1-3
Figure 1-2 RADIUS server components
z Users: Stores user information such as the usernames, passwords, applied protocols, and IP
addresses.
z Clients: Stores information about RADIUS clients, such as the shared keys and IP addresses.
z Dictionary: Stores information about the meanings of RADIUS protocol attributes and their values.
Security and Authentication Mechanisms
Information exchanged between a RADIUS client and the RADIUS server is authenticated with a
shared key, which is never transmitted over the network. This enhances the information exchange
security. In addition, to prevent user passwords from being intercepted in non-secure networks,
RADIUS encrypts passwords before transmitting them.
A RADIUS server supports multiple user authentication methods, for example, the Password
Authentication Protocol (PAP) and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). Moreover, a
RADIUS server can act as the client of another AAA server to provide authentication proxy services.
Basic Message Exchange Process of RADIUS
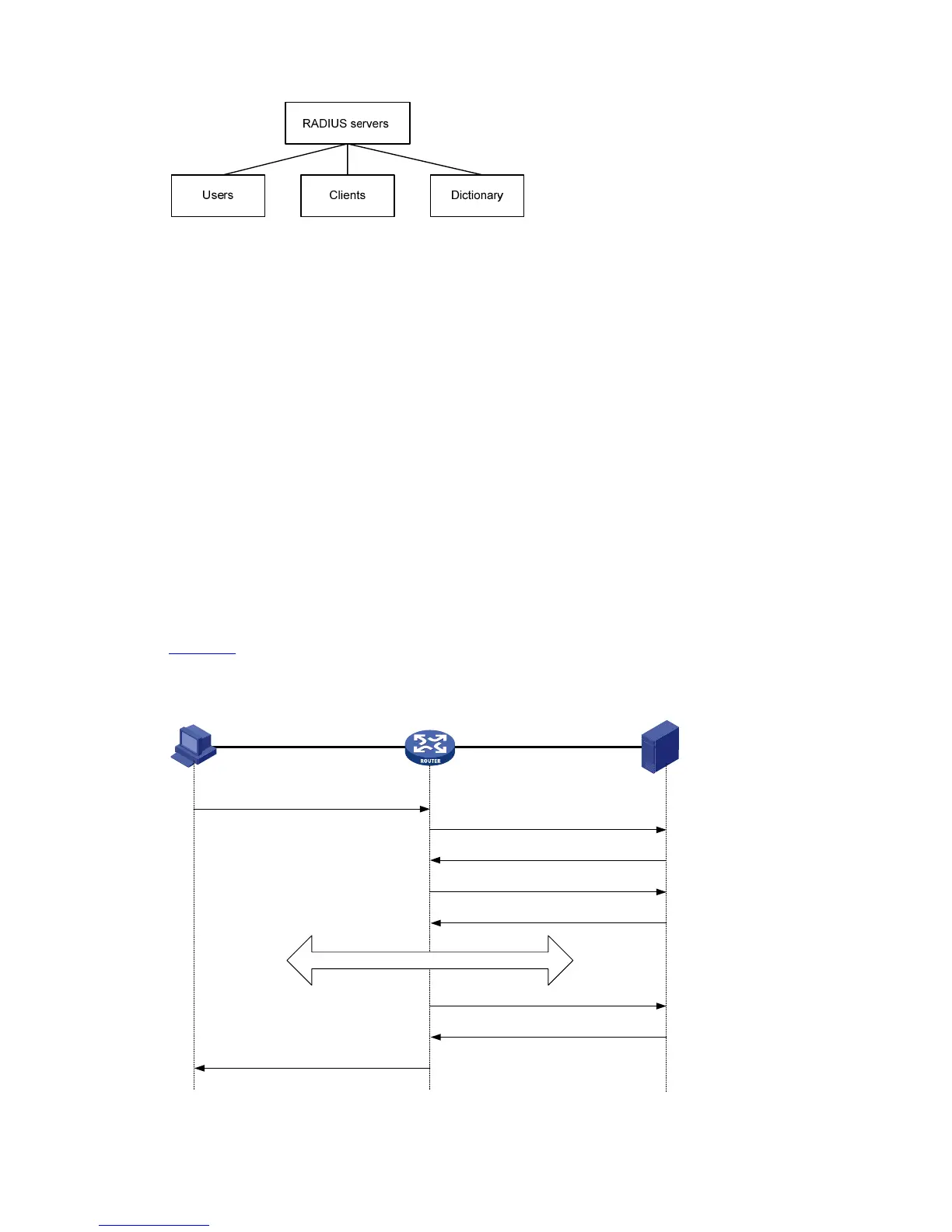
Figure 1-3 illustrates the interaction of the host, the RADIUS client, and the RADIUS server.
Figure 1-3 Basic message exchange process of RADIUS
RADIUS client
RADIUS server
1) Username and password
3) Access-Accept/Reject
2) Access-Request
4) Accounting-Request (start)
5) Accounting-Response
7) Accounting-Request (stop)
8) Accounting-Response
9) Notification of access termination
Host
6) The host accesses the resources
The following is how RADIUS operates:

 Loading...
Loading...











