Chapter 2. API Reference
Indicating Write or Read After sending a slave address (see Step 3 on both diagrams above), the master either
writes or reads from the slave.
The information on what the master will actually do is hidden in the least significant bit of the slave’s address.
For this reason, the command link sent by the master to write data to the slave contains the address
(ESP_SLAVE_ADDR << 1) | I2C_MASTER_WRITE and looks as follows:
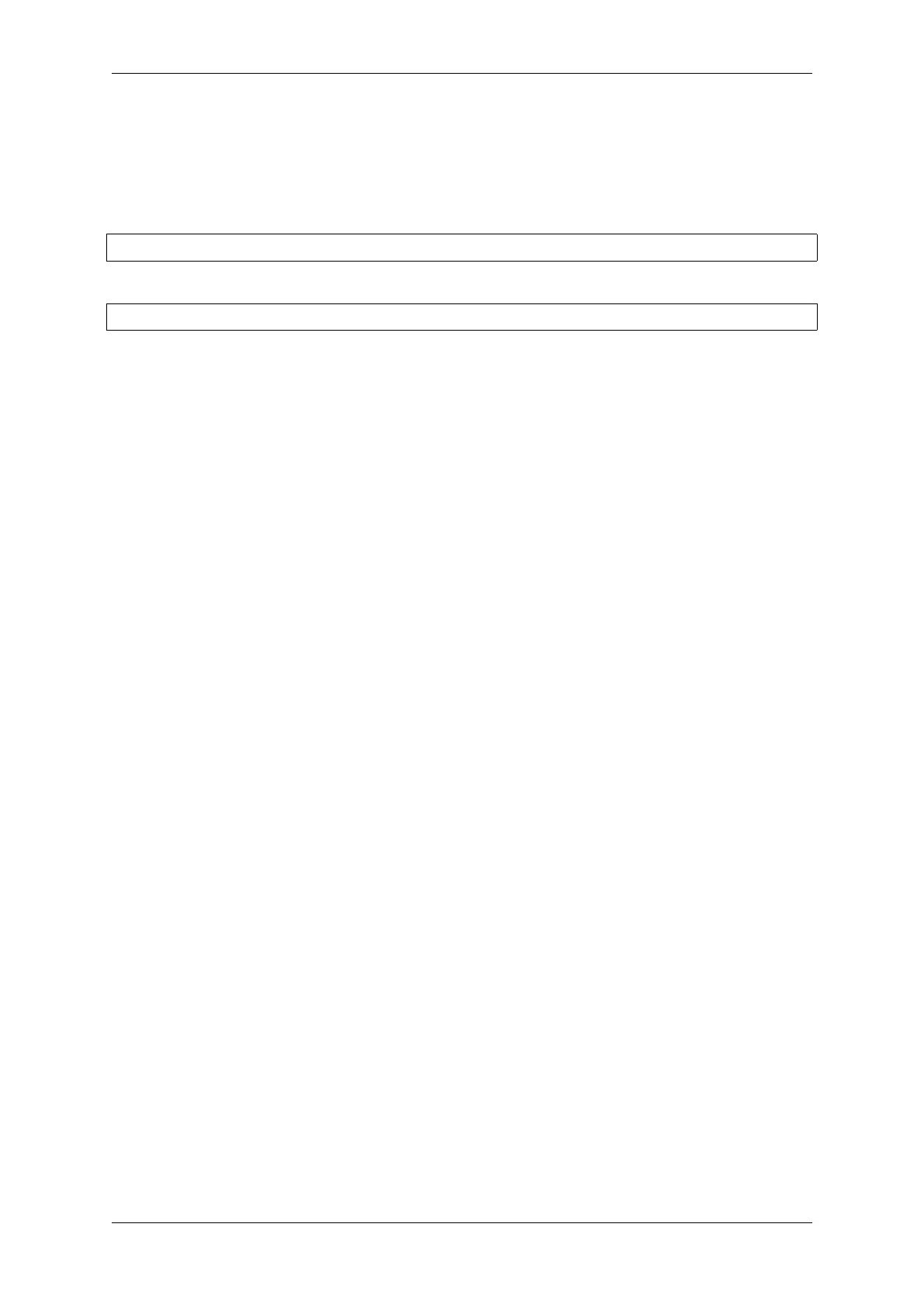
i2c_master_write_byte(cmd, (ESP_SLAVE_ADDR << 1) | I2C_MASTER_WRITE, ACK_EN);
Likewise, the command link to read from the slave looks as follows:
i2c_master_write_byte(cmd, (ESP_SLAVE_ADDR << 1) | I2C_MASTER_READ, ACK_EN);
Communication as Slave After installing the I2C driver, ESP32-S2 is ready to communicate with other I2C
devices.
The API provides the following functions for slaves
• i2c_slave_read_buffer()
Whenever the master writes data to the slave, the slave will automatically store it in the receive
buffer. This allows the slave application to call the function i2c_slave_read_buffer() at
its own discretion. This function also has a parameter to specify block time if no data is in the
receive buffer. This will allow the slave application to wait with a specified timeout for data to
arrive to the buffer.
• i2c_slave_write_buffer()
The send buffer is used to store all the data that the slave wants to send to the mas-
ter in FIFO order. The data stays there until the master requests for it. The function
i2c_slave_write_buffer() has a parameter to specify block time if the send buffer is
full. This will allow the slave application to wait with a specified timeout for the adequate amount
of space to become available in the send buffer.
A code example showing how to use these functions can be found in peripherals/i2c.
Interrupt Handling During driver installation, an interrupt handler is installed by default. However, you can
register your own interrupt handler instead of the default one by calling the function i2c_isr_register().
When implementing your own interrupt handler, refer to ESP32-S2 Technical Reference Manual > I2C Controller
(I2C) > Interrupts [PDF] for the description of interrupts triggered by the I2C controller.
To delete an interrupt handler, call i2c_isr_free().
Customized Configuration As mentioned at the end of Section Configuration, when the function
i2c_param_config() initializes the driver configuration for an I2C port, it also sets several I2C communication
parameters to default values defined in the I2C specification. Some other related parameters are pre-configured in
registers of the I2C controller.
All these parameters can be changed to user-defined values by calling dedicated functions given in the table be-
low. Please note that the timing values are defined in APB clock cycles. The frequency of APB is specified in
I2C_APB_CLK_FREQ.
Espressif Systems 284
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4
 Loading...
Loading...