28
> SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol for supervision of network devices. There are two
entities: an SNMP manager and agents (e.g. Netsilon). The manager queries the agent, which will send messages
to it, known as ‘traps’.
Traps
SNMP traps are messages sent using the SNMP protocol from a monitored device to a monitoring server.
The monitoring server must be have the necessary features to translate the received event in order to understand it.
For this purpose, it must have a database containing the MIB files.
Click Configure then refer to Chapter 4.7.2 SNMP trap configuration.
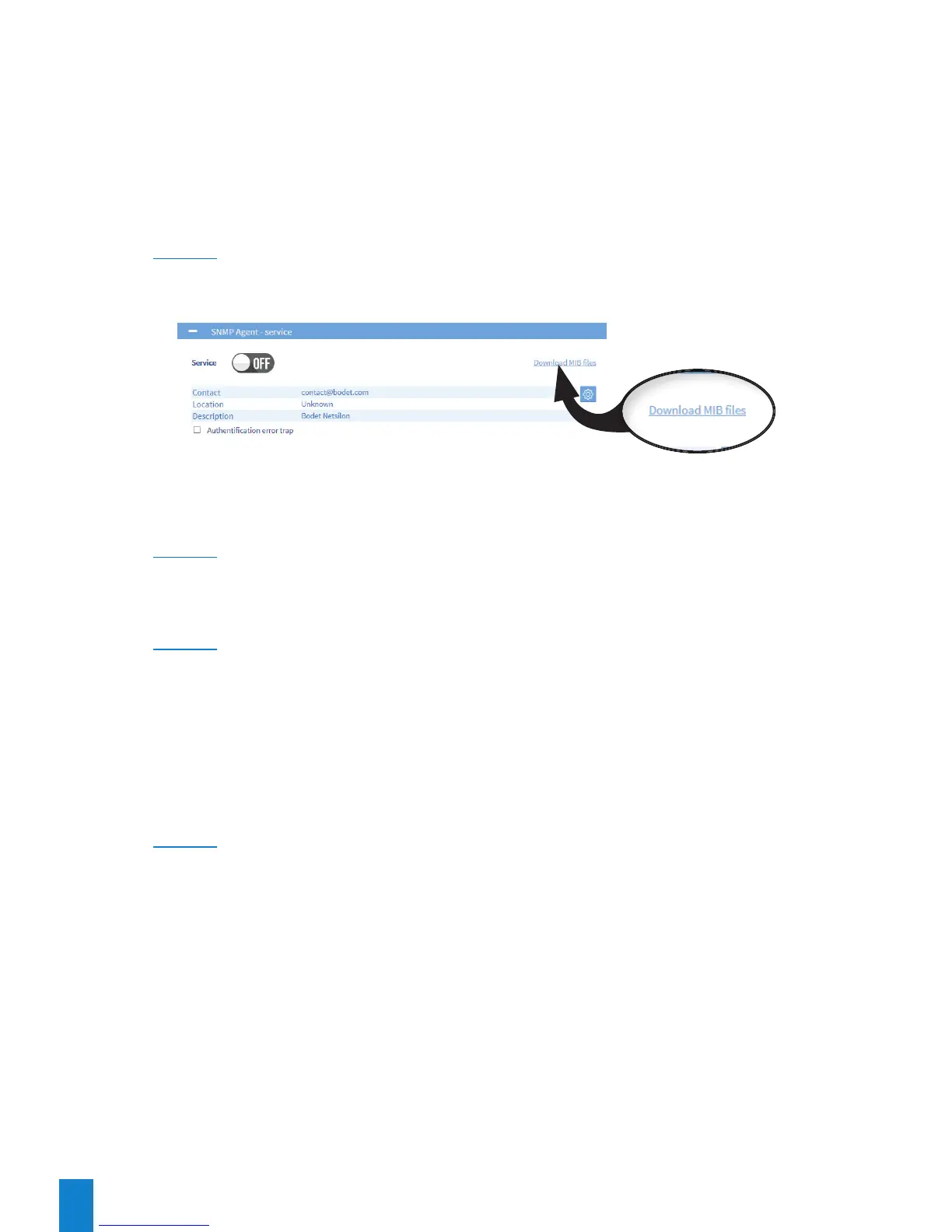
DownloadingtheMIBfile
The MIB file can be obtained from SAFETY > SNMP Agent > SNMP Agent - Service:
The downloaded file is in ZIP format.
Agents
The agents are responsible for transmitting messages related to the management of the equipment in SNMP format.
Click Configure then refer to Chapter 4.8Systemsupervision.
> SMTP
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used to transfer electronic messages (alarms) within a computer network.
An SMTP server is a service which listens on port 25. Its primary purpose is to route mail to a recipient.
Click Configure then refer to Chapter 4.7.1 SMTP configuration.
> NTP
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a client/server protocol for time synchronisation on IP networks.
The NTP service can be enabled or disabled. When NTP is disabled, no NTP data will be sent to the network. When
enabled, the NTP service operates in Unicast mode by default.
All parameters can be changed to configure specific NTP applications: NTP client, NTP servers, NTP peers, NTP
Key and NTP Autokey.
Click Configure then refer to Chapter 4.5.2NTPsynchronisation.
> TIME PROTOCOL and DAYTIMEPROTOCOL
Activating these parameters allows Netsilon to send the UTC time and date (not configurable) to multiple devices on
the network.
 Loading...
Loading...