Chapter 2. API Reference
The driver supports two types of transactions: the interrupt transactions and polling transactions. The programmer
can choose to use a different transaction type per Device. If your Device requires both transaction types, see Notes
on Sending Mixed Transactions to the Same Device.
Interrupt Transactions Interrupt transactions will block the transaction routine until the transaction completes,
thus allowing the CPU to run other tasks.
An application task can queue multiple transactions, and the driver will automatically handle them one-by-one in the
interrupt service routine (ISR). It allows the task to switch to other procedures until all the transactions complete.
Polling Transactions Polling transactions do not use interrupts. The routine keeps polling the SPI Host’s status
bit until the transaction is finished.
All the tasks that use interrupt transactions can be blocked by the queue. At this point, they will need to wait for the
ISR to run twice before the transaction is finished. Polling transactions save time otherwise spent on queue handling
and context switching, which results in smaller transaction duration. The disadvantage is that the CPU is busy while
these transactions are in progress.
The spi_device_polling_end() routine needs an overhead of at least 1 us to unblock other tasks when
the transaction is finished. It is strongly recommended to wrap a series of polling transactions using the functions
spi_device_acquire_bus() and spi_device_release_bus() to avoid the overhead. For more in-
formation, see Bus Acquiring.
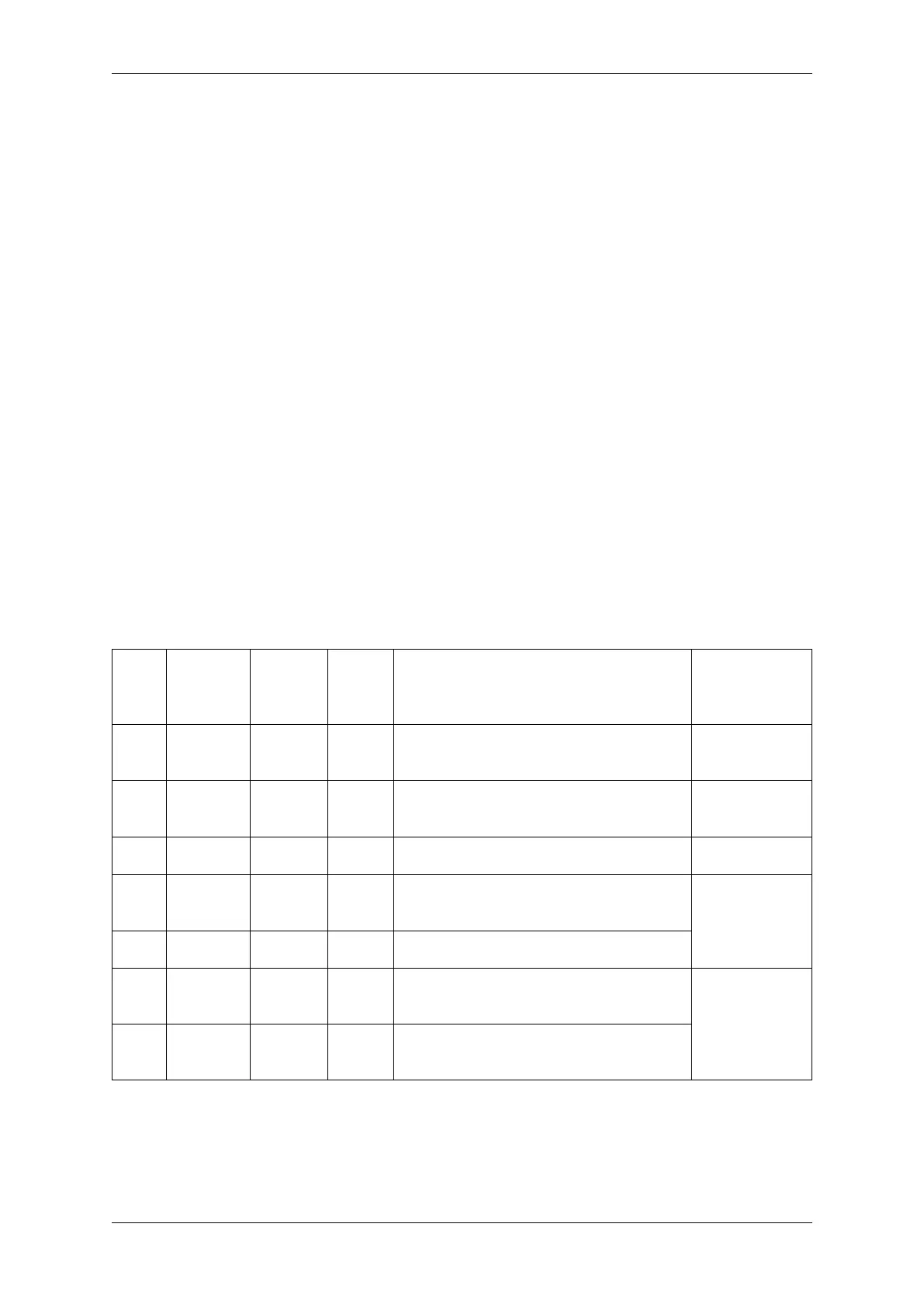
Transaction Line Mode Supported line modes for ESP32-S2 are listed as follows, to make use of these modes,
set the member flags in the struct spi_transaction_t as shown in the Transaction Flag column. If you want
to check if corresponding IO pins are set or not, set the member flags in the spi_bus_config_t as shown in the
Bus IO setting Flag column.
Mode
name
Com-
mand
Line
Width
Address
Line
Width
Data
Line
Width
Transaction Flag Bus IO setting
Flag
Nor-
mal
SPI
1 1 1 0 0
Dual
Out-
put
1 1 2 SPI_TRANS_MODE_DIO SPICOM-
MON_BUSFLAG_DUAL
Dual
I/O
1 2 2 SPI_TRANS_MODE_DIO |
SPI_TRANS_MULTILINE_ADDR
Quad
Out-
put
1 1 4 SPI_TRANS_MODE_QIO SPICOMMON_BUSFLAG_QUAD
Quad
I/O
1 4 4 SPI_TRANS_MODE_QIO |
SPI_TRANS_MULTILINE_ADDR
Octal
Out-
put
1 1 8 SPI_TRANS_MODE_OCT SPICOMMON_BUSFLAG_OCTAL
OPI 8 8 8 SPI_TRANS_MODE_OCT |
SPI_TRANS_MULTILINE_ADDR |
SPI_TRANS_MULTILINE_CMD
Command and Address Phases During the command and address phases, the members cmd and addr in the
struct spi_transaction_t are sent to the bus, nothing is read at this time. The default lengths of the command
and address phases are set in spi_device_interface_config_t by calling spi_bus_add_device().
If the flags SPI_TRANS_VARIABLE_CMD and SPI_TRANS_VARIABLE_ADDR in the member
Espressif Systems 367
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4

 Loading...
Loading...