The various programmable functions are:
Search:
The robot will serach for an object as it moves towards a programmed
position. The search is successful when one of the sensors has found the
object.T he result of a search can be used as:
• a parameter for conditional jumps in the program.
• reference for program displacement.
Speed control:
A sensor controls the speed during movement towards a programmed
position.
Contour following
Sensor signals control the course of the robot during movement towards
a programmed position.
NOTE!
To enable use of the adaptive functions, they must be supplmented by sensors.
• Palletizing function (if option 481, MH/GL/SW is selected)
The positions of all parts on a pallet can quickly be defined by feeding in the positions
of the parts at three corner points and the number of columns and lines. The plane
can have any slope.
• Relative tool displacement (if option 481, MH/GL/SW is selected)
Execution of movement or rotation in tool-oriented coordinates.
The arguments are set during programming or brought up from a numerical
register during programmed running.
• Glue and Air flow (if option 481, MH/GL/SW is selected)
Glue and Air flow reference signals are put out on two analog outputs at the
same time as the robot is positioned. Due to the lag in the robot movemnt
and the delay in the gluing equipment, there is also a delay function which
enables compensation during execution. Furthermore, it is possible to
choose wheter or not the Glue or Air Flow should be proportional to the TCP
velocity.
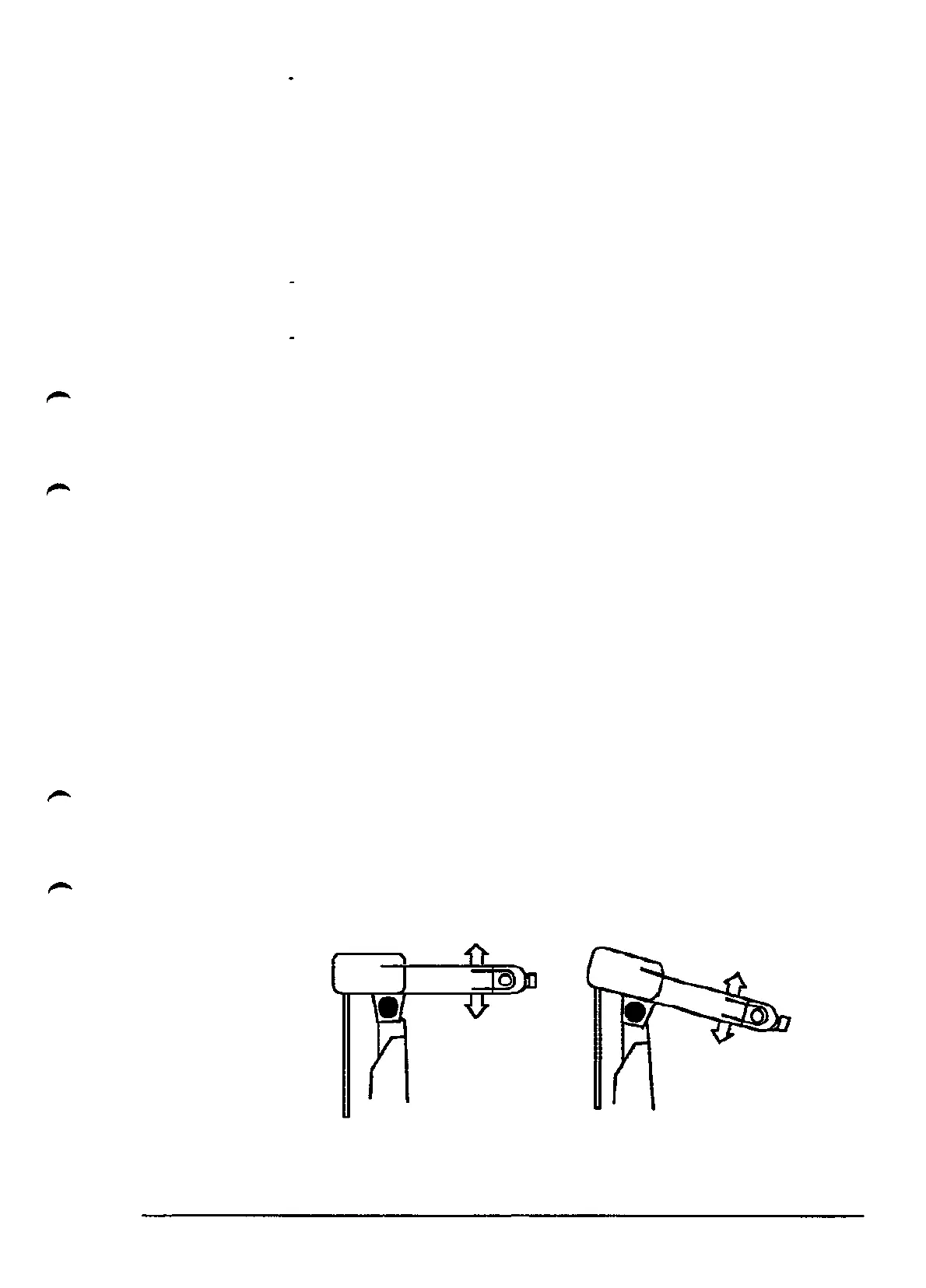
• Soft servo (if option 481, MH/GL/SW is selected)
A function giving the robot a compliance individually controllable for each axis. The
force towards the programmed position is proportional to the deviation. Soft servo is
defined individually for each axis. To obtain a "softness" in a certain direction (e.g.
the Z-direction), the position of the robot arm must be such that the movemnt
direction of the axis concerned coincides with the direction of the softness. See figure
below.
Figure. The direction of the "softness" of axis 3 at different robot arm positions.
Control and logical functions
Description
1KB 2000
21
 Loading...
Loading...