5 - 41
XTC/3 Operating Manual
5.3.5.4 XTC/2 UPDATE Command
The Update command replaces the current parameter value with the DATA Sent.
To update film parameters the format of the update command is:
U pp F vvv - Parameter pp of film F, value vvv.
Update parameter pp of film F, with value vvv, a space is used as a delimiter
between the pp and F values as well as the F and vvv values, where F is a digit
between 1 and 9. Refer to Table 5-7 for a numbered list of parameters and their
limits. If value vvv is left blank, the command will be accepted and a value of 0 will
be transmitted.
NOTE: If pp is set to 99, the data is a list of all parameters in the order specified.
This command allows a rapid block transfer of data which is convenient for
downloading films. Each parameter value must be separated by a space.
To update layers, the format of the update command is:
U 40 L v
Where 40 designates a layer is to be updated. The value L indicates which layer to
update. The value of L can be 1, 2, or 3, and v designates the film number to insert
into layer L.
For example, the update command
U 40 1 4
will enter film number 4 into layer 1.
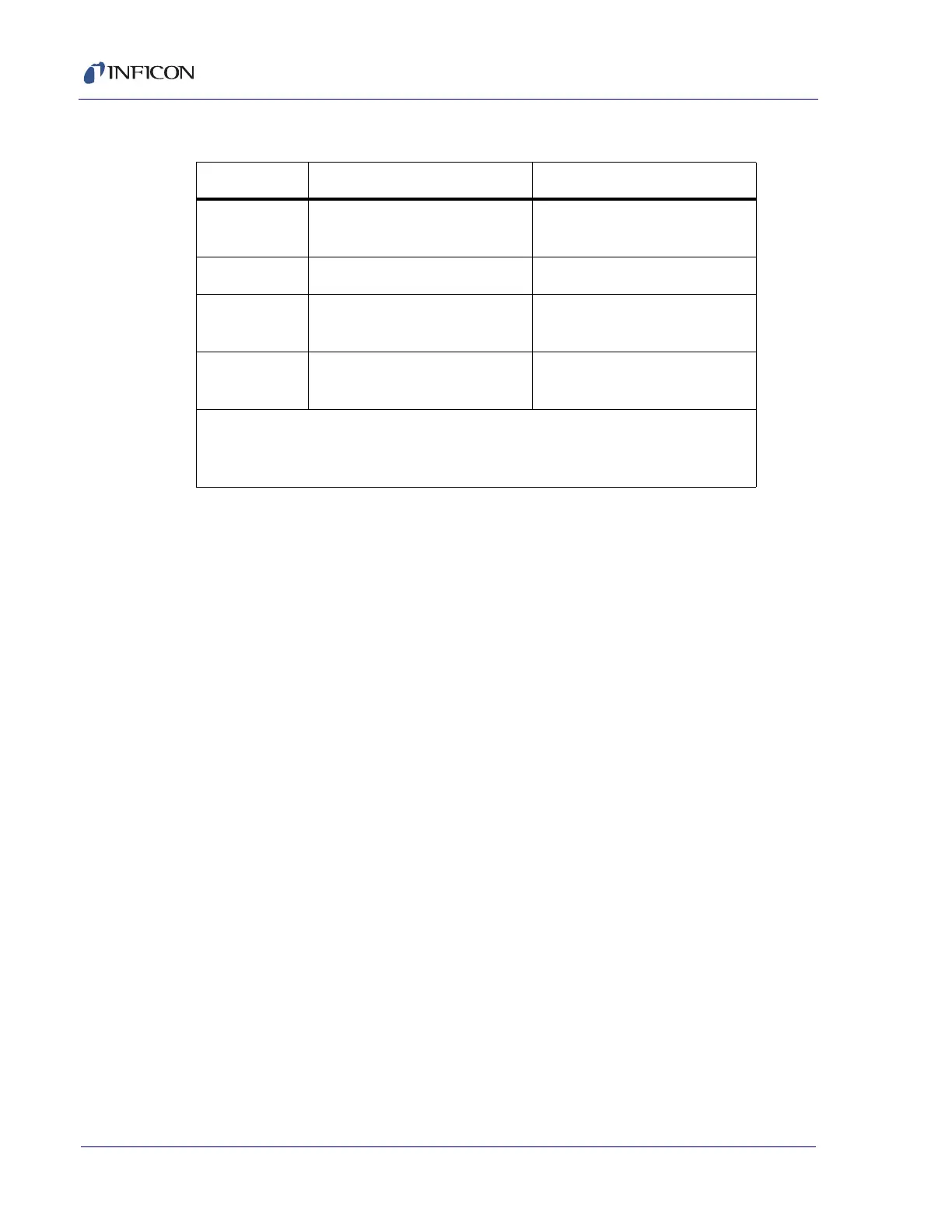
Table 5-8 Q40 command responses
Command XTC/3S Response XTC/3M Response
Q40 0 "a 0 0 " (a = 1 to 9,
0 = no film in layer)
"a b c" (a = 1 to 32, b = 0 to 32,
c = 0 to 32)
Q40 1 "a" (a = 1 to 9) "a" (a = 1 to 32)
Q40 2 "No Data" error "b" if b = 1 to 32
"No Data" error if b = 0
Q40 3 "No Data" error "c" if c = 1 to 32
"No Data" error if c= 0
a = Film # in Layer 1
b = Film # in Layer 2
c = Film # in Layer 3
 Loading...
Loading...