Chapter 2. API Reference
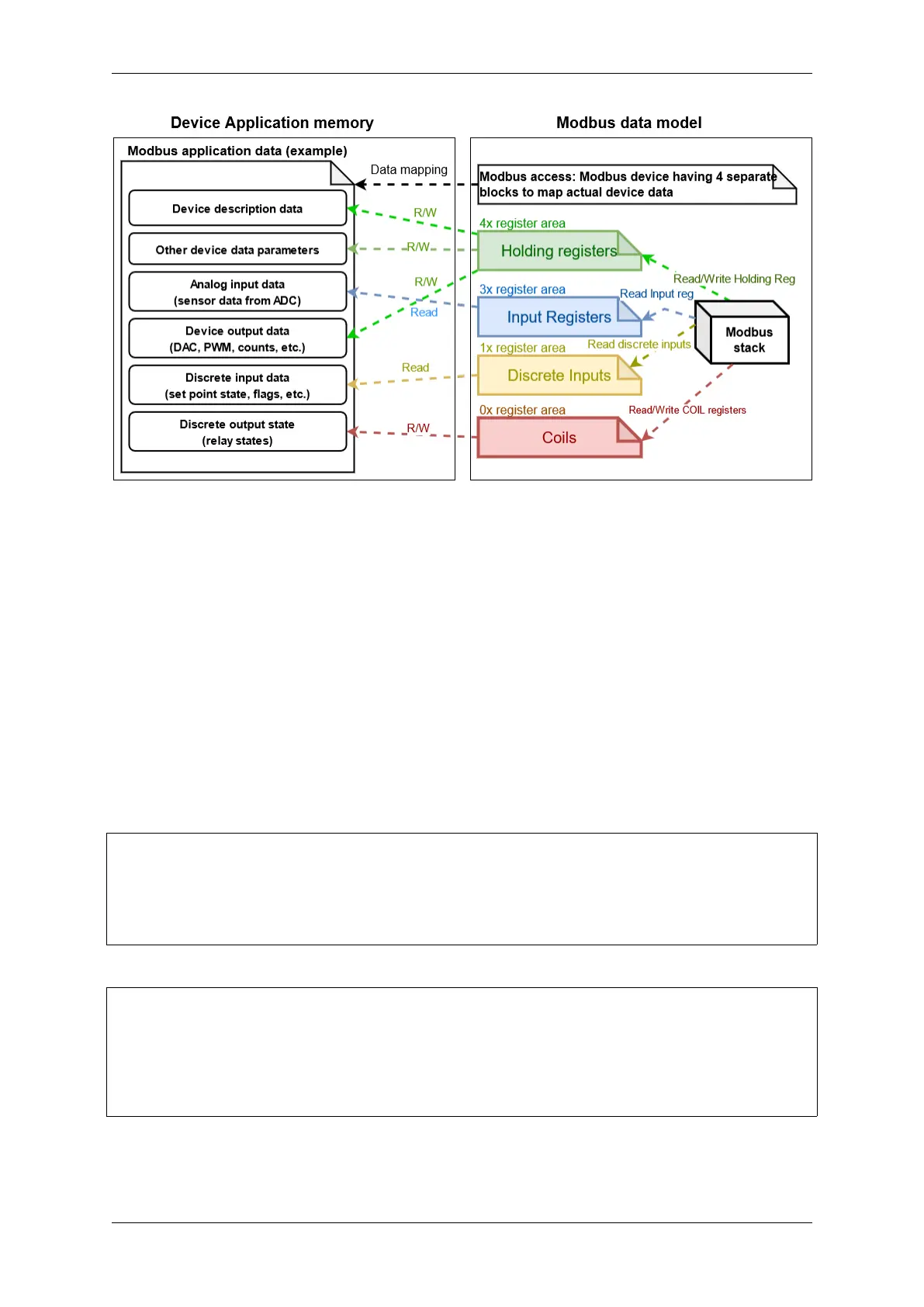
Fig. 26: Modbus data mapping
• Modbus Slave API Overview
• Modbus Master API Overview
Modbus Port Initialization The ESP_Modbus supports Modbus SERIAL and TCP ports and a port must be
initialized before calling any other Modbus API. The functions below are used to create and then initialize Modbus
controller interface (either master or slave) over a particular transmission medium (either Serial or TCP/IP):
• mbc_slave_init()
• mbc_master_init()
• mbc_slave_init_tcp()
• mbc_master_init_tcp()
The API call uses the first parameter to recognize the type of port being initialized. Supported enumeration
for different ports: MB_PORT_SERIAL_MASTER, MB_PORT_SERIAL_SLAVE accordingly. The parameters
MB_PORT_TCP_MASTER, MB_PORT_TCP_SLAVE are reserved for internal usage.
void* master_handler = NULL; // Pointer to allocate interface structure
// Initialization of Modbus master for serial port
esp_err_t err = mbc_master_init(MB_PORT_SERIAL_MASTER, &master_handler);
if (master_handler == NULL || err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "mb controller initialization fail.");
}
This example code to initialize slave port:
void* slave_handler = NULL; // Pointer to allocate interface structure
// Initialization of Modbus slave for TCP
esp_err_t err = mbc_slave_init_tcp(&slave_handler);
if (slave_handler == NULL || err != ESP_OK) {
// Error handling is performed here
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "mb controller initialization fail.");
}
Espressif Systems 623
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4

 Loading...
Loading...