BeagleBone Black System
Reference Manual
Page 41 of 108
6.1.7 Power Consumption
The power consumption of the board varies based on power scenarios and the board boot
processes. Measurements were taken with the board in the following configuration:
DC powered and USB powered
HDMI monitor connected
USB HUB
4GB Thumbdrive
Ethernet connected @ 100M
Serial debug cable connected
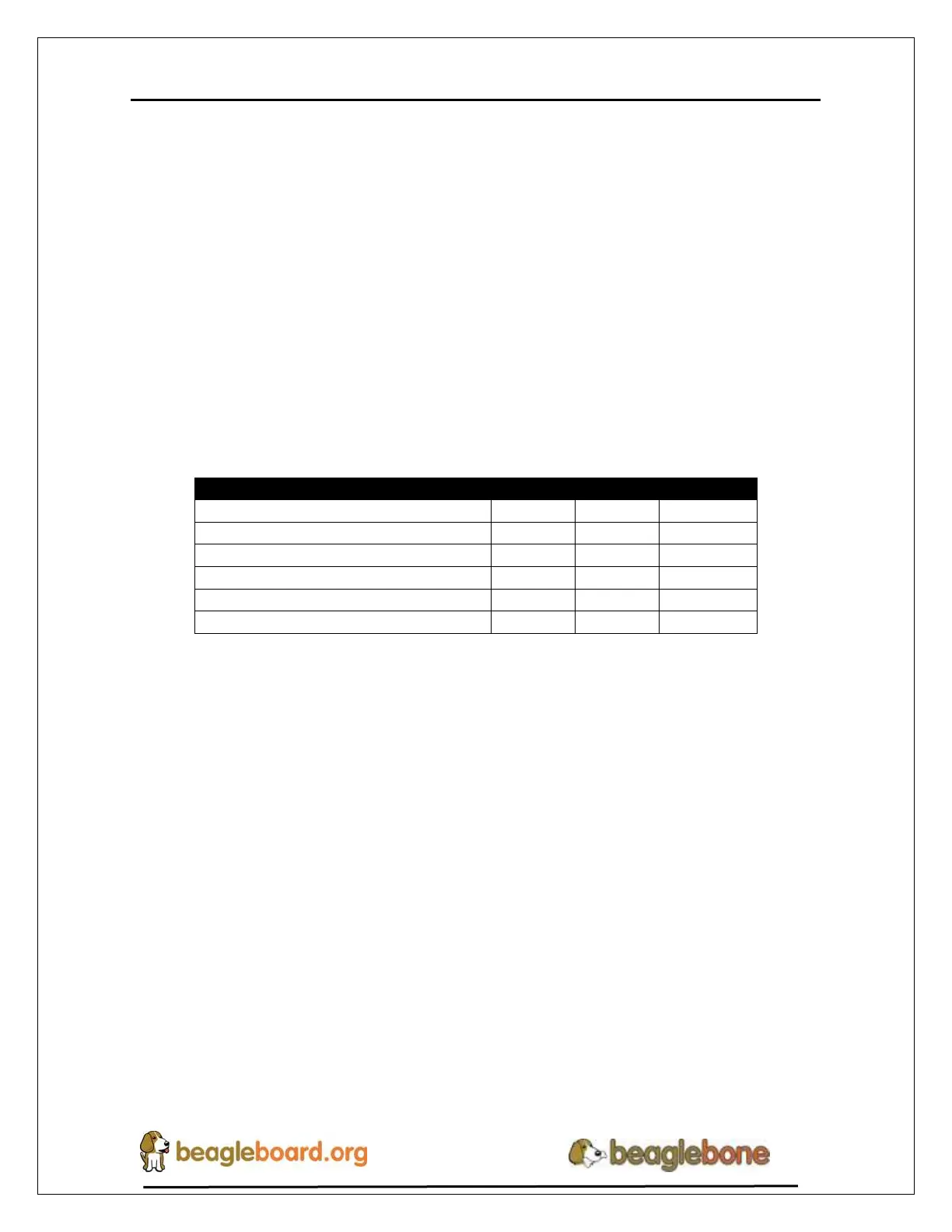
Table 4 is an analysis of the power consumption of the board in these various scenarios.
Table 4. BeagleBone Black Power Consumption(mA@5V)
Kernel Idling Display Blank
The current will fluctuate as various activates occur, such as the LEDs on and
uSD/eMMC accesses.
6.1.8 Processor Interfaces
The processor interacts with the TPS65217C via several different signals. Each of these
signals is described below.
6.1.8.1 I2C0
I2C0 is the control interface between the processor and the TPS65217C. It allows the
processor to control the registers inside the TPS65217C for such things as voltage
scaling and switching of the input rails.
6.1.8.2 PMC_POWR_EN
On power up the VDD_RTC rail activates first. After the RTC circuitry in the processor
has activated it instructs the TPS65217C to initiate a full power up cycle by activating
the PMIC_POWR_EN signal by taking it HI. When powering down, the processor can
take this pin low to start the power down process.

 Loading...
Loading...