13.10 Calculation Formula
208
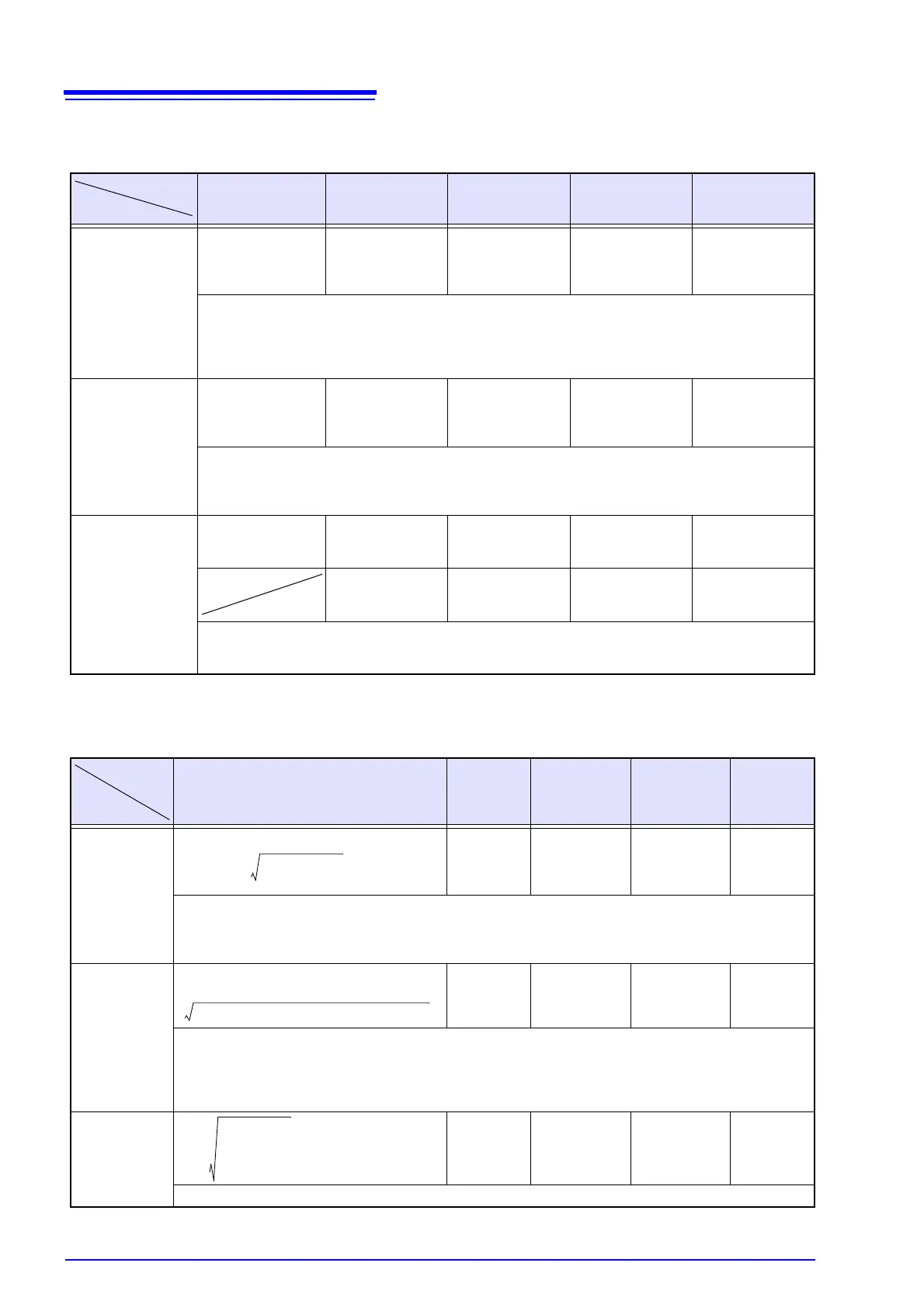
Note: c: measurement channel; k: order of analysis; r: resistance after FFT; i: reactance after FFT
Note: c: measurement channel
Harmonic Voltage Phase Angle (Uphase), Harmonic Current Phase Angle (Iphase),
Phase Difference Of Harmonic Voltage And Harmonic Current (Pphase)
Single Phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single Phase 3-wire
1P3W
3-Phase, 3-Wire,
2-Measurement
3P3W2M
3-Phase, 3-Wire,
3-Measurement
3P3W3M
3-Phase, 4-Wire
3P4W
Uphase[deg]=Uk
U1k
U4k
Uck=tan
-1
U1k
U2k
U4k
U12k
U32k
U4k
U12k
U23k
U31k
U4k
U1k
U2k
U3k
U4k
• For 3-phase 3-wire connections, indicated values represent harmonic calculation results obtained using line voltage.
• The harmonic voltage phase angle is displayed after correction using the reference channel’s fundamental
wave to 0.
• When Uckr=Ucki=0,
uk=0
• The harmonic voltage used in calculations is calculated using only whole-number orders.
Iphase[deg]=Ik
I1k
I4k
Ick=tan
-1
I1k
I2k
I4k
I1k
I2k
4k
I1k
I2k
I3k
I4k
I1k
I2k
I3k
I4k
• The harmonic voltage phase angle is displayed after correction using the reference channel’s fundamental
wave to 0.
• When Ickr=Icki=0,
Ik=0
• The harmonic voltage used in calculations is calculated using only whole-number orders.
Pphase[deg]=k
1k
ck
=
cIk
-
cUk
1k
2k
1k
2k
3k
sum
=tan
-1
sum
=tan
-1
sum
=tan
-1
sum
=tan
-1
• When Psumk=Qsumk=0,
k=0
• Psumk indicates the total harmonic power (see the equations for harmonic power).
• Qsumk indicates total harmonic reactive power (see the equations for harmonic reactive power).
Voltage Flicker (dV10), Short Interval Voltage Flicker (Pst), and Long Interval Voltage
Flicker (Plt)
Single Phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single Phase
3-wire
1P3W
3-Phase,
3-Wire,
2-Measurement
3P3W2M
3-Phase,
3-Wire,
3-Measurement
3P3W3M
3-Phase,
4-Wire
3P4W
dV10=V10
V10
(1)
V10
(c)
=
V10
(1)
V10
(2)
V10
(12)
V10
(32)
V10
(12)
V10
(23)
V10
(31)
V10
(1)
V10
(2)
V10
(3)
• Uf represents the reference voltage for voltage flicker and indicates the 1-minute average of RMS voltage values.
• an represents the flicker luminosity coefficient corresponding to the fluctuation frequency fn [Hz] calculated from
the flicker luminosity curve.
• Un represents the voltage fluctuation in fn.
Pst Pst
1
Pst
c
=
Pst
1
Pst
2
Pst
1
Pst
2
Pst
1
Pst
2
Pst
3
Pst
1
Pst
2
Pst
3
• Indicates values for K1=0.0314, K2=0.0525, K3=0.0657, K4=0.28, and K5=0.08.
• Calculations are performed using a 1,024-class cumulative probability function (CPF).
• Results are calculated from cumulative probability (Pi) values using linear interpolation, smoothed using the fol-
lowing methods, and used to calculate the cumulative probability (Pis):
P1s=(P0.7+P1+P1.5)/3, P3S=(P2.2+P3+P4)/3, P10s=(P6+P8+P10+P13+P17)/5, P50s=(P30+P50+P80)/3
Plt Plt
1
Plt
c
=
Plt
1
Plt
2
Plt
1
Plt
2
Plt
1
Plt
2
Plt
3
Plt
1
Plt
2
Plt
3
• N indicates the number of measurements (N=12). (When N<12, the number of measurements is used as N.)
Uckr
Ucki–
----------------
Ickr
Icki–
----------------
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
100
U
f
2
-------- -
a
n
U
n
2
K
1
P
0.1
K
2
P
1s
K
3
P
3s
K
4
P
10s
K
5
P
50s
+++ +
Pstn
3
n 1=
N
N
-------------------------------
3

 Loading...
Loading...