Appendix 7 Terminology
A
27
Appendix
Harmonic content
percentage
The ratio of the K-order size to the size of the fundamental wave, expressed as a percent-
age using the following equation:
K-order wave / fundamental wave × 100 [%]
By observing this value, it is possible to ascertain the harmonic component content for indi-
vidual orders. This metric provides a useful way to track the harmonic content percentage
when monitoring a specific order.
RMS value
The root mean square of instantaneous values for a quantity obtained over a particular time
interval or bandwidth.
Frequency cycle
(Freq wav or fwav)
The frequency of a single waveform. By measuring the frequency cycle, it is possible to
monitor frequency fluctuations on an interconnected system at a high degree of detail.
10-sec frequency
(Freq10s or f10s)
The frequency measured value as calculated according to IEC61000-4-30, consisting of a
10-second average of the frequency. It is recommended to measure this characteristic for
at least one week.
Interruption
A phenomenon in which the supply of power stops momentarily or for a short or long period
of time due to factors such as a circuit breaker tripping as a result of a power company
accident or power supply short-circuit.
Swell
A phenomenon in which the voltage rises momentarily due to a lightning strike or the
switching of a high-load power line.
Slide reference voltage
The voltage used as the reference for judging voltage dip and swell thresholds. The slide
reference voltage is calculated from a 1st-order filter with a time constant of 1 minute rela-
tive to RMS values. Although the fixed nominal input voltage value is usually used as the
reference voltage, dips and swells can be detected when the voltage value is fluctuating
gradually by using the fluctuating voltage value as the reference.
Zero suppression
Functionality for treating values that are less than a certain threshold as zero.
Zero, positive,
and negative phases
The positive phase can be considered normal 3-phase power consumption, while the neg-
ative phase functions to operate a 3-phase motor backwards. The positive phase causes
the motor to operate in the forward direction, while the negative phase act as a break and
causes heat to be generated, exerting a negative impact on the motor. Like the negative
phase, the zero phase is unnecessary. With a 3-phase 4-wire connection, the zero phase
causes current to flow and heat to be generated. Normally, an increase in the negative
phase causes an increase of the same magnitude in the zero phase.
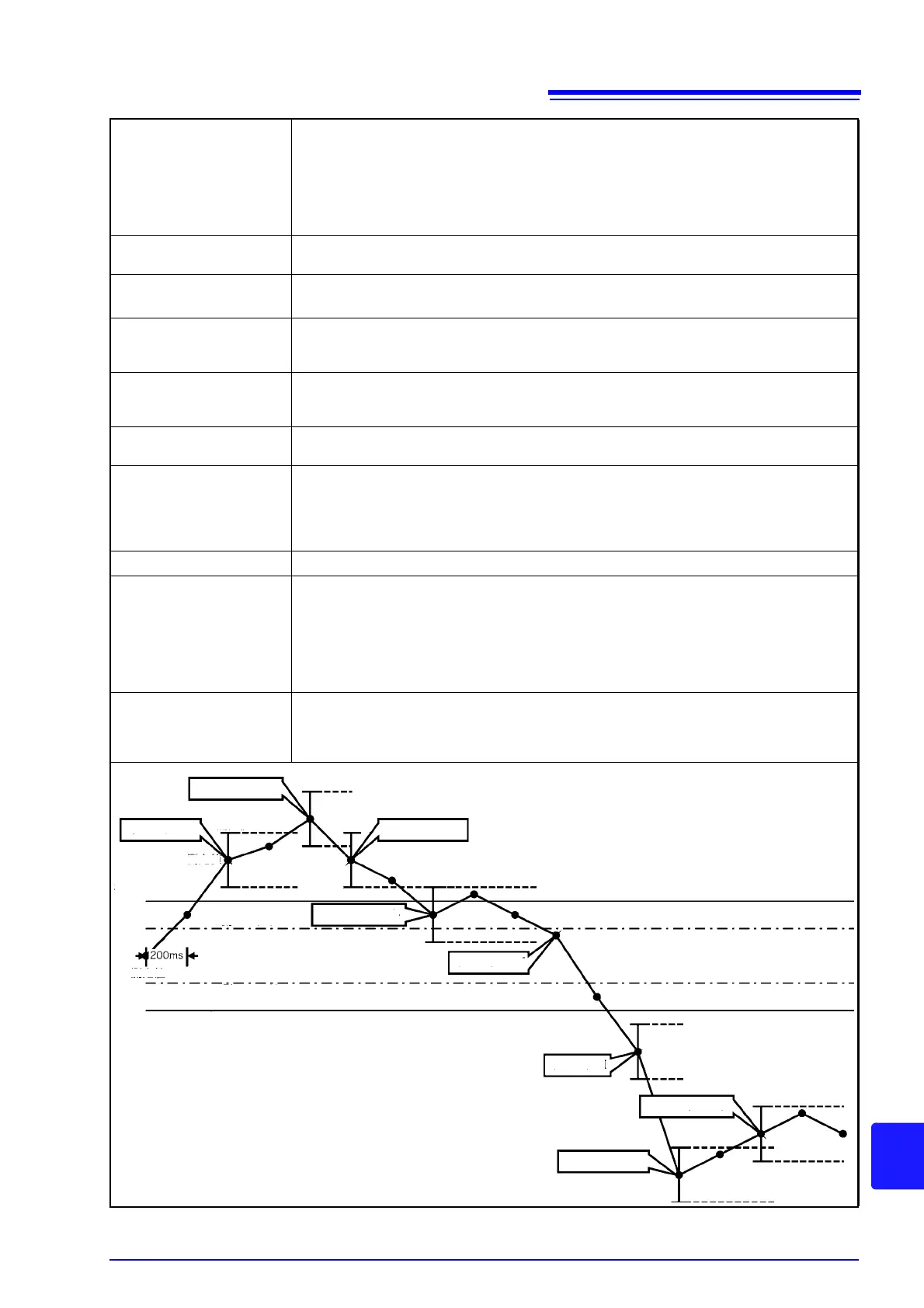
Sense
Measured values are continuously compared with the range defined by (the measured
value the last time the event occurred + the sense threshold) and (the measured value the
last time the event occurred - the sense threshold). When the value falls outside this range,
a sense event occurs, and the sense range is updated.
Sense event
High threshold
Low hysteresis
High hysteresis
Low threshold
Sense event
Sense event
Sense event
Event IN
Event IN
Event OUT
Sense event
Measurement
value + Sense
Measurement
value - Sense
Measurement value
Measurement value

 Loading...
Loading...