CLOSED-CASE CALIBRATION
Remote AM Calibration Procedure 3-7.
This following paragraphs describe the remote AM calibration procedure, the remote
commands used in the procedure, and the elements required to build a functioning
controller program. Refer to the heading "Remote Calibration" (earlier in Section 3)
for general information relating to all remote calibration procedures.
A complete program listing that runs on a Fluke 1722A controller is provided in
Appendix G.
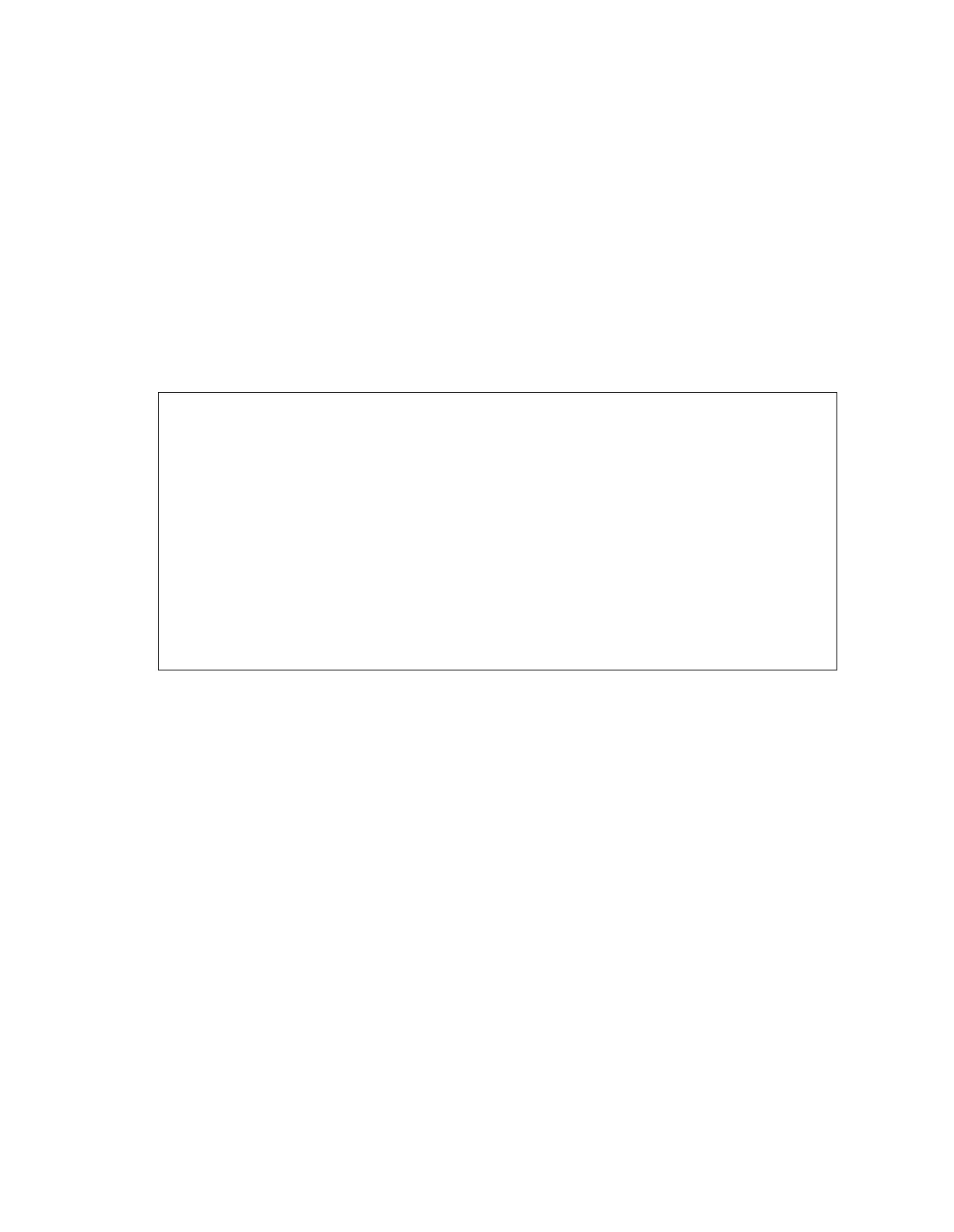
The basic structure of the AM calibration program is shown in the program in Figure
3-2.
initiate the AM calibration procedure with "CAL_AM"
initialize modulation meter
MAIN_LOOP:
request the RF frequency with "CC_FREQ?"
if( frequency = 9e9) goto DONE
read modulation meter
send reading to 6080A/AN with "CC_RDAM"
goto MAIN_LOOP
DONE:
store new data in calibration memory with "CC_SAVE"
end
Figure 3-2. Structure of the AM Calibration Program
The procedure is initiated by the command CAL_AM. The controller requests the
signal generator's center frequency with the command CC_FREQ? and waits for a
response. When a response is received, the controller gets a mod meter reading and
sends it to the signal generator with the command CC_RDAM. The program remains
in the main loop until the signal generator returns the end code "9E+09, Hz" in
response to the CC_FREQ? command. The main loop is then exited and the data is
saved with the CC_SAVE command.
Each time the signal generator receives a reading from the controller, it adjusts its
internal settings and programs the new AM depth. When the signal generator receives
two consecutive readings within 0.1% of the target value (50.0%), it considers the
adjustment value correct and returns the end code.
The controller program must ensure that each mod meter reading is settled before
sending the reading to the 6080A/AN. The program listing in Appendix G uses a
simple but effective method to obtain valid mod meter readings.
The programming commands used in a remote AM calibration procedure are listed in
the Table 3-2. See Table 5B-3 in Section 5B of the Operator Manual for a complete
syntax description of each command.
3-6
 Loading...
Loading...