Chapter 2. API Reference
esp_err_t _http_event_handle(esp_http_client_event_t *evt)
{
switch(evt->event_id) {
case HTTP_EVENT_ERROR:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_ERROR");
break;
case HTTP_EVENT_ON_CONNECTED:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_ON_CONNECTED");
break;
case HTTP_EVENT_HEADER_SENT:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_HEADER_SENT");
break;
case HTTP_EVENT_ON_HEADER:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_ON_HEADER");
printf("%.*s", evt->data_len, (char*)evt->data);
break;
case HTTP_EVENT_ON_DATA:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_ON_DATA, len=%d", evt->data_len);
if (!esp_http_client_is_chunked_response(evt->client)) {
printf("%.*s", evt->data_len, (char*)evt->data);
}
break;
case HTTP_EVENT_ON_FINISH:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_ON_FINISH");
break;
case HTTP_EVENT_DISCONNECTED:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "HTTP_EVENT_DISCONNECTED");
break;
}
return ESP_OK;
}
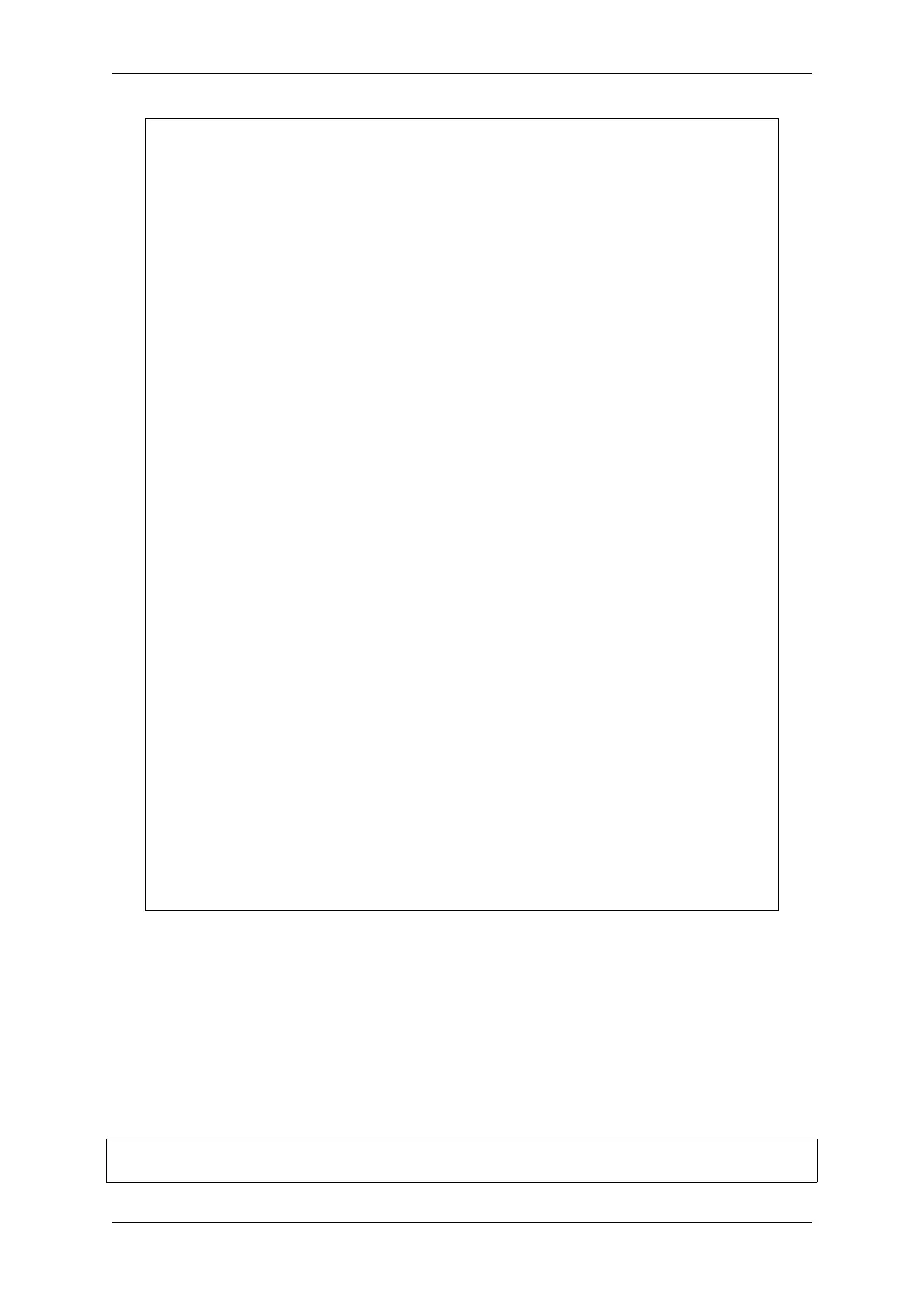
esp_http_client_config_t config = {
.url = "http://httpbin.org/redirect/2",
.event_handler = _http_event_handle,
};
esp_http_client_handle_t client = esp_http_client_init(&config);
esp_err_t err = esp_http_client_perform(client);
if (err == ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Status = %d, content_length = %d",
esp_http_client_get_status_code(client),
esp_http_client_get_content_length(client));
}
esp_http_client_cleanup(client);
Persistent Connections
Persistent connections means that the HTTP client can re-use the same connection for several transfers. If the server
does not request to close the connection with the Connection: close header, the new transfer with sample ip
address, port, and protocol.
To allow the HTTP client to take full advantage of persistent connections, you should do as many of your file transfers
as possible using the same handle.
Persistent Connections example
esp_err_t err;
esp_http_client_config_t config = {
(continues on next page)
Espressif Systems 558
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4
 Loading...
Loading...