Network Planning
3-7
• Reliability compared to the backbone network; if there is an
accidental break in the wire, only service on the affected
branch will be interrupted .
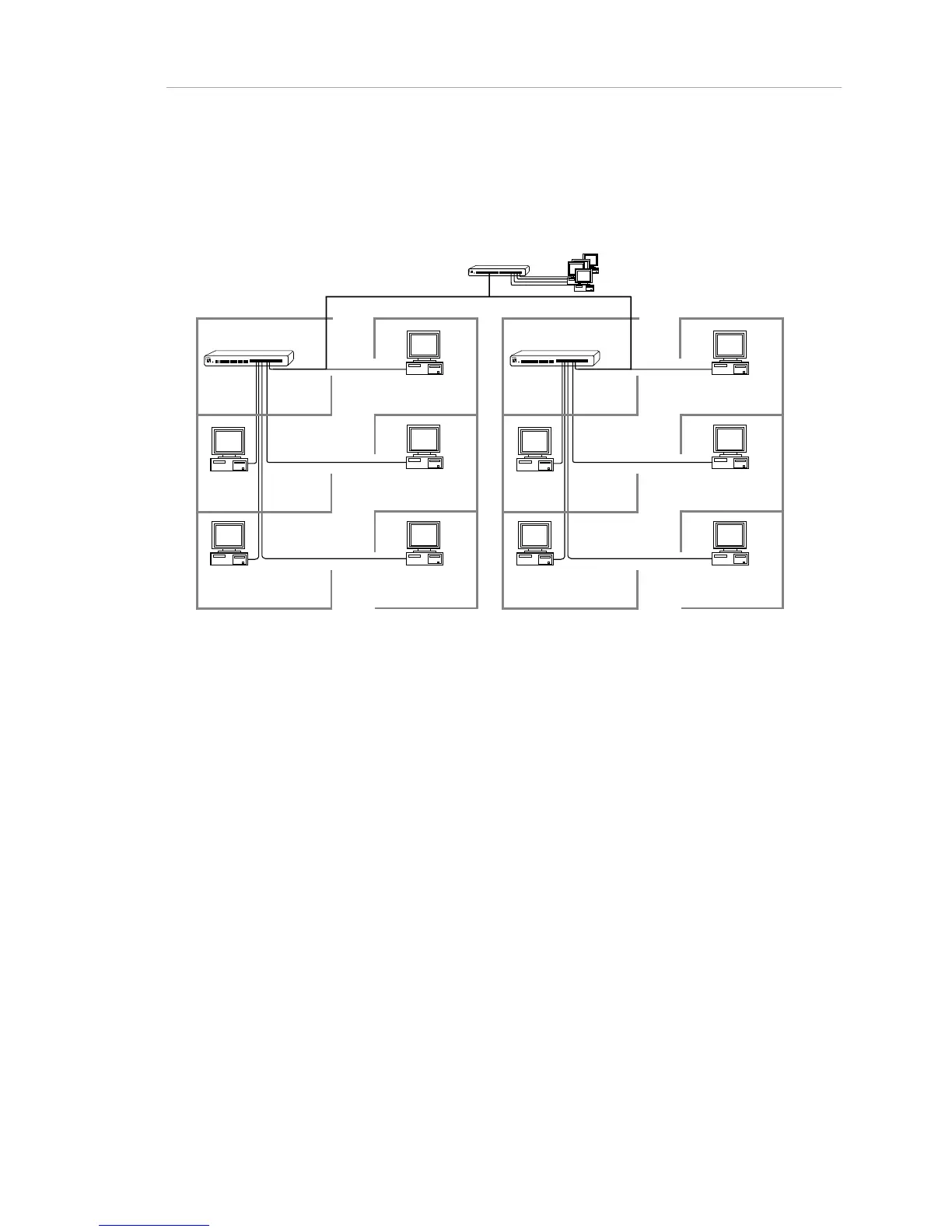
Figure 3-3. Tree Network
Backbone Network
A backbone network suspends hubs from a linear length of cable, either thin or
thick Ethernet cable.
In a thin backbone network, T-connectors integrated into the backbone cable are
connected to the rear panel BNC ports of the AsantéHub. I n a thick backbone
network, the AsantéHub is connected to a thick Ethernet backbone by way of the
rear panel AUI port. Drop cables connected to external transceivers on the
backbone cable, extend to each hub.
Some advantages of a backbone topology are:
• Longer distances between hubs; thick coaxial can span 500
meters and thin coaxial 185 meters, vs. 100 meter limit for
unshielded twisted-pair
• Possible cost reductions since no central hub is required;
compare costs of hub vs. costs of more expensive wiring
 Loading...
Loading...