MAN-05359-001 -001 Rev. 001 page 5 of 32
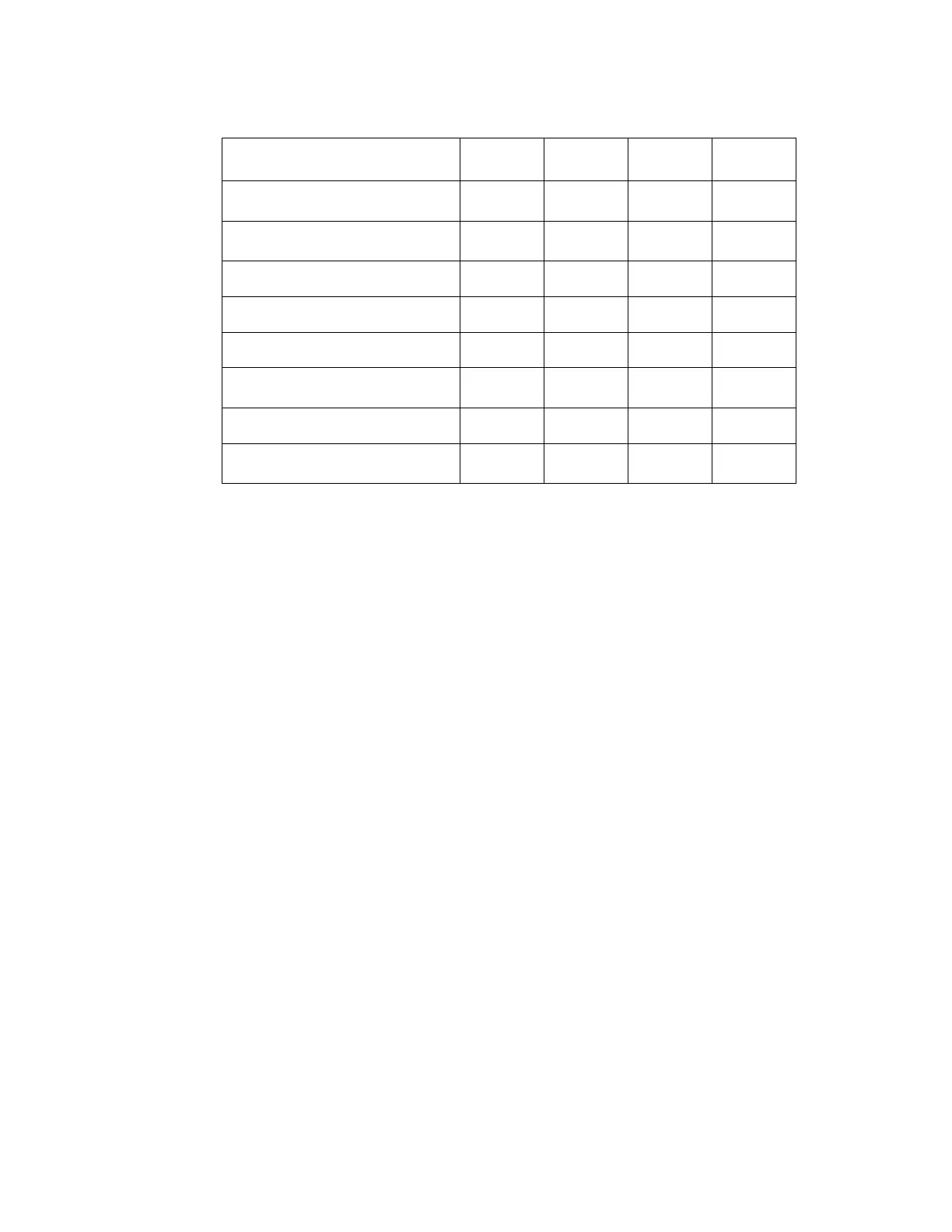
Table 1. Site Characteristics
Site 1 2 3 4
Screening (Low Risk)
Population
88% 82% 90% 94%
Referral (High Risk)
Population
12% 18% 10% 6%
HSIL+ prevalence
1.1% 0.7% 0.4% 0.6%
ThinPrep Pap Tests Per Year
120,000 70,200 280,000 105,000
Number of Cytotechnologists
14 9 32 11
Number of Cytotechnologists
in Study
2 2 2 2
Number of Cytopathologists
6 5 6 14
Number of Cytopathologists
in Study
1 2 1 2
G.1.2 Descriptive Diagnosis Sensitivity and Specificity Estimates
A panel of three independent cytopathologists adjudicated slides from all discordant (one-grade
or higher cytologic difference) descriptive diagnosis cases (639), all concordant positive cases
(355) and a random 5% subset of the 8550 negative concordant cases (428). The
cytopathologists on the adjudication panel were board-certified, all of whom had a subspecialty
certification in cytopathology. Their experience levels in cytopathology ranged from 6 to 12
years. Two of the adjudicators were from university practices and one adjudicator was from a
private medical center. The volumes for the adjudicators’ institutions ranged from 12,000 to
30,000 ThinPrep Pap Tests annually.
A consensus diagnosis was defined as agreement by at least 2 of 3 cytopathologists. All slides
sent to the panel of cytopathologists were not identified by site nor ordered in any fashion.
When a consensus diagnosis could not be obtained by at least 2 of 3 cytopathologists, the full
panel of cytopathologists reviewed each case simultaneously using a multi-headed microscope
to determine a consensus diagnosis.
The adjudicated results were used as a “gold standard” to define the following major “true”
descriptive diagnosis classifications of the Bethesda System: Negative, ASCUS, AGUS, LSIL,
HSIL, Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SQ CA) and Glandular Cell Carcinoma (GL CA). Estimates
of sensitivity and specificity together with 95% confidence intervals were calculated for the
Manual Review and Imager Review arms of the study. The differences in sensitivity and
specificity between the two arms, together with their 95% confidence intervals were also
calculated. Among the random 5% subset of 8,550 cases (428 slides) that were found to be
negative by both arms and adjudicated, there were 425 “true” negative and 3 “true” ASCUS
slides. A multiple imputation technique was used to adjust the numbers of true positives and
true negatives for the 8,550 negative concordant cases based on the 5% of cases that were
adjudicated
2
.
Table 2 summarizes the descriptive diagnosis sensitivity and specificity estimates with 95%
confidence intervals for all sites combined for “true” ASCUS+, LSIL+ and HSIL+.
 Loading...
Loading...