9. Advanced OPTIC-4 Features
9.1 Automated Solvent Vent Mode
One of the frequently used gas chromatography injection techniques is a large volume injection. In
this technique the sample is injected with the split line open at an inlet temperature below the
solvent boiling point. After the injection, the solvent front passes across the head of the capillary GC
column and is vented through the split line. This solvent elimination step is largely completed in
approximately 5 to 80 seconds, depending on the solvent type and injection volume and vent flow.
The optimization of the vent time is straightforward but can be time-consuming. OPTIC-4 has a
solvent monitor (SM) built in the split line of the inlet, which makes it easier to determine the
solvent elimination time during the vent transfer. Depending on the value of Vent Mode parameter
the vent time is determined manually (Vent Mode = Fixed Time) or automatically by the solvent
monitor (Vent Mode = SM Threshold or SM Level). The diagram below illustrates the automatic
absolute and relative modes.
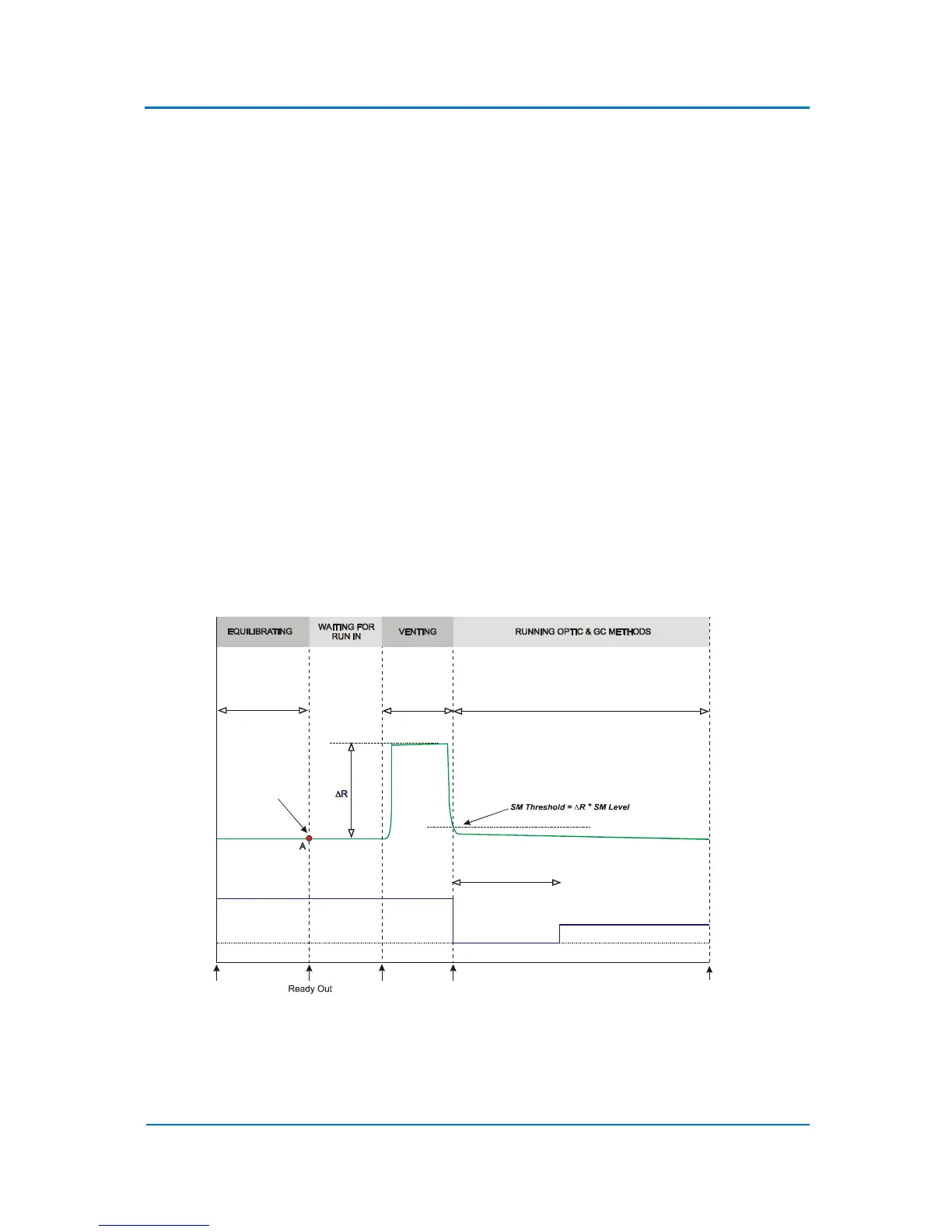
In the absolute mode (Vent Mode = SM Threshold) the split line is closed when the solvent monitor
signal drops below the SM Threshold set point defined by the user (Fig. 9.1). In the relative mode
(Vent Mode = SM Level) the system calculates the SM Threshold at which the split line is closed. For
this purpose, OPTIC-4 measures the solvent monitor zero (baseline) level (point A in the diagram)
and the maximum value of the solvent peak R. The SM Threshold is then calculated as R SM
Level.
Figure 9.1 Solvent monitor signal in absolute and relative vent modes

 Loading...
Loading...