63
Device Comparison process
Configuration BPDU on
ports after comparison
• Device C finds that the root path cost of Port C1 (10)
(root path cost of the received configuration BPDU (0)
plus path cost of Port C1 (10)) is larger than that of Port
C2 (9) (root path cost of the received configuration BPDU
(5) plus path cost of Port C2 (4)), decides that the
configuration BPDU of Port C2 is the optimum, and
selects Port C2 as the root port with the configuration
BPDU unchanged.
• Based on the configuration BPDU and path cost of the
root port, Device C calculates a designated port
configuration BPDU for Port C1 {0, 9, 2, Port C1} and
compares it with the existing configuration BPDU of Port
C1 {0, 0, 0, Port A2}. Device C finds that the existing
configuration BPDU is superior to the calculated one and
blocks Port C1 with the configuration BPDU unchanged.
Then Port C1 does not forward data until a spanning
tree calculation process is triggered by a new event, for
example, the link between Device B and Device C is
down.
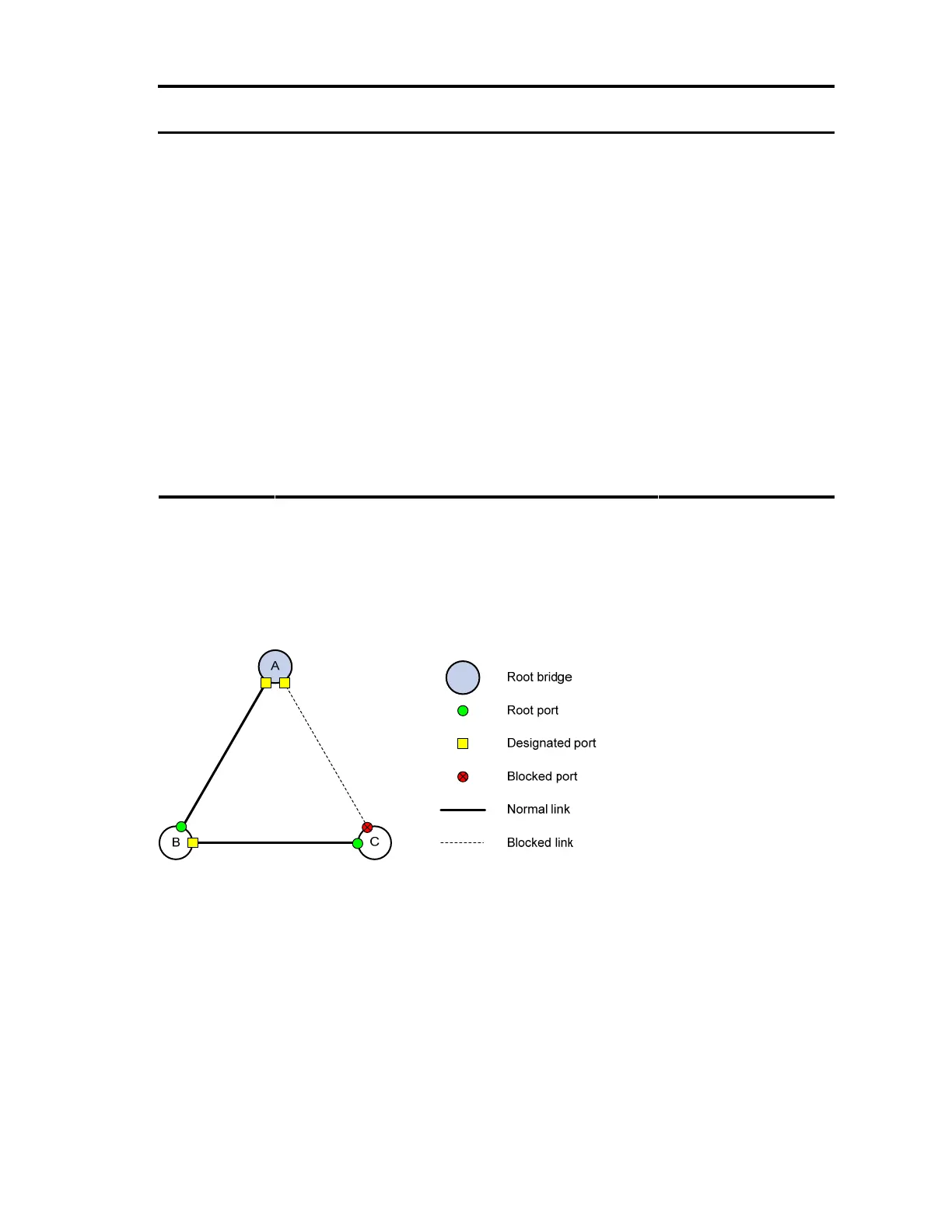
• Blocked port (Port C1):
{0, 0, 0, Port A2}
• Root port (Port C2):
{0, 5, 1, Port B2}
In Table 13, each configuration BPDU contains the following fields: root bridge ID, root path cost,
designated bridge ID, and designated port ID.
After the comparison processes described in Table 13,
a spanning tree with Device A as the root bridge
is established, and the topology is shown in Figure 19.
Figure 19 Topology of the final calculated spanning tree
The spanning tree calculation process in this example is only simplified process.
The BPDU forwarding mechanism in STP
STP forwards configuration BPDUs following these guidelines:
• Upon network initiation, every switch regards itself as the root bridge, generates configuration
BPDUs with itself as the root, and sends the configuration BPDUs at a regular hello interval.
• If it is the root port that received a configuration BPDU and the received configuration BPDU is
superior to the configuration BPDU of the port, the device increases the message age carried in the
configuration BPDU following a certain rule and starts a timer to time the configuration BPDU while
sending out this configuration BPDU through the designated port.
• If the configuration BPDU received on a designated port has a lower priority than the configuration
BPDU of the local port, the port immediately sends out its own configuration BPDU in response.

 Loading...
Loading...