EasyBalancer EB 3500 Evaluation - Interpretation of vibration measurements
10 - 9
10.4 Interpretation of vibration measurements
Possible cause Comment Appearance Confirmation of cause
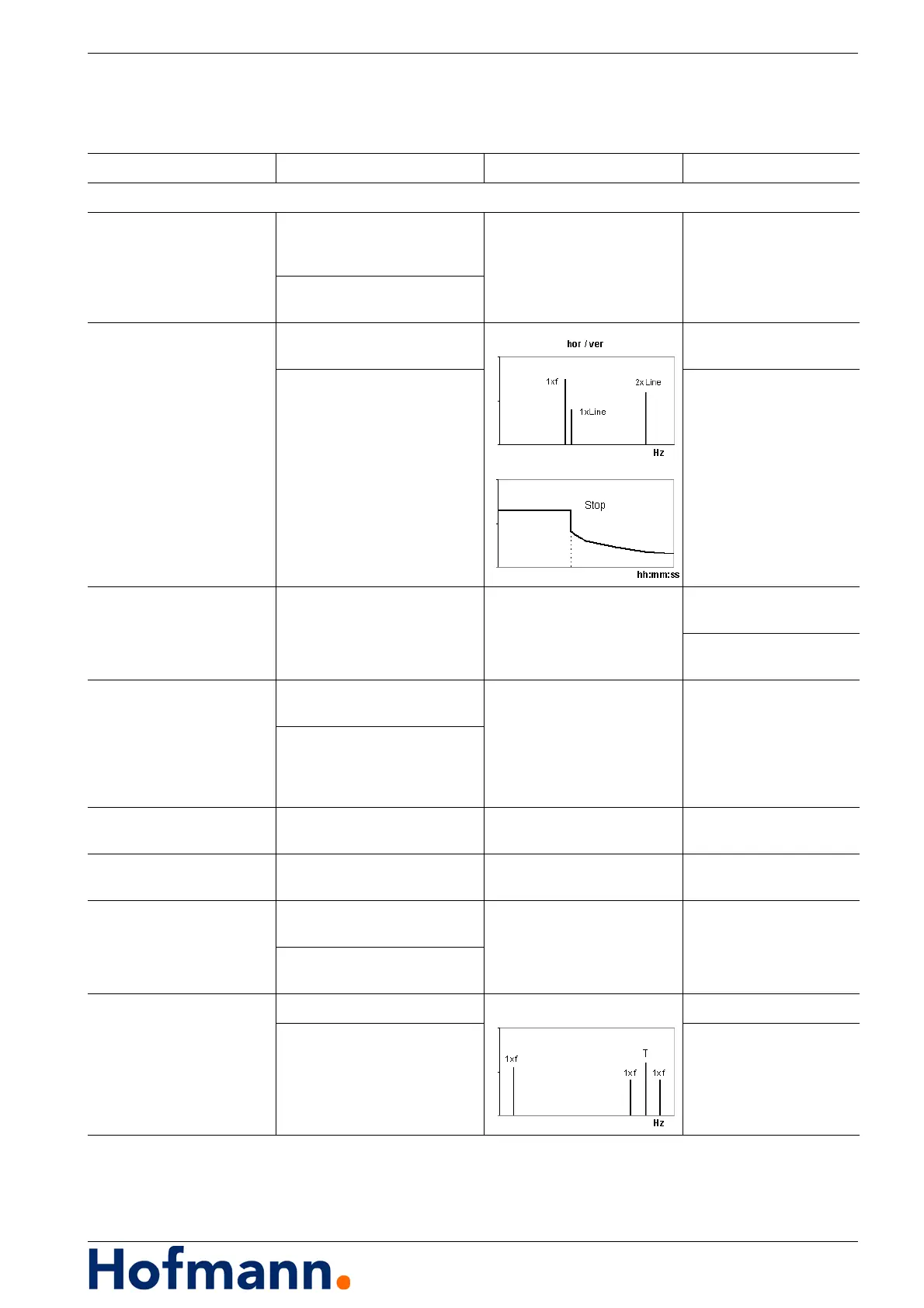
Vibrations with the machine speed 1x f
Unbalance High radial and low axial vibra-
tions with rotors located be-
tween bearings.
Balancing
High radial and high axial vibra-
tion with overhanging rotors.
Magnetic pull on electrical
machines
- Out-of-round rotor
- Eccentric bearing journal
- Bent rotor
- Broken winding
High radial and low
axial vibration
Measure concentricity
and clearance.
Possibly also single
and double line frequency
Vibration disappears
when switching off.
Magnetic pull on electrical
machines
- Axial offset
High radial and high
axial vibration
Check axial position
of rotor to stator.
Vibration disappears
when switching off.
Flat and centring errors
in couplings
High radial and high
axial vibration
Check alignment.
Often proportion with 2x f,
more rarely
3x f for couplings with flexible
intermediate elements
Bent shaft See flat and centring errors
in couplings
Check concentricity.
Bearing offset See flat and centring errors
in couplings
Check alignment of bear-
ing seats.
Eccentricity of pulley High radial and low
axial vibration
Check concentricity
Maximum amplitude in direction
of shaft centres
Eccentricity of gear wheel See eccentricity of pulley Check concentricity.
Tooth meshing frequency T with
1x f side straps
Tooth mesh frequency =
Rotational frequency x
Number of teeth.

 Loading...
Loading...