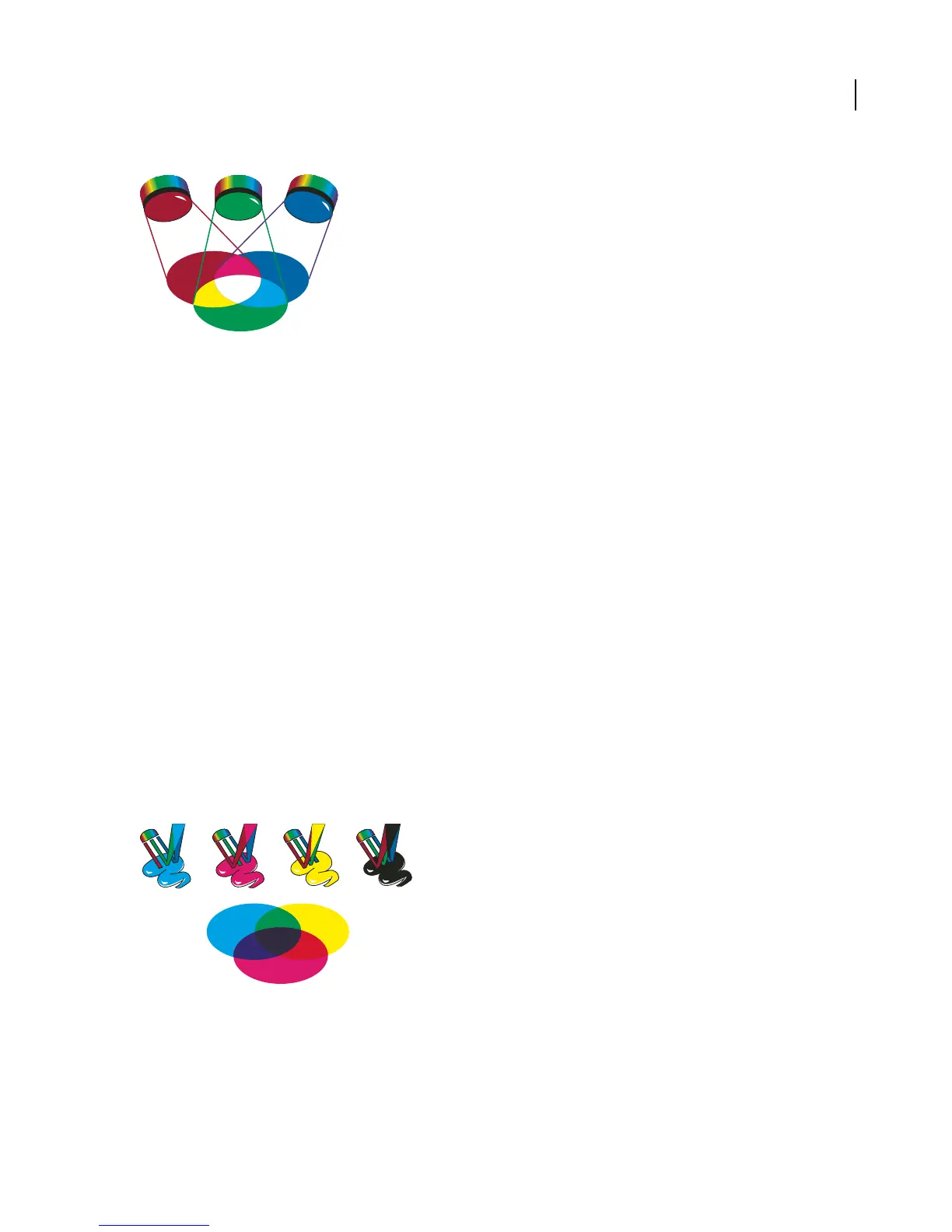182
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS2
User Guide
R
G
B
Additive colors (RGB)
R. Red G. Green B. Blue
Youcan work with colorvaluesusing theRGB colormode, whichisbased on theRGB colormodel.InRGB mode,
each of the RGB components can use a value ranging from 0 (black) to 255 (white). For example, a bright red color
might have an R value of 246, a G value of 20, and a B value of 50. When the values of all three components are equal,
the result is a shade of gray. When the value of all components is 255, the result is pure white; when all components
have values of 0, the result is pure black.
Illustrator also includes a modified RGB color mode called Web Safe RGB, which includes only those RGB colors
that are appropriate for use on the web.
See also
“To change the color mode of a document” on page 185
About CMYK
Whereas the RGB model depends on a light source to create color, the CMYK model is based on the light-absorbing
quality of ink printed on paper. As white light strikes translucent inks, a portion of the spectrum is absorbed. Color
that is not absorbed is reflected back to your eye.
Combining pure cyan (C), magenta (M), and yellow (Y) pigments would result in black by absorbing, or subtracting,
all colors. For this reason they are called subtractive colors. Black (K) ink is added for better shadow density. (The
letter K came into use because black is the “key” color for registering other colors, and because the letter B also stands
for blue.) Combining these inks to reproduce color is called four-color process printing.
C M Y K
Subtractive colors (CMYK)
C. Cyan M. Magenta Y. Yell ow K. Black
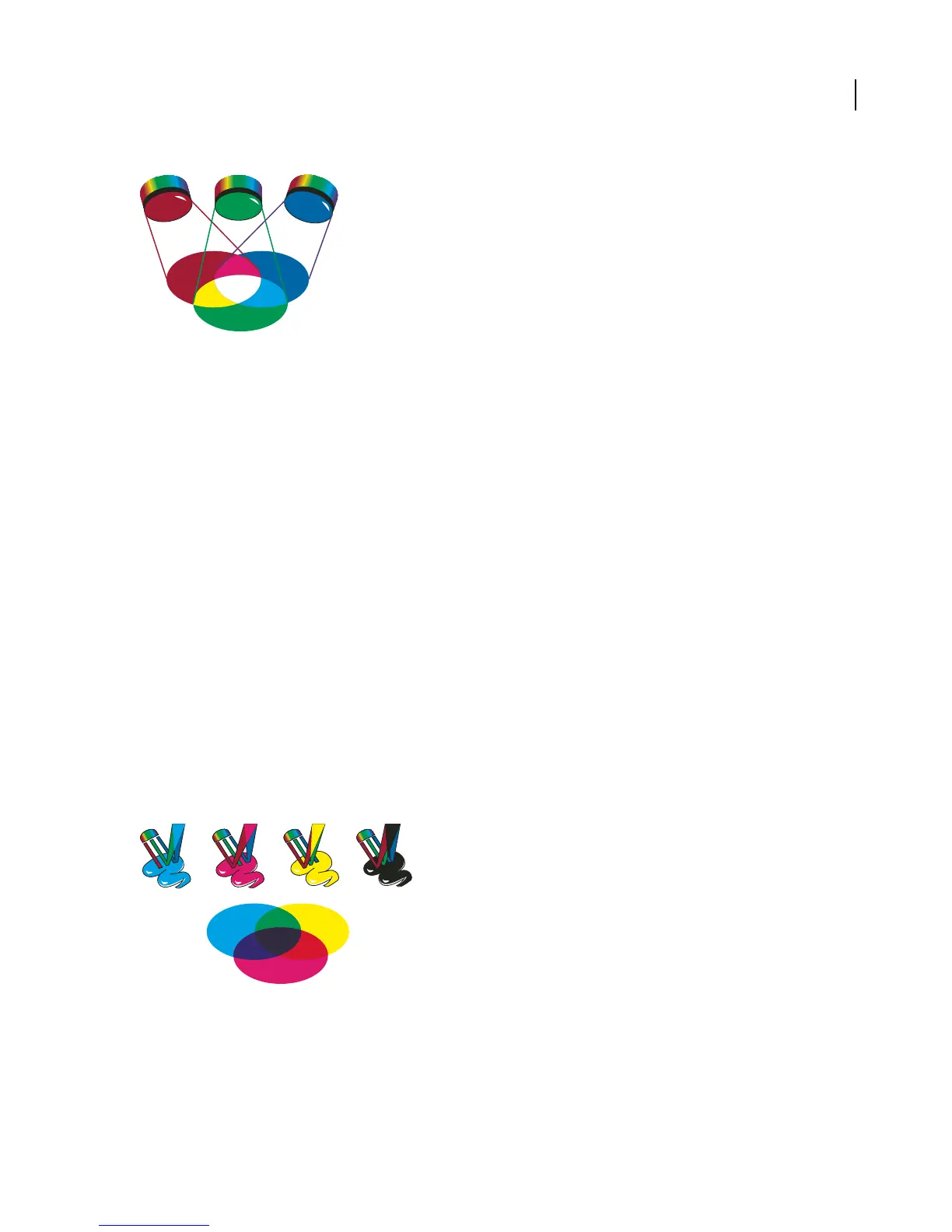 Loading...
Loading...