Service
98-175666-A Chapter 4: Setup of the antenna 4-30
Azimuth calibration (user controlled)
1. On the page SERVICE > Calibration, in the section Azimuth calibration (user
controlled), select User defined in the Satellite drop down list.
2. Type in the longitude of the satellite.
3. Type in its tracking frequency, 19.707 GHz.
4. Select Satellite identifier: GSC, NID, Orbital position (DVB-S, DVB-S2)
1
.
5. Click Start and wait typically 5 minutes for the azimuth calibration to finish. A progress
bar is shown during calibration and a message is displayed when the calibration has
completed. In case of failure, see the table in the following section for a description of
error codes during calibration.
If you do not want to enter the satellite data on the calibration page you can
select a dedicated satellite service profile for calibration and select it.
Check that the satellite transponder is visible from the location of the installation
and that it is at an elevation angle between 5 and 85 degrees.
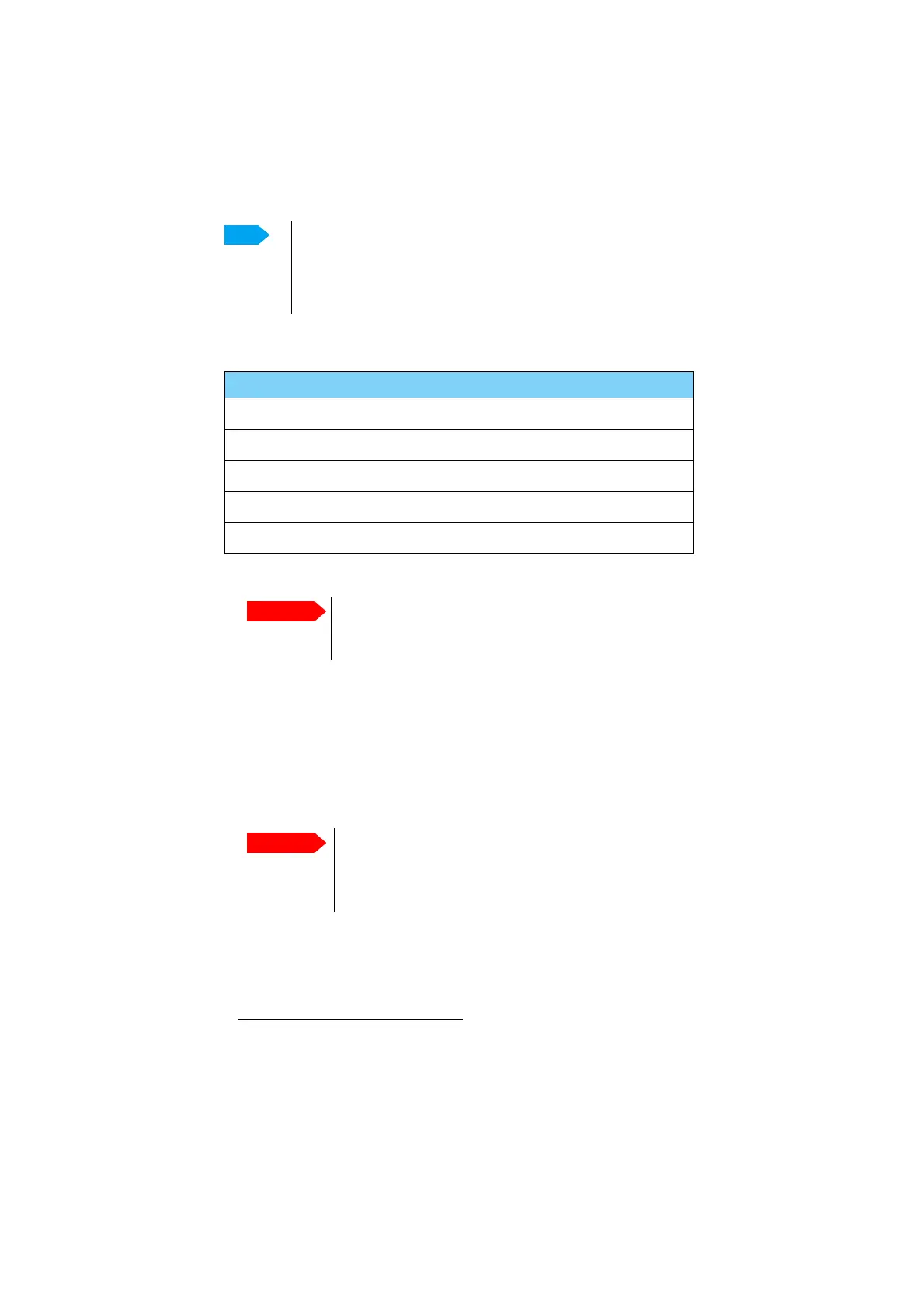
Satellite Position Frequency Polarisation Satellite identifier
GX1 –IOR 62.6 E 19.707 GHz LHC GSC
GX2 –AOR 55 W 19.707 GHz LHC GSC
GX3 –POR 179.6 E 19.707 GHz LHC GSC
GX4 –IOR 56.6 E 19.707 GHz LHC GSC
GX5 –EME 11.0 E 19.701 GHz LHC GSC
Table 4-12: Inmarsat GSC satellite information
The calibration function is not able to verify the correctness or precision of
the supplied longitude. It is therefore important to supply the correct
longitude including the first decimal.
1. Use Orbital position and NID if you want to use NID or orbital position or other KA band
satellites with DVB-S2 support. The DVB symbol rate must be >5 Ms/s. For NID use
preferably a unique NID (ONID). An azimuth calibration without NID can be useful in
regions where the satellite operators do not broadcast NID (US, China, Australia etc.). For
NID=0 the NID is not used when checking the satellite link. For NID 1 to 65535 the
supplied NID is matched against the Network ID broadcast by the satellite. For orbital
position the supplied longitude is matched with the orbital position broadcast by the
satellite. Not all service providers broadcast the orbital position.
It is strongly recommended to verify the result of a calibration performed
with user defined data. This can be done by making a new calibration on a
different satellite and verify that the resulting Azimuth calibration value
differs less than one degree.

 Loading...
Loading...










