212 www.xilinx.com 7 Series FPGAs GTP Transceivers User Guide
UG482 (v1.9) December 19, 2016
Chapter 4: Receiver
The state machine works by keeping track of valid and invalid synchronization headers. Upon reset,
block lock is deasserted, and the state is LOCK_INIT. The next state is RESET_CNT where all
counters are zeroed out. The synchronization header is analyzed in the TEST_SH state. If the header
is valid, sh_cnt is incremented in the VALID_SH state, otherwise sh_count and sh_invalid_count
are incremented in the INVALID_SH state.
For the block synchronization state machine shown in Figure 4-57, sh_cnt_max and
sh_invalid_cnt_max are both constants that are set to 64 and 16, respectively. From the VALID_SH
state, if sh_cnt is less than the value sh_cnt_max and test_sh is High, the next state is TEST_SH. If
sh_cnt is equal to sh_cnt_max and sh_invalid_cnt equals 0, the next state is GOOD_64 and from
there block_lock is asserted. Then the process repeats again and the counters are cleared to zeros. To
achieve block lock, the state machine must receive sh_cnt_max number of valid synchronization
headers in a row without getting an invalid synchronization header. However, when block lock is
achieved sh_invalid_cnt_max – 1, the number of invalid synchronization headers can be received
within sh_cnt_max number of valid synchronization headers. Thus, once locked, it is harder to break
lock.
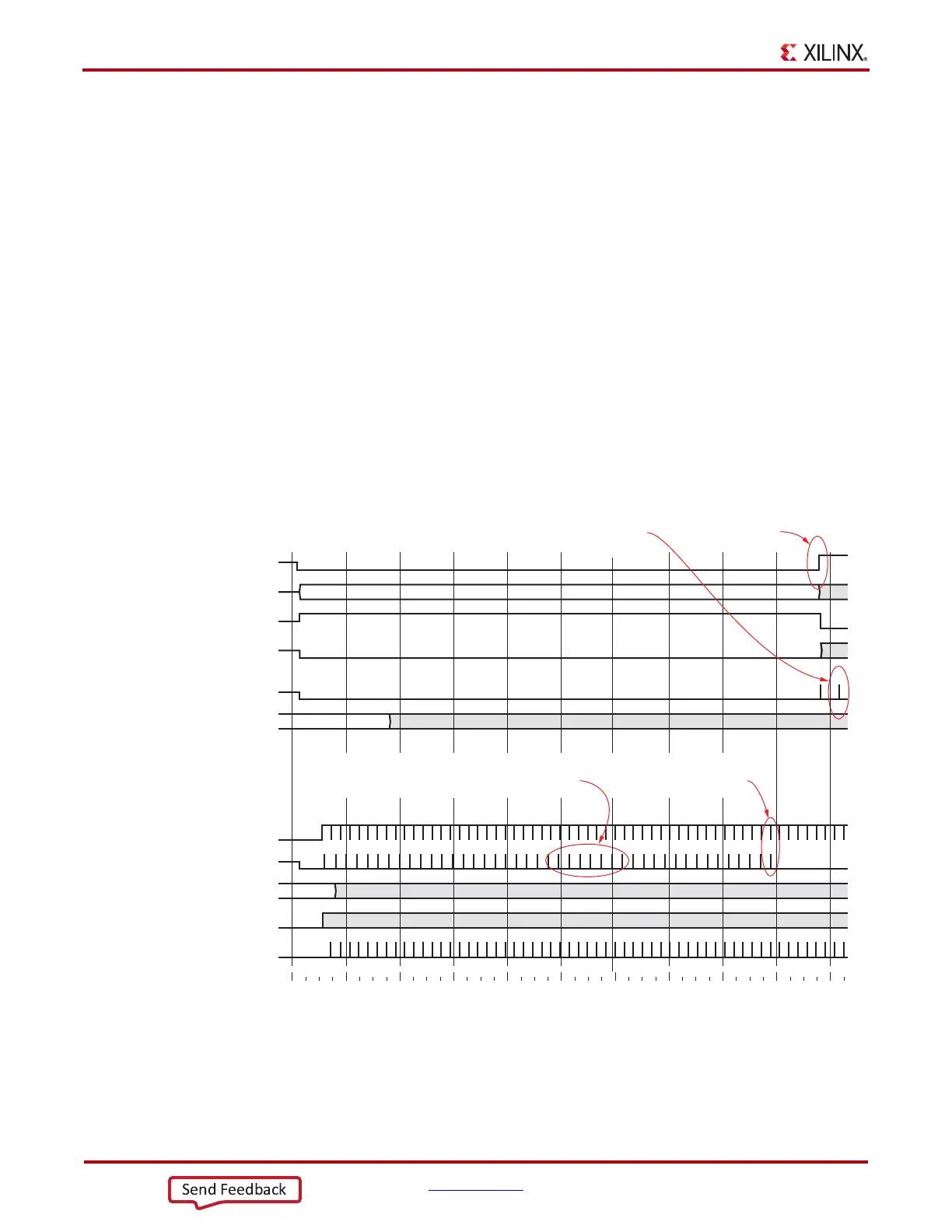
Figure 4-58 shows a waveform of the block synchronization state machine asserting
RXGEARBOXSLIP numerous times because of invalid synchronization headers before achieving
data alignment. After the RXGEARBOXSLIP is issued, the state machine waits
32 RXUSRCLK2 cycles before checking for valid synchronization headers.
X-Ref Target - Figure 4-58
Figure 4-58: RX Gearbox with Block Synchronization
UG482_c4_40_111011
Data alignment
achieved
Data check on
unscrambled data
block_sync_i
unscrambled_data_i
begin_r
track_data_r
start_of_packet_detected_r
RXDATA
RXDATAVALID
RXGEARBOXSLIP
RXHEADER
RXHEADERVALID
RXSTARTOFSEQ
0
Slip data
alignment
Closely spaced slip pulses. State machine
asserts slip as soon as it sees bad header.
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
 Loading...
Loading...











