4G9 ENGINE (E-W)
-
Crankshaft, Cylinder Block, Flywheel and Drive Plate
11A-12-6
PWEE9502-A
E
Nov. 1995Mitsubishi Motors Corporation Revised
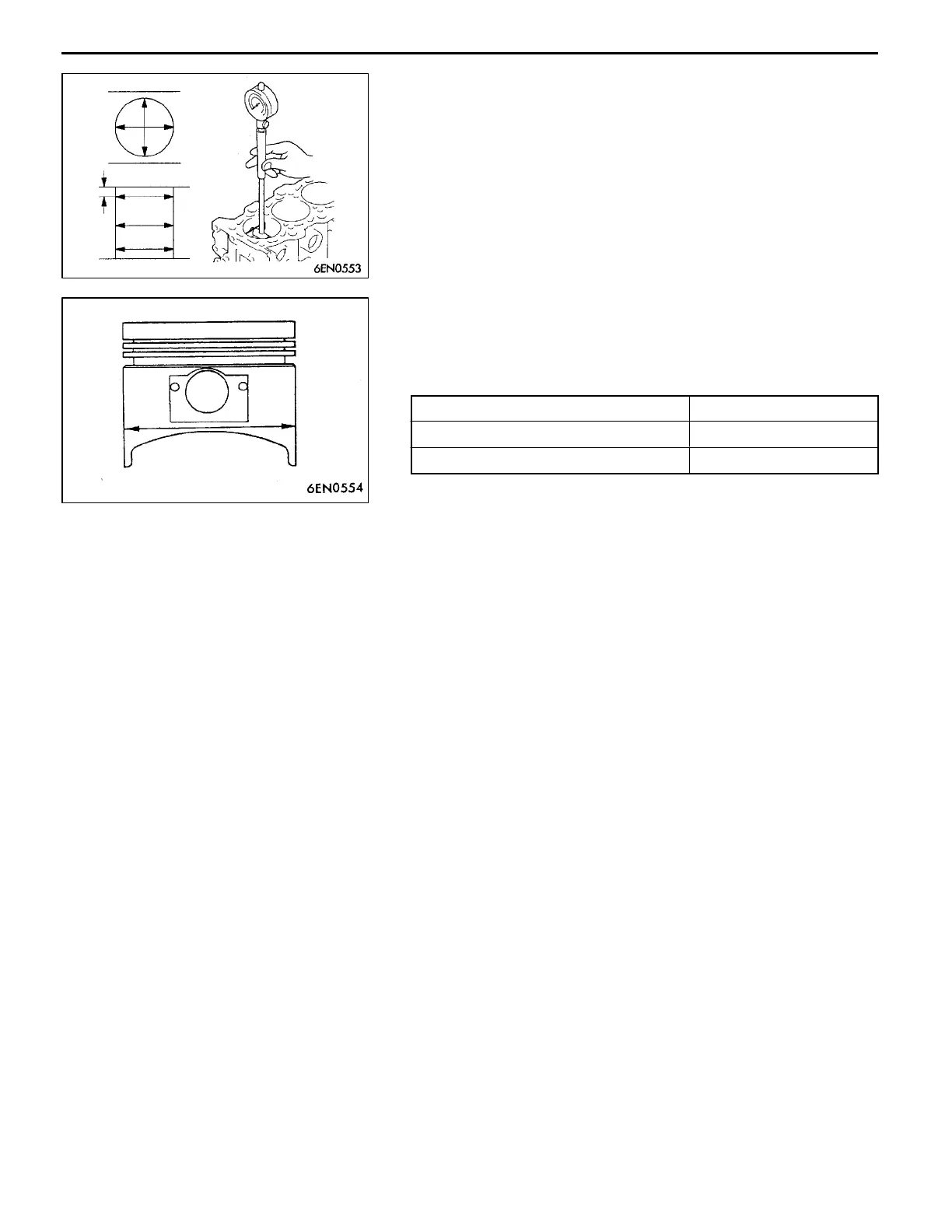
(4) Using a cylinder gauge, measure the cylinder bore and
cylindricity. If worn badly, correct the cylinder to an
oversize a nd replace the piston and piston rings. Measure
at the points shown in illustration.
Standard value:
Cylinder inner diameter: 81.00 - 81.03 mm
Out-of-roundness and taper of cylinder bore: 0.01
mm or less
BORING CYLINDER
(1) Oversize pistons to be used should be determined on
the basis of the largest bore cylinder.
Piston size identification
Size Identification mark
0.50 mm O.S. 0.50
1.00 mm O.S. 1.00
NOTE
Size mark is stamped on the piston top.
(2) Measure outside diameter of piston to be used. Measure
it in thrust direction as shown.
(3) Based on the measured piston O.D., calculate the boring
finish dimension.
Boring finish dimension = Piston O.D. + (Clearance
between piston O.D. and cylinder) - 0.02 mm
(honing margin)
(4) Bore all cylinders to the calculated boring finish dimension.
Caution
To prevent distortion that may result from temperature
rise during honing, bore cylinders, in the order of
No. 2, No. 4, No.1 and No. 3.
(5) Hone to the final finish dimension (Piston O.D. + clearance
between piston O.D. and cylinder.)
(6) Check the clearance between piston and cylinder.
Clearance between piston and cylinder:
0.02 - 0.04 mm
NOTE
When boring cylinders, finish all of four cylinders to the
same oversize. Do not bore only one cylinder to an
oversize.
A
B
12 mm
Centre
Bottom
Piston O.D.
Thrust
direction

 Loading...
Loading...