503
FX3G/FX3U/FX3GC/FX3UC Series
Programming Manual - Basic & Applied Instruction Edition
18 Floating Point – FNC110 to FNC139
18.12 FNC124 – EXP / Floating Point Exponent
11
FNC30-FNC39
Rotation and
Shift
12
FNC40-FNC49
Data Operation
13
FNC50-FNC59
High-Speed
Processing
14
FMC60-FNC69
Handy
Instruction
15
FNC70-FNC79
External FX I/O
Device
16
FNC80-FNC89
External FX
Device
17
FNC100-FNC109
Data
Transfer 2
18
FNC110-FNC139
Floating Point
19
FNC140-FNC149
Data
Operation 2
20
FNC150-FNC159
Positioning
Control
Program example
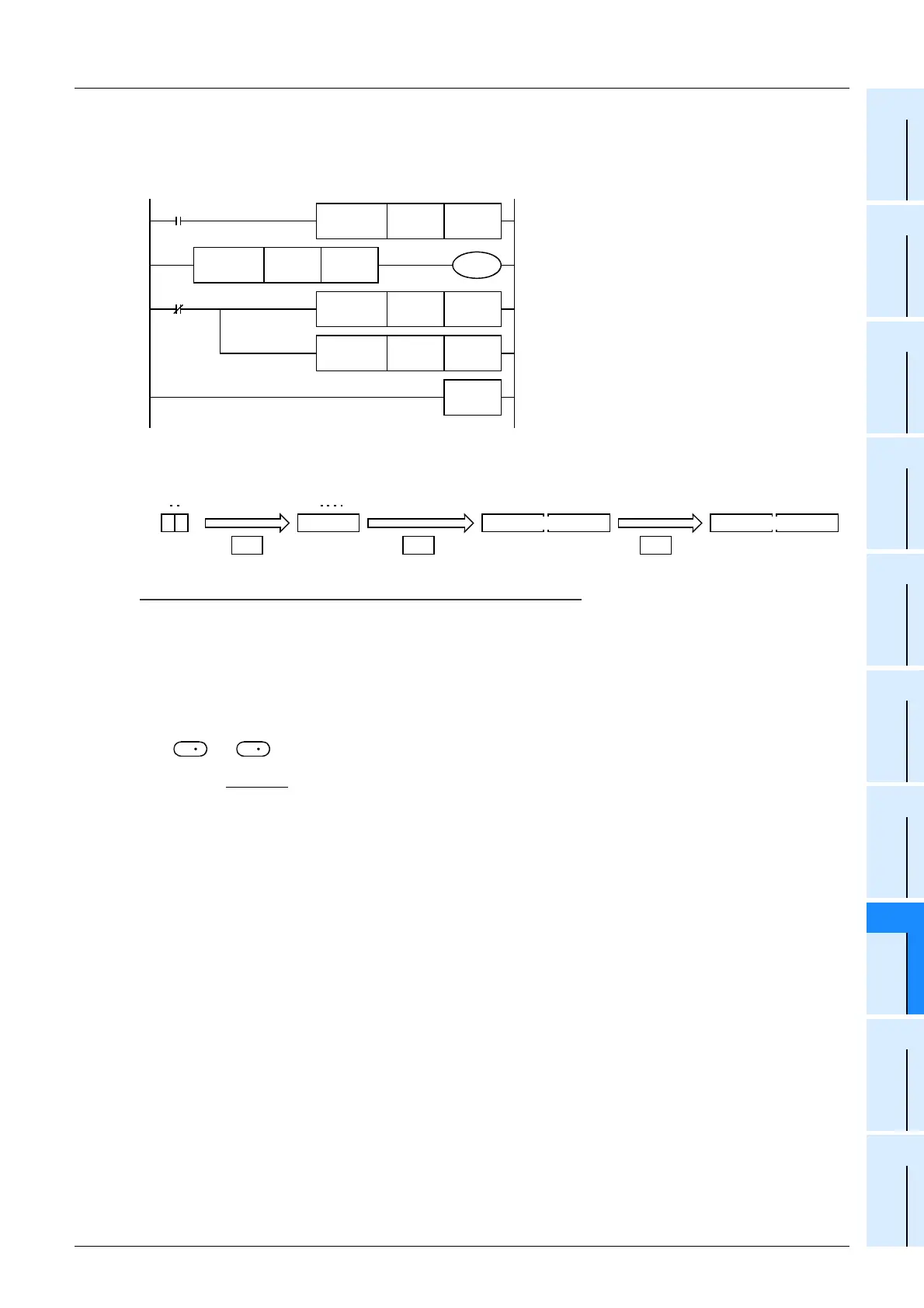
In the program example shown below, the exponential operation is executed for a value set in the 2-digit BCD format
in X020 to X027, and the operation result is stored in the binary floating point format to D0 and D1 when X000 turns
ON.
Operation when "13" is specified in X020 to X027
Points
1) The operation result becomes less than "2
128
" when the BCD value set in X020 to X027 is "88" or less because of
"loge2
128
= 88.7".
If a value "89" or more is set, an operation error occurs. To prevent this operation error, when a value more than
"89" is set, M0 is set to ON so that the exponential operation is not executed.
2) Conversion from natural logarithm into common logarithm
In the CPU, operations are executed in natural logarithm.
For obtaining a value in common logarithm, specify a common logarithm value divided by "0.4342945" in
[+1, ].
X000
FNC224
LD >
D20
M0
Data used in the exponential operation is input ([1]).
The range of the value to be operated is checked.
(Refer to 1) in "Points" below.)
The input data is converted into binary floating point
(real number) ([2]).
The exponential operation is executed ([3]).
K88
FNC 19
BIN
K2X20 D20
FNC 49
FLT
D20 D10
FNC124
DEXP
D10 D0
END
M0
Binary floating point
(real number) value
13
1 3
[1]
Conversion
into binary
BIN
13
b15 b0
[2] Conversion into
binary floating point
(real number)
[3]
Exponential
operation
EXP
D11 D10
Binary floating point
(real number) value
442413.4
D1 D0
FLT
D20
X027 X020
BCD value
Binary value
S
S
10
X
=
e
0.4342945
X

 Loading...
Loading...