Chapter 2. API Reference
Configure and Install driver
esp_async_memcpy_install() is used to install the driver with user’s configuration. Please note that async
memcpy has to be called with the handle returned from esp_async_memcpy_install().
Driver configuration is described in async_memcpy_config_t: backlog: This is used to configured the max-
imum number of DMA operation that can be working at the background at the same time. sram_trans_align:
Declare SRAM alignment for both data address and copy size, set to zero if the data has no restriction in alignment.
If set to a quadruple value (i.e. 4X), the driver will enable the burst mode internally, which is helpful for some
performance related application. psram_trans_align: Declare PSRAM alignment for both data address and
copy size. User has to give it a valid value (only 16, 32, 64 are supported) if the destination of memcpy is located in
PSRAM. The default alignment (i.e. 16) will be applied if it’s set to zero. Internally, the driver configures the size
of block used by DMA to access PSRAM, according to the alignment. flags: This is used to enable some special
driver features.
ASYNC_MEMCPY_DEFAULT_CONFIG provides a default configuration, which specifies the backlog to 8.
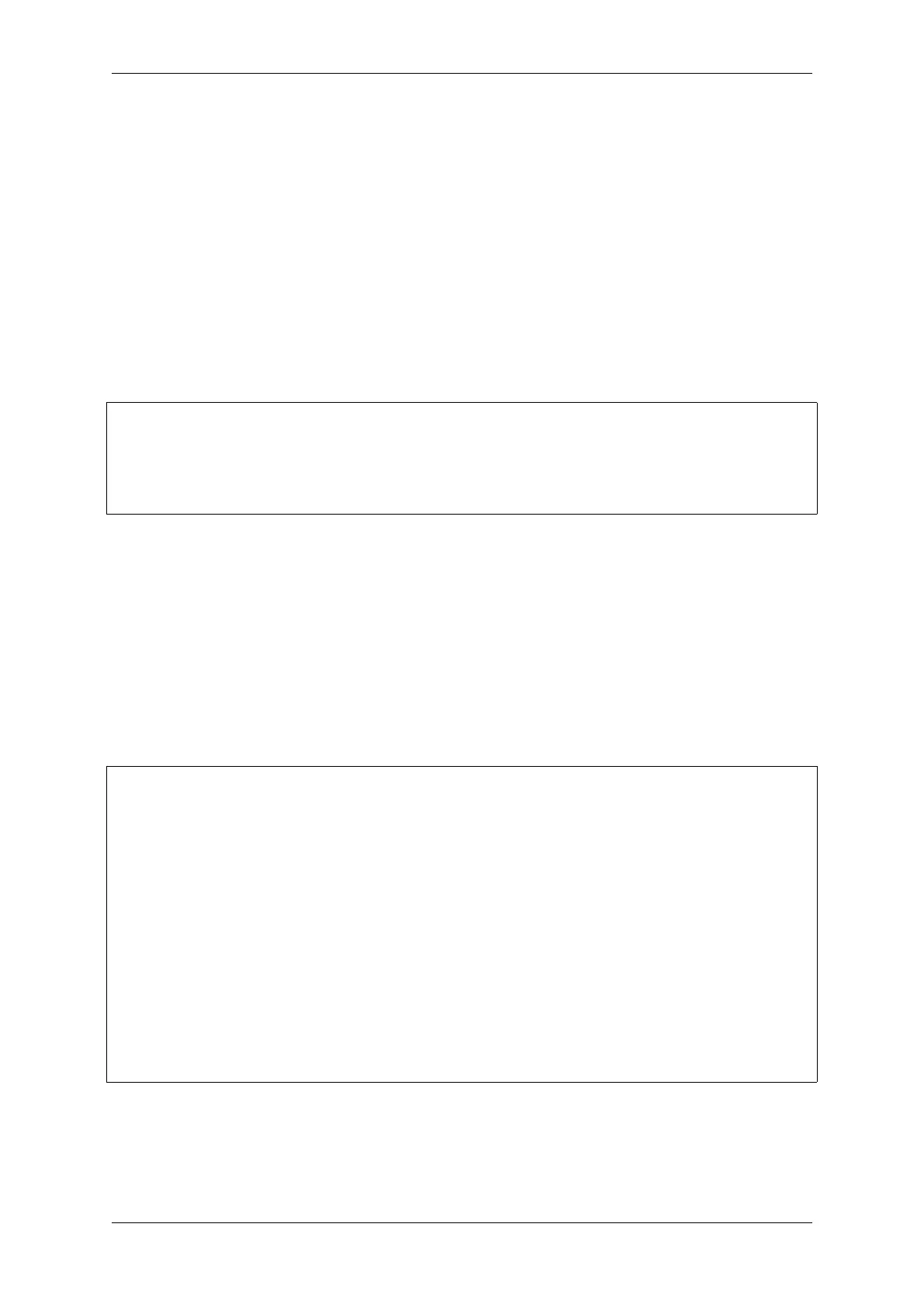
async_memcpy_config_t config = ASYNC_MEMCPY_DEFAULT_CONFIG();
// update the maximum data stream supported by underlying DMA engine
config.backlog = 16;
async_memcpy_t driver = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_async_memcpy_install(&config, &driver)); // install driver,␣
,→return driver handle
Send memory copy request
esp_async_memcpy() is the API to send memory copy request to DMA engine. It must be called after driver
is installed successfully. This API is thread safe, so it can be called from different tasks.
Different from the libc version of memcpy, user should also pass a callback to esp_async_memcpy(), if it’s
necessary to be notified when the memory copy is done. The callback is executed in the ISR context, make sure you
won’t violate the the restriction applied to ISR handler.
Besides that, the callback function should reside in IRAM space by applying IRAM_ATTR attribute. The prototype
of the callback function is async_memcpy_isr_cb_t, please note that, the callback function should return true
if it wakes up a high priority task by some API like xSemaphoreGiveFromISR().
Semphr_Handle_t semphr; //already initialized in somewhere
// Callback implementation, running in ISR context
static IRAM_ATTR bool my_async_memcpy_cb(async_memcpy_t mcp_hdl, async_memcpy_
,→event_t *event, void *cb_args)
{
SemaphoreHandle_t sem = (SemaphoreHandle_t)cb_args;
BaseType_t high_task_wakeup = pdFALSE;
SemphrGiveInISR(semphr, &high_task_wakeup); // high_task_wakeup set to pdTRUE␣
,→if some high priority task unblocked
return high_task_wakeup == pdTRUE;
}
// Called from user's context
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_async_memcpy(driver_handle, to, from, copy_len, my_async_
,→memcpy_cb, my_semaphore));
//Do something else here
SemphrTake(my_semaphore, ...); //wait until the buffer copy is done
Uninstall driver (optional)
esp_async_memcpy_uninstall() is used to uninstall asynchronous memcpy driver. It’s not necessary to
uninstall the driver after each memcpy operation. If you know your application won’t use this driver anymore, then
Espressif Systems 795
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4

 Loading...
Loading...