IPC@CHIP SC123/SC143
Hardware Manual V1.06 [18.02.2010]
©2000-2008 BECK IPC GmbH Page 25
6.1.2 Memory Organization
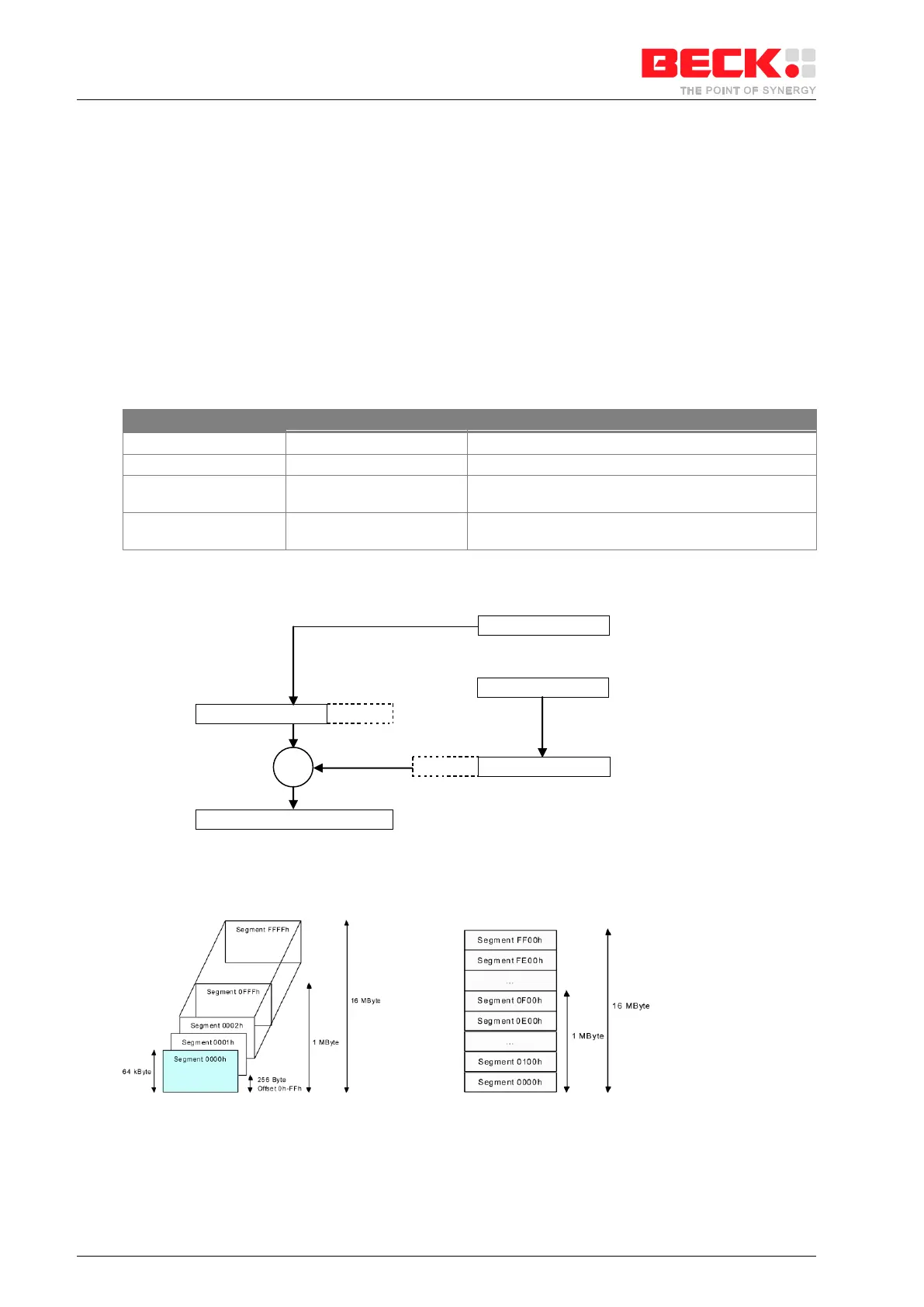
The CPU can address 16MB of physical memory. Memory is organized in sets of segments. Each segment is a
linear contiguous sequence of up to 64K 8-bit bytes. To address memory, two 16-bit pointers must be added
together. The 24-bit address is generated by shifting a segment value left by 8-bits and adding it to a 16-bit
offset or effective address (see Figure 6-1).
All instructions that address operands in memory must specify a segment register and the 16-bit offset value.
Segment registers used for physical address generation are implied by the addressing mode used (see Table
6-3). These rules follow the way programs are written as independent modules that require areas for code,
data, stack, and external data areas. Special segment override instruction prefixes allow the implicit segment
register selection rules to be overridden for special cases.
Implicit Segment Selection Rule
Instruction prefetch and immediate data
All other data references
All stack pushes and pops; any memory references
that use BP as a base register.
All string instruction references that use the DI
register as an index.
Table 6-3: Segment Register Selection Rules
Figure 6-1: 24-Bit Address Generation
6.1.3 24-Bit Address Mode
Figure 6-2: Contiguously segments in memory
The SC1x3 divides it’s address space into segments of 64k. Each segment overlaps 256 bytes to the next
segment.
Concatenate 00\h to Offset
Address Left 4 Bits
Shift Segment Address
Left 8 Bits
 Loading...
Loading...