M211322EN-D
The RVP900 performs discrete Fourier transforms (DFT) and fast Fourier
transforms (FFT). FFT is more computationally efficient than DFT, but the
sample size is limited to a power of two (16, 32, 64, etc.) This is too
restrictive on the scan strategy for a modern Doppler radar since this
means, for example, that a 1 degree azimuth radial must be constructed
from exactly 64 input I/Q values. The RVP900 has the processing power
such that when the sample size is not a power of two, a DFT is performed
instead of an FFT.
2.9.1 General Processing Features
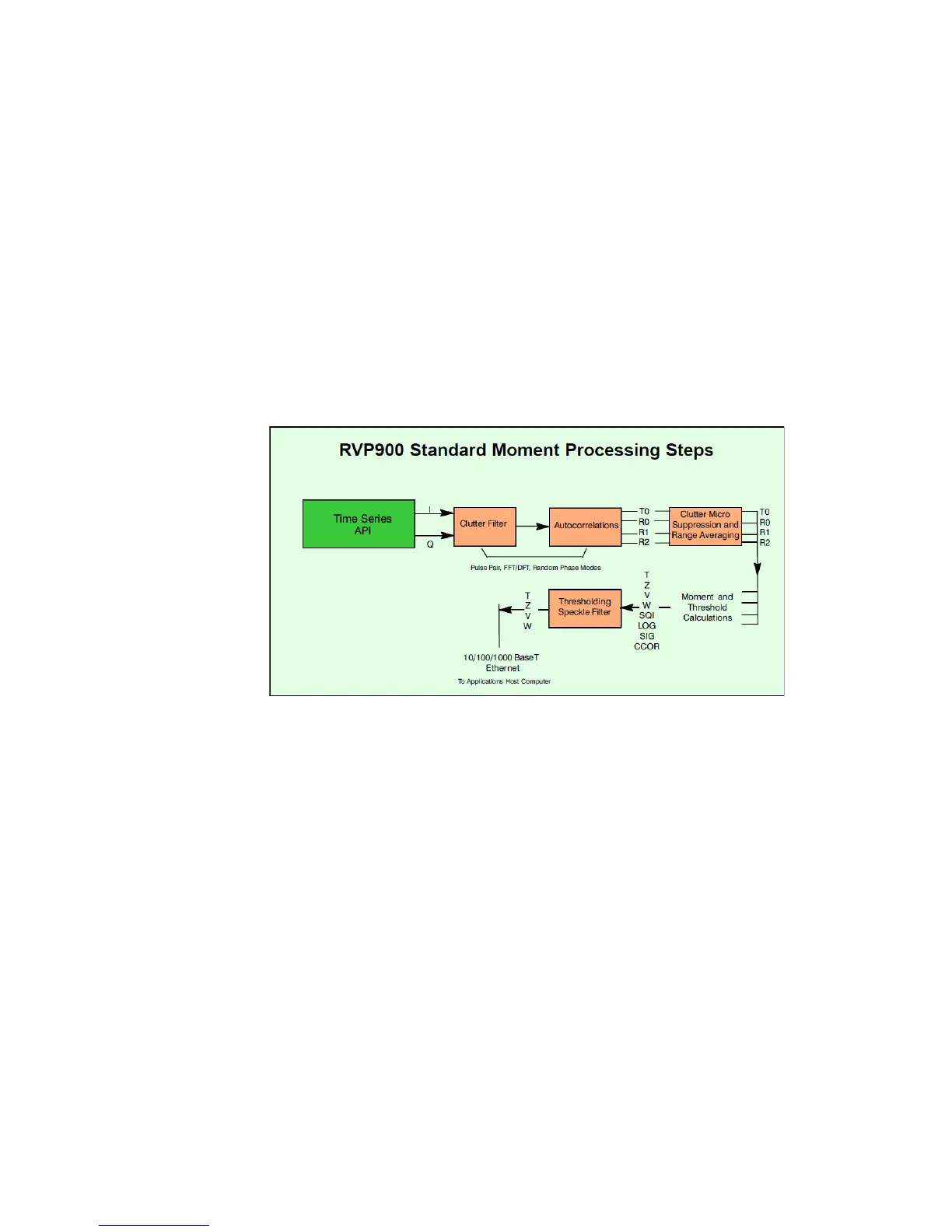
Figure 15 shows a block diagram of the processing steps.
0916-023
Figure 15 I/Q Processing for Weather Moment Extraction
The use of the R2 lag provides improved estimation of signal-to-noise ratio
and spectrum width. Processors that do not use R2 cannot effectively
measure the SNR and spectrum width.
2.9.1.1 Autocorrelations
The autocorrelations R0, R1, and R2 are produced by Pulse Pair, Random
Phase, and DFT/FFT modes. However, the way that they are produced is
different for the three modes, particularly with regard to the filtering that
is performed:
- Pulse Pair Mode—Filtering for clutter removal may be performed in
the time domain or frequency domain. Traditional IIR type clutter
filters are available in the time domain. However, the frequency
domain filter is much more adaptable. Clutter filtering can be
optionally performed in the frequency domain, and then inverse FFT

 Loading...
Loading...