AUX air conditioner service manual
4
your hand will feel heated.
Different materials have different heat conductivity. In this case, the heat conductivity coefficient was
introduced as the unit of the value for measuring purpose. Such coefficient represents the amount of
heat that passes by conduction through a one meter thickness of homogeneous material, per one hour
and per one square meter Measured as 1℃ difference between the two surfaces of the material. Its unit
is kJ/ (m.h.℃) and stood for by symbol λ.
The heat conductivity coefficients of some common materials are listed in table 1-2.
The quantity of heat “Q” transferred from the surface is directly proportional to the heat conductivity
coefficient of the material, temperatures’ difference, dimension of the surface and the heat
transmission time while inversely proportional to the surface’s thickness. See Graph 1-4. The Algebra
expression formula is as below:
Q=λSZ(t
1
-t
2
)/δ (kJ)
In the expression formula:
λ——Stands for the heat conductivity coefficient of the material. kJ/(m·h·℃);
S——Stands for the surface dimension,m
2
;
δ——Stands for the thickness of the surface,m;
Z——Stands for the heat transmission time ,h;
t
1
、t
2
——The temperatures of the two surfaces,℃。
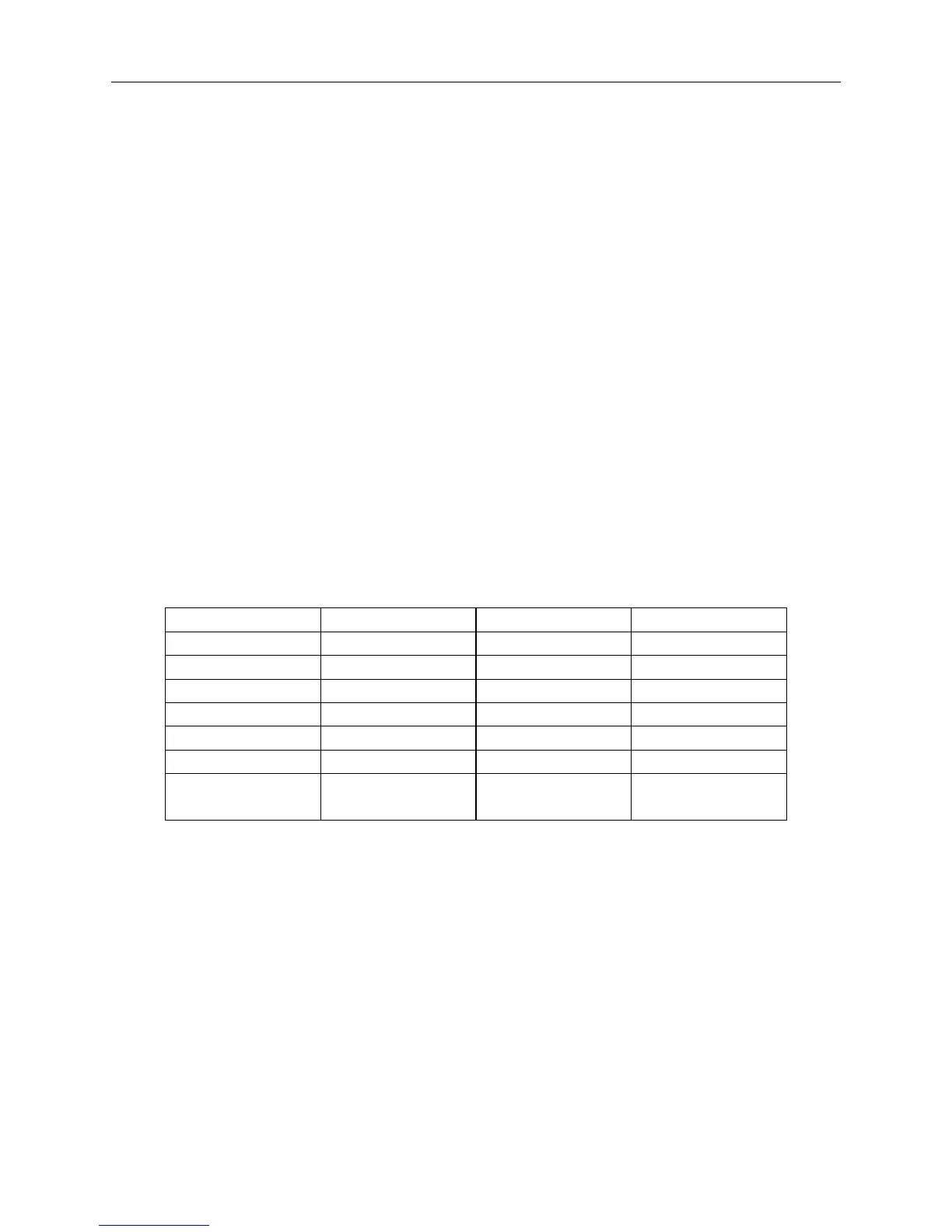
Table 1-2 the heat conductivity coefficients of some common materials
Material λ(kJ/m·h·℃) Material λ(kJ/m·h·℃)
Copper 1382 Softwood 0.17-0.25
Aluminum 733 Air casing 0.25
Steel 163 Water 2.1
Frost layer 2.1 Glass 2.7-2.9
Glass filament 0.17-0.21 Wood 0.25-0.34
Glass wool 0.13 Plywood 0.62-0.84
Slag wool 0.21-0.34
Polyester formed
plastic
0.042-0.11
⑵Convection
The transfer of the quantity of heat caused by the relative movement of the fluid at higher temperature
and the fluid at lower temperature is called convection heat transfer. The convection is only applied to
and only specifically exists in the fluid and gas. The convection heat transfer exists between the fluids
or may exist between the fluid and solid, and may be accompanied by the heat conduction. The main
heat transmission applied in the refrigeration technology usually contains the heat conduction and
convection. The coefficient α stands for the intensity of the convection heat transfer and mainly
affected by the flow speed of the fluid.
The types of convection heat transfer include natural convection and forced convection. Natural
convection is formed by the changes to the density of the molecules of the liquid or gas, such as the
cooling function of the refrigerator’s condenser is mainly based on the effected natural convection of
air. The forced convection is formed and caused by the accelerating flow speed of gas or liquid being

 Loading...
Loading...











