You can also specify the timer setpoint value with a decimal value stored in a data register. See
section 5.7.1 for details.
Retentive timers
In addition to the normal timers described above the controllers of the MELSEC System Q also
have retentive timers that retain their current time counter value even if the device controlling
them is switched off.
The current timer counter value is stored in a memory that is retained even in the event of a
power failure.
The device identifier for retentive timer is "ST". Similar to "normal" timers, retentive timers can
be programmed as low speed or high speed timers.
NOTE When shipped, 2048 (2k) normal timers are set in the parameters of an PLC CPU and no re-
tentive timers. In order to use retentive timers, the number of these timers must be set in the
PLC parameters.
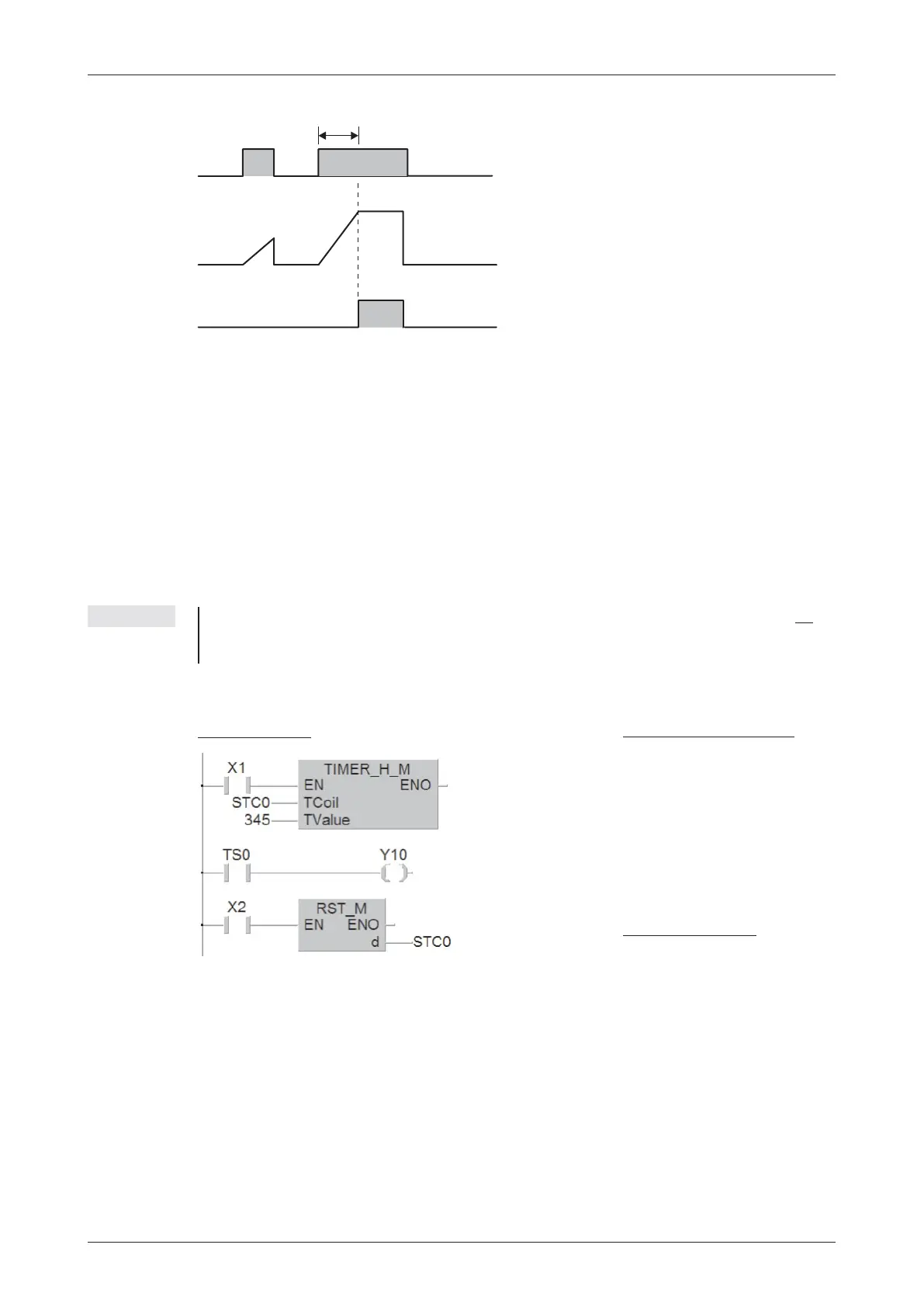
Example of a program using a retentive timer as high speed timer:
Timer T0 is started when input X1 is switched on. The setpoint value is 345 x 10ms = 3.45s.
When the setpoint value is reached T0 switches output Y10 on. Input X2 resets the timer and
switches its output off.
MELSEC System Q Beginners Manual 5 – 7
Devices in Detail Timers
The timer continues to count the internal
100ms pulses as long as X0 remains on.
When the setpoint value is reached the
output of T1 is switched on.
If input X0 or the power supply of the PLC
are switched off the timer is reset and its
output is also switched off.
Ladder Diagram
MELSEC Instruction List
LD X1
OUTH ST0
K345
LD ST0
OUT Y10
LD X2
RST ST0
IEC
Instruction List
LD X1
TIMER_H_M STC0, 345
LD STS0
OUT Y10
LD X2
RSTC0
X0
T1
Y10
12,3 s

 Loading...
Loading...











