Page 36 / 89 Section 5. Software control – Using Lightware Device Controller (LDC)
There are two types of EDID emulation: static and dynamic.
Static EDID emulation happens, when an EDID from the Factory or User EDID
list is selected. In this case the Emulated EDID will remain the same until the user
emulates another EDID.
Dynamic EDID emulation can be enabled by selecting D1 or D2 EDID memory.
The attached monitor’s EDID is copied to the input; if a new monitor is attached to
the output, the emulated EDID changes automatically.
5.8.2. Changing emulated EDID
Step 1. Select the desired EDID list from one of the three sources by pressing its button.
Step 2. Select an EDID from the Source panel to emulate.
Step 3. Press Emulated button on the top of the Destination panel.
Step 4. Select desired port on the right panel (more than one ports can also be selected);
the EDID(s) will be highlighted with yellow cursor.
Step 5. Press Transfer button to change the emulated EDID.
5.8.3. Exporting an EDID
Source EDID can be downloaded as a file (*.bin, *.dat or *.edid) to the computer.
Step 1. Select the desired EDID from the Source panel (highlighted with yellow cursor).
Step 2. Press the Save button to open the Save as dialog and download the file to the
computer.
5.8.4. Importing an EDID
Previously saved EDID (*.bin, *.dat or *.edid file) can be uploaded to the user memory:
Step 1. Press the User button on the top of the Source panel.
Step 2. Select a memory slot from the Source panel.
Step 3. Press the Upload button below the Source panel.
Step 4. Browse the file in the opening window then press the Open button. Browsed EDID
is imported into the selected User memory.
Info: The imported EDID overwrites the selected memory place even if it is not empty.
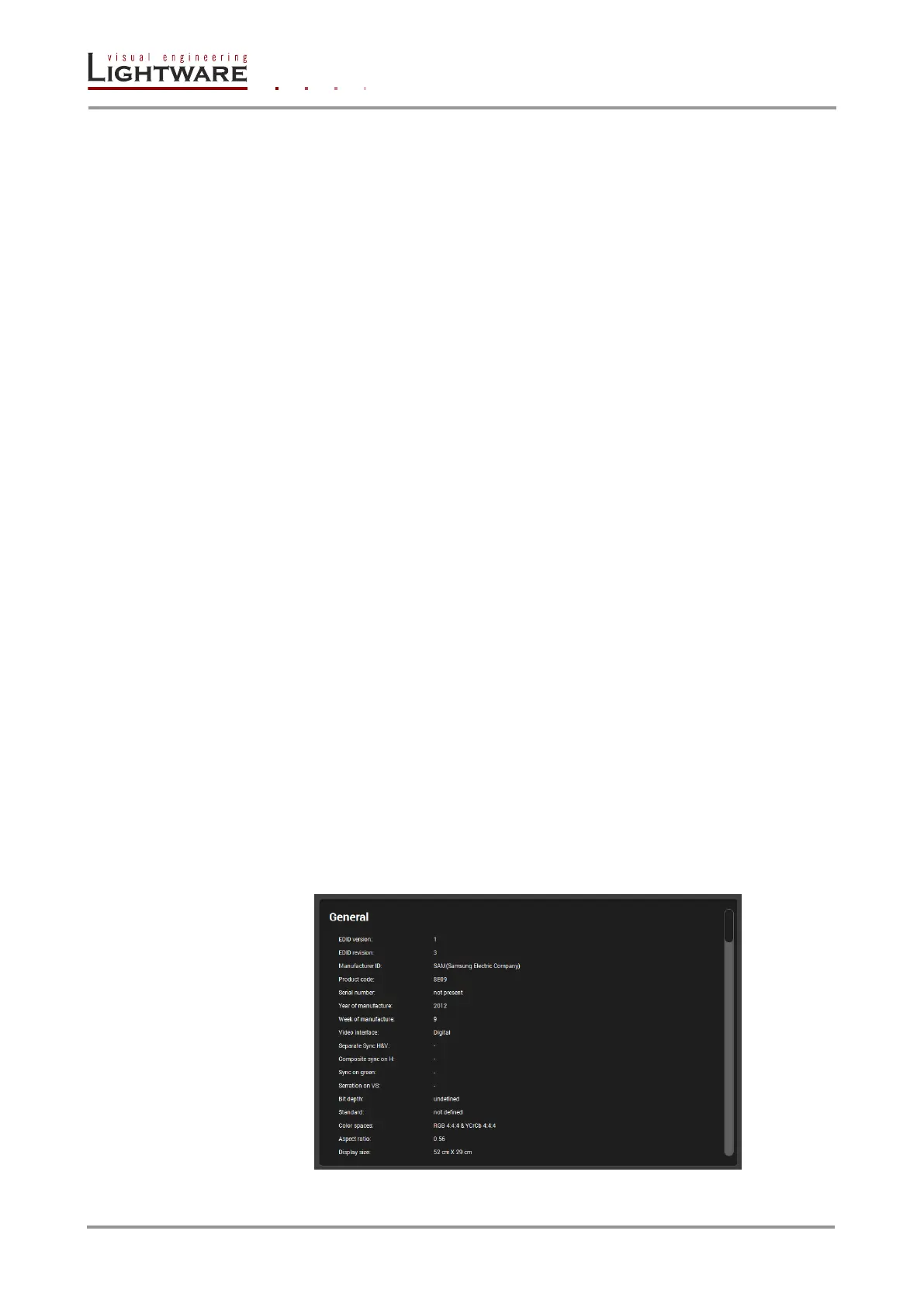
5.8.5. EDID Summary window
Select an EDID from Source panel and press Info button to display the EDID summary.
Figure 5-4. EDID Summary

 Loading...
Loading...











