Chapter 4. API Guides
6. Channel Switching
7. Performance
8. Further Notes
4.8.2 Introduction
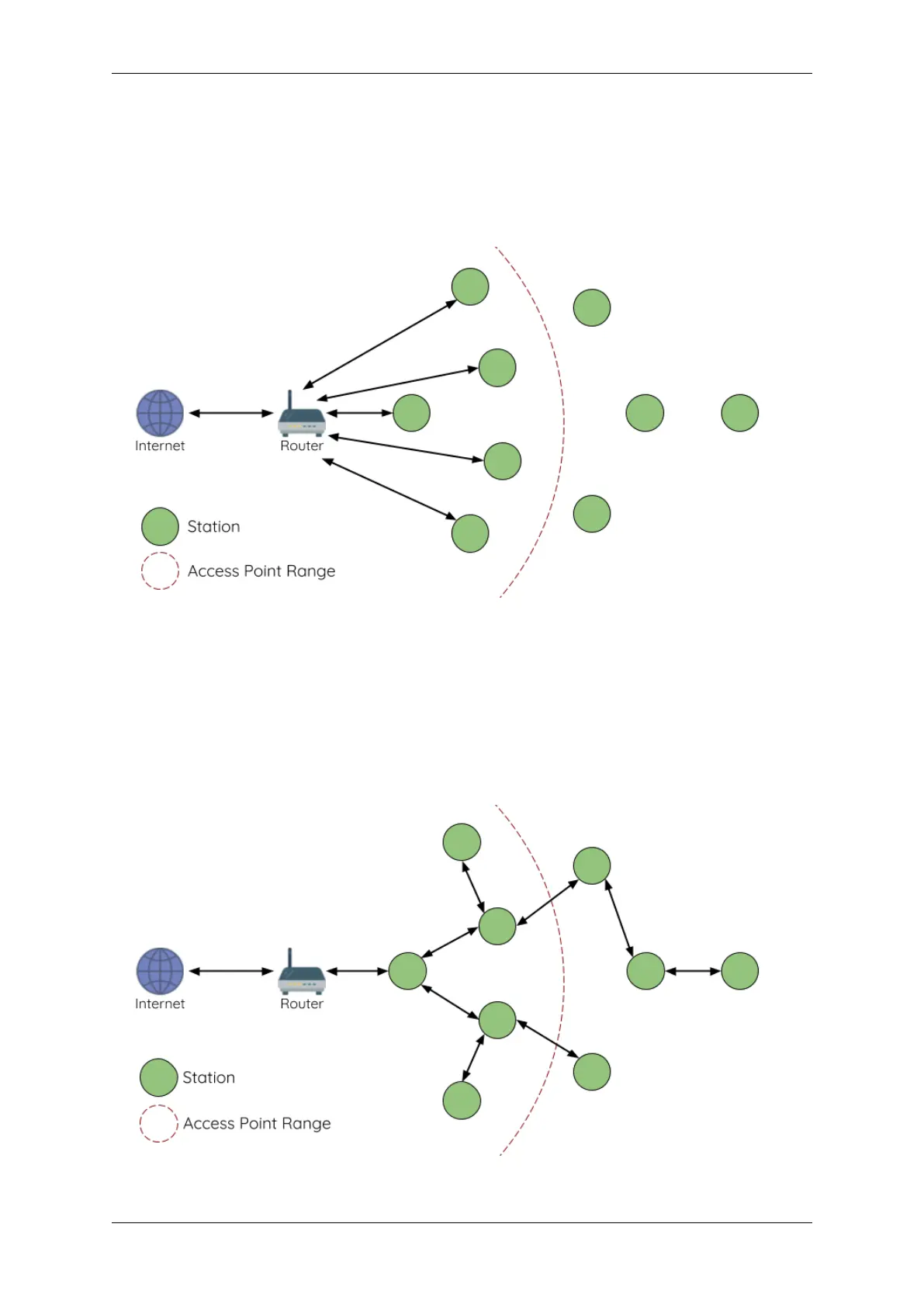
Fig. 3: Traditional Wi-Fi Network Architecture
A traditional infrastructure Wi-Fi network is a point-to-multipoint network where a single central node known as the
access point (AP) is directly connected to all other nodes known as stations. The AP is responsible for arbitrating and
forwarding transmissions between the stations. Some APs also relay transmissions to/from an external IP network
via a router. Traditional infrastructure Wi-Fi networks suffer the disadvantage of limited coverage area due to the
requirement that every station must be in range to directly connect with the AP. Furthermore, traditional Wi-Fi
networks are susceptible to overloading as the maximum number of stations permitted in the network is limited by
the capacity of the AP.
Fig. 4: ESP-WIFI-MESH Network Architecture
Espressif Systems 1307
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4

 Loading...
Loading...