Rockwell Automation Publication 6000-UM002E-EN-P - April 2018 31
Drive System Layout Chapter 2
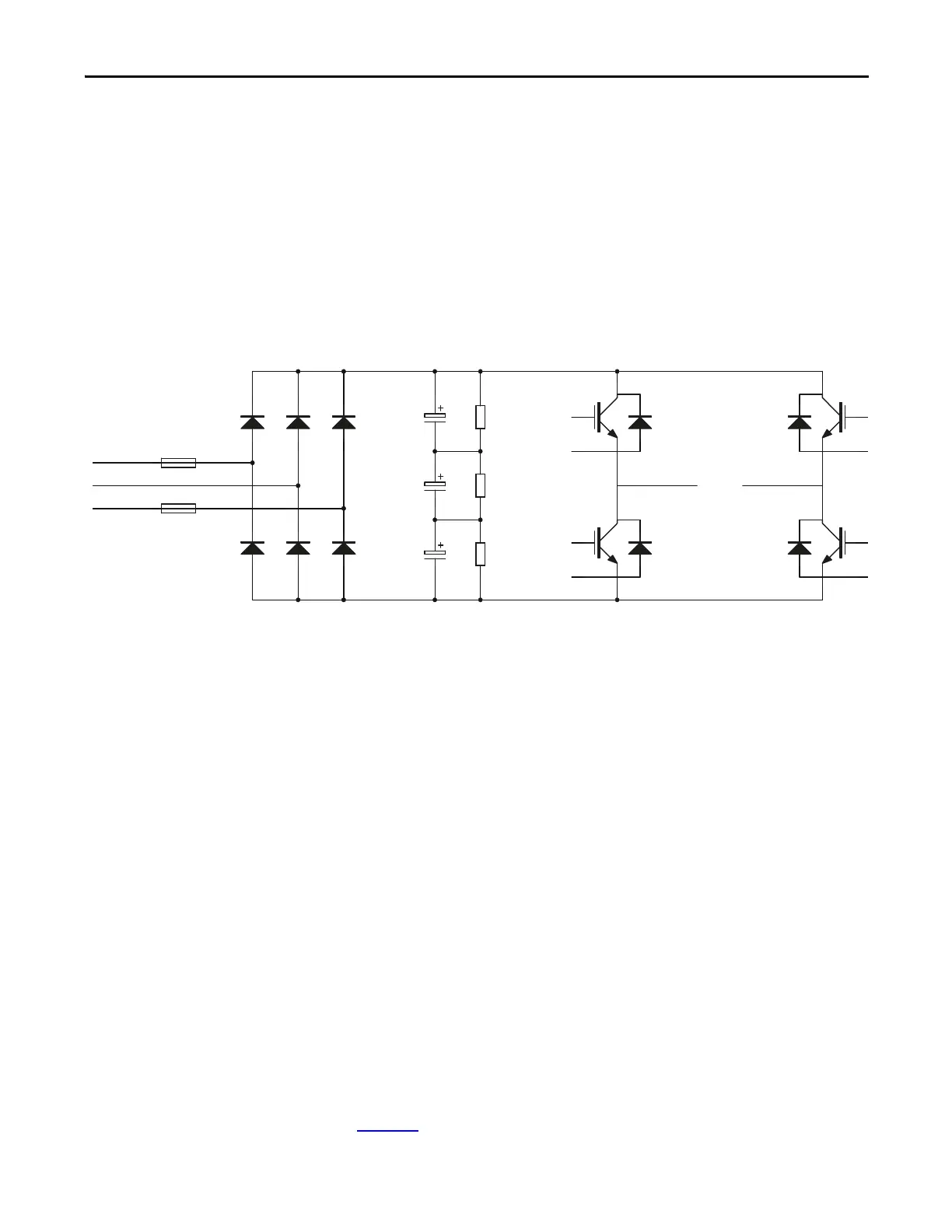
Basic Principle of Power Module
The Power Module combines a three phase rectifier and an “H” bridge inverter,
powered from the secondary side windings of the Isolation Transformer. After
rectifying and filtering, it outputs AC current with variable frequency and
variable voltage under the control of four IGBTs using a PWM switching pattern.
Several Power Modules, after being connected in series and superposed, can
output three-phase AC current with adjustable frequency and voltage to control
an AC motor.
Figure 22 - Low Voltage Power Module
Control signals to the Power Module and the feedback signals from the Power
Module are transmitted by fiber optic cables which provide electrical isolation
between the medium voltage and low voltage sections of the drive, and protects
against electromagnetic interference.
The control signals from the main control unit, through the optical-electrical
converter, are sent to the Power Module control board for further processing and
to the corresponding gate drive circuits to turn the IGBTs on or off.
The status information of the Power Module is transmitted through the
electrical-optical converter and sent to the main control unit. When there is a
fault, the main control unit sends control signals to lockout or bypass the affected
Power Module.
The Power Module cabinet consists of Power Modules, current transformers and
high-voltage cable.
The Power Modules are divided evenly into three phases (U, V, and W). The
units in each phase are connected end-to-end at the output terminals. Then
individual phases are formed, using a star connection. Current transformers are
installed into the U phase and W phase.
Different models of Power Modules are used for drives of different power ratings
(Figure 23
).
Input U
Input V
Input W
Fuse 1
Fuse 2
Three-phase diode
rectifier bridge
DC Bus
capacitor network
Single phase IGBT
inverter network
IGBT 1 IGBT 2
Output A Output B
D1 D2 D3
D4 D5 D6
C1 R1
C2 R2
C3 R3

 Loading...
Loading...