AUX air conditioner service manual
1
Chapter 1 the operation theory of the home Air-Conditioner
Section one the basic knowledge of pyrology and ventilation
1. Basic Definition
⑴ Temperature
Temperature is a physical value for the definition of the percentage of the cold and heat to an object.
It’s the one of those basic parameters used in confirming the substance’s status. Currently, the world
standard common thermometric scales include the absolute thermometric scale, the Celsius scale, and
the Fahrenheit scale.
The Celsius scale is the most common thermometric scale in usage that has 100parts between the
freezing point of 0 and the boiling point of water of 100 under a standard atmosphere (760mmHg, ℃℃
e.g.1.013×105Pa). Each part is one centigrade with the abbreviation of 1 , and usually a “t” stands ℃
for its reading. The Fahrenheit scale has 180 parts between the freezing point at 32 and boiling ℉
point at 212 of water under a standard atmosphere. Each part is one Fahrenheit with the ℉
abbreviation of 1 , and usually a”t1” stands for its reading. All the temperatures defined by the ℉
Celsius scale and the Fahrenheit scale are called relative temperature.
Absolute temperature is also called thermodynamics scale or Kelvin scale, which is adopted in the
International Unit System. It deduces the temperature at the absolute stop stage of the heating activity
of the molecules inside the substance is 0 degree (e.g. -273.15 ), which ℃ the absolute temperature is
stood for by “K”. Usually, a “T” represents its reading. 1K of the absolute temperature scale is
absolutely equal to 1 of the Celsius scale on value.℃
The conversion relation between the Absolute temperature T, the Celsius scale t and the Fahrenheit
scale t1 is as below:
t=T-273.16≈T-273( )℃
F= (9/5) t+32(℉) =1.8t+32( )℉
The glass thermometer, thermocouple thermometer, Electric-Contact Thermometer, resistance
thermometer and semiconductor thermometer are the common meters in measuring the temperature
during the refrigeration project.
Pressure⑵
The pressure means Force applied uniformly and vertically over a surface, measured as force per unit
of area. It’s also called intensity of pressure by the express of “P” with the unit Newton/m²(N/m2) in
the shortened form Pa. In addition, there are other expresses by the way of kilogram force(kgf/cm2),
liquid height(mmHg 或 mmH2O), and atmospheric pressure(atm)or bar etc.
The conversion relation between the above pressure units is as below:
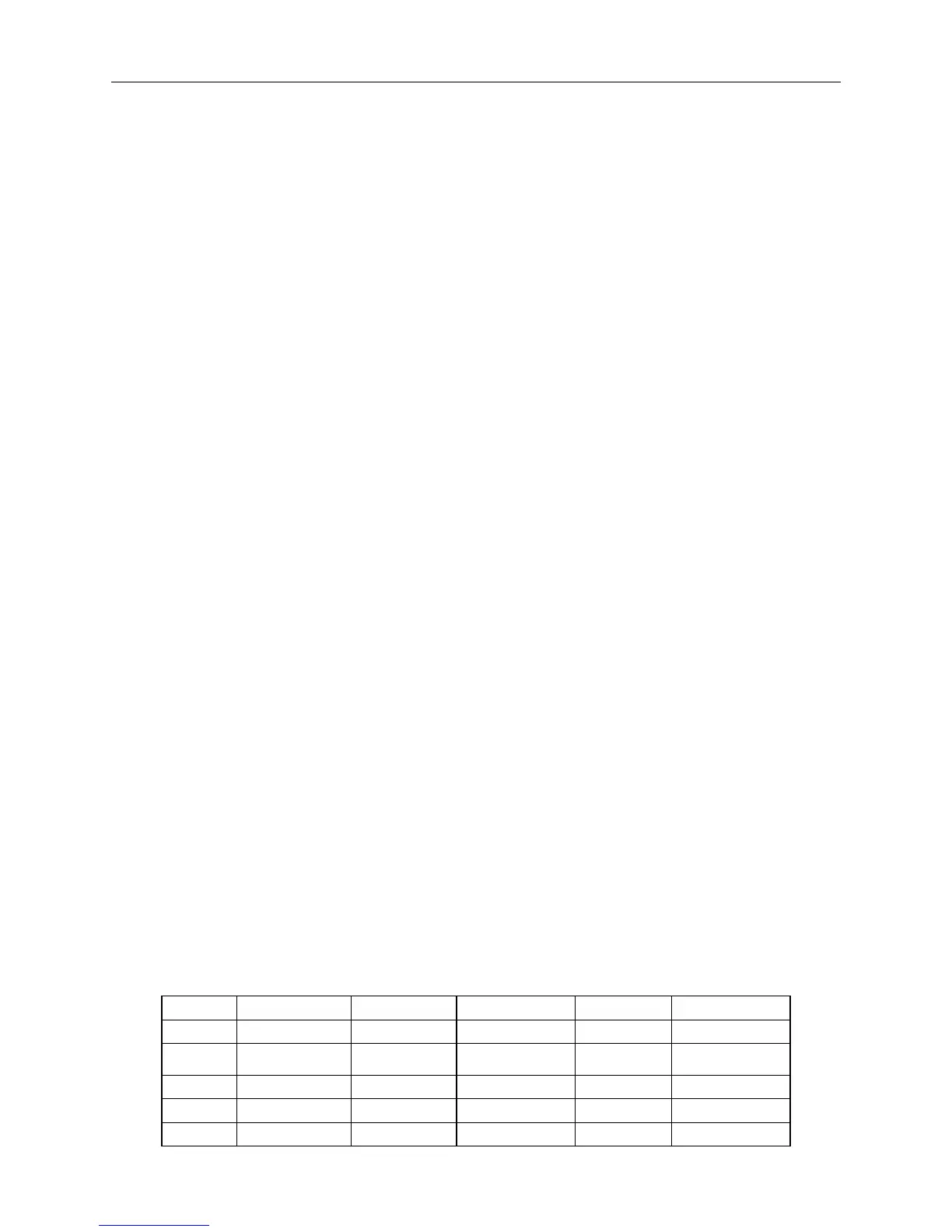
Table 1-1 the Pressure Units Conversion Table
Unit Pa kgf/cm
2
Atm mmHg Psi
Pa 1 1.02×10
-5
9.87×10
-6
7.5×10
-3
1.450×10
4
kgf/cm
2
9.8×10
4
1 9.68×10
-1
7.36×10
2
1.421×10
9
Atm 1.013×10
5
1.033 1 7.6×10
2
1.46885×10
9
mmHg 1.333×10
2
1.36×10
-3
1.316×10
-3
1 1.93285×10
6
Psi 0.68948×10
4
7.0327×10
-2
6.80517×10
-2
51.711 1

 Loading...
Loading...











