76 Program features
Settings
Parameters 20.25 Jogging enable (page 208), 20.26 Jogging 1 start source (page
208), 20.27 Jogging 2 start source (page 209), 22.42 Jogging 1 ref (page 222), 22.43
Jogging 2 ref (page 222), 28.42 Jogging 1 frequency ref (page 246) 28.43 Jogging 2
frequency ref (page 246),23.20 Acc time jogging (page 227) and 23.21 Dec time
jogging (page 227).
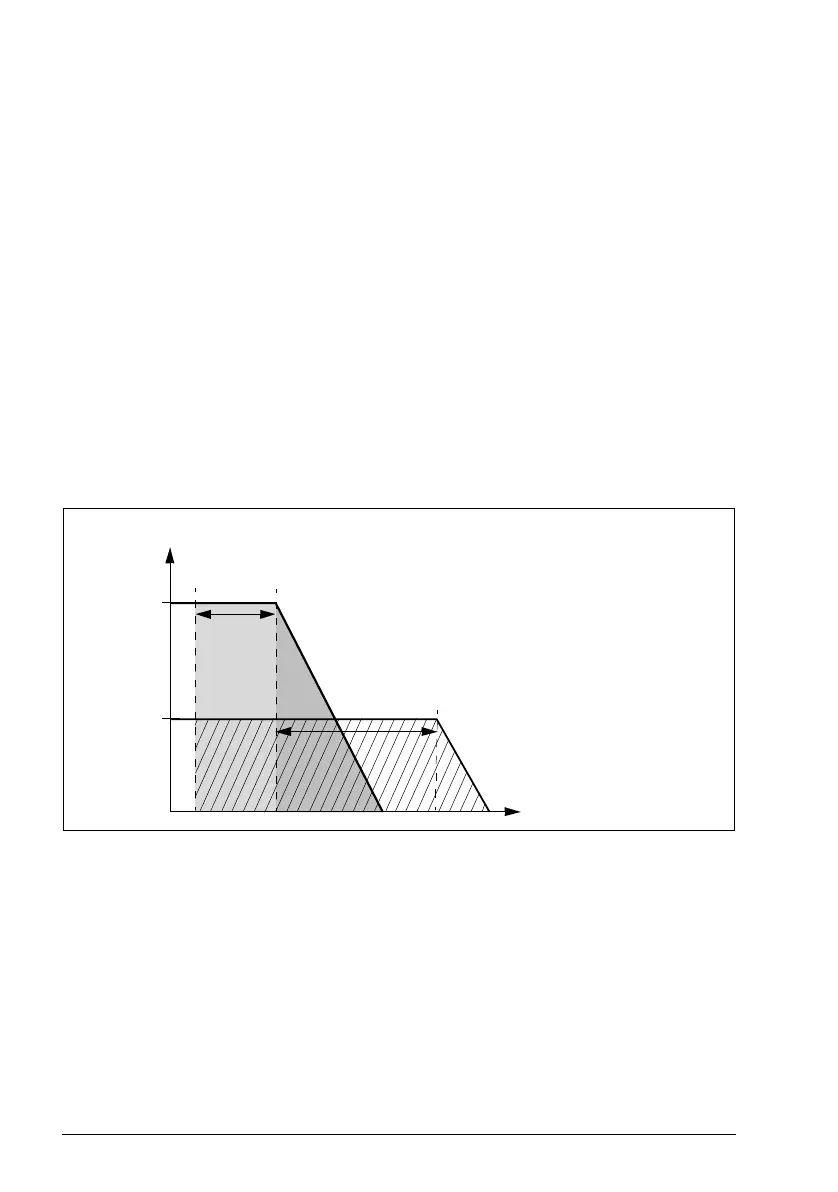
Speed compensated stop
Speed compensation stop is available for example for applications where a conveyer
needs to travel a certain distance after receiving the stop command. At maximum
speed, the motor is stopped normally along the defined deceleration ramp, after the
application of a user defined delay to adjust the distance traveled. Below maximum
speed, stop is delayed still more by running the drive at current speed before the
motor is ramped to a stop. As shown in the figure, the distance traveled after the stop
command is the same in both cases, that is, area A + area B equals area C. Speed
compensation does not take into account shape times (parameters 23.32 Shape time
1 and 23.33 Shape time 2). Positive shape times lengthen the distance traveled.
Speed compensation can be restricted to forward or reverse rotating direction.
Speed compensation is supported in both vector and scalar motor control.
Settings
Parameters 21.30 Speed compensated stop mode (page 216), 21.31 Speed comp
stop delay (page 216) and 21.32 Speed comp stop threshold (page 216).
Used
speed
A
Motor speed
Max.
speed
B
C
t (s)
Area A + Area B = Area C
Stop
command
D1
D1 = Delay defined by parameter
21.31
D2 = Additional delay calculated by
speed compensated stop
D2
 Loading...
Loading...