Utility Requirements
H157655_1_008 67
8.6.1 Heat Dissipation into the Room
Most of the heat dissipated into the room is generated by the system electronics. The magnet
itself does not dissipate any heat. The following table details the heat dissipation into the
room:
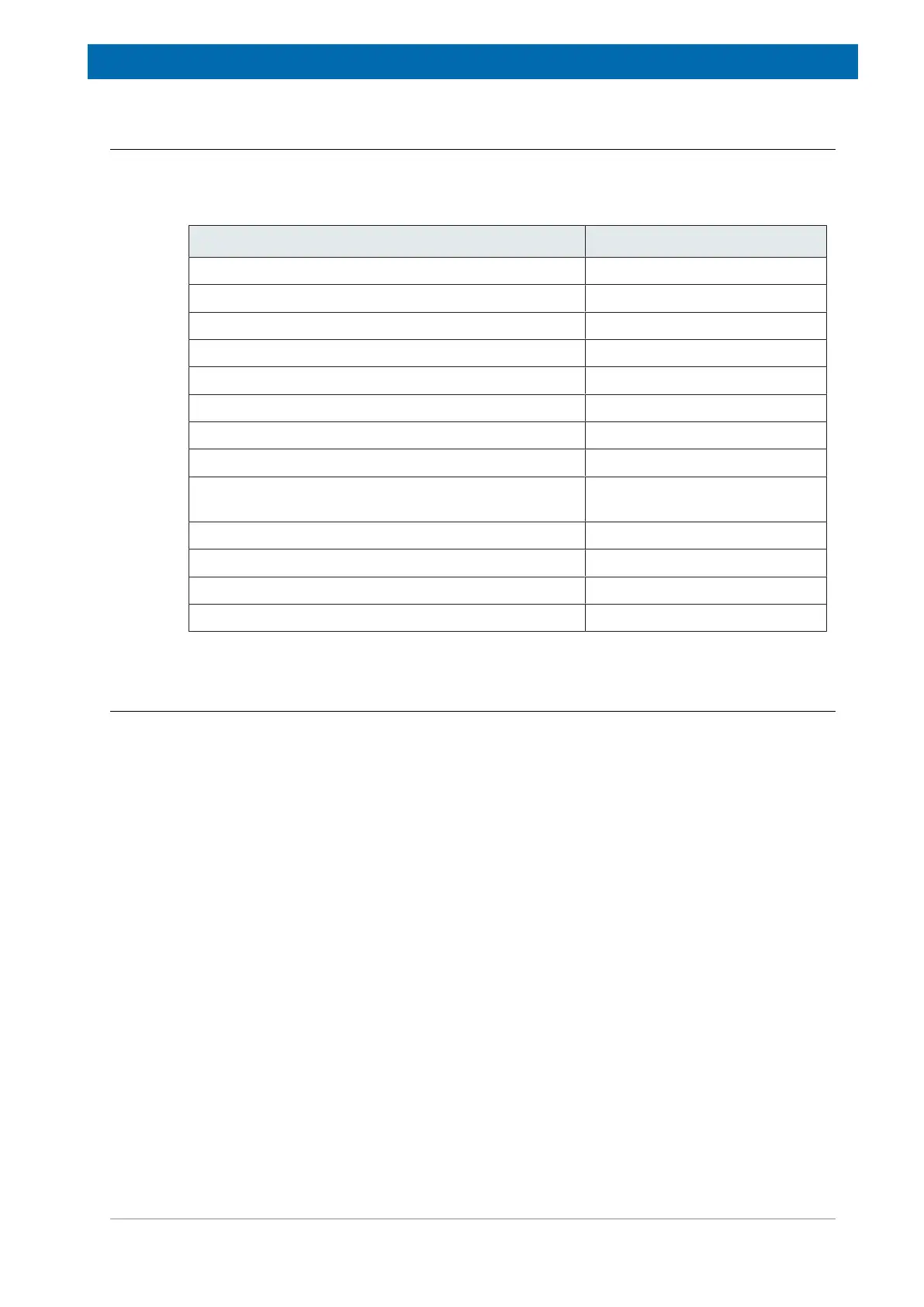
System Heat Dissipation into Room
AVANCE TwoBay (with 3 channels & BCU-I) 2.5 kW
AVANCE TwoBay (configured for solids) 5.0 kW
AVANCE OneBay 2.0 kW
AVANCE NanoBay 1.0 kW
Imaging Cabinet 2.4 kW
BCU-I, BCU-II BCU-I: 0.5 kW, BCU-II: 2.4 kW
Gradient Chiller 0.5 kW
CryoCooling Unit 0.8 kW
He Compressor (note: heat from the outdoor He
compressor is not dissipated inside the room)
0.5 kW - residual
He Compressor CryoProbe - indoor water-cooled 0.5 kW
He Compressor CryoProbe - outdoor air-cooled 8.5 kW
He Compressor BNL - inside water-cooled 2.0 kW
He Compressor BNL - outside air-cooled 2.2 kW
Table8.5: Heat Dissipation into the Room by Typical AVANCE Systems
8.6.2 System Stability
Air Temperature
The heat dissipation of the magnet system is constant over time. It is essential to minimize or
avoid short term oscillations of the HVAC system, and provide a continuous slow flow of air
that in turn reduces the speed of any temperature changes. It is recommended to have a
continuous and slow exchange of air in the laboratory, hence minimizing fluctuations.
Air Diffuser and Return Ducts
• Avoid any air drafts in the room, especially towards the magnet or system electronics.
• Use low velocity diffusers or a perforated duct (e.g. a duct sock).
• In order to remove heat directly from the source it is recommended placing the air return
ducts closer to the rear side of the system electronics.
 Loading...
Loading...











