6.2.3 Moving blocks of data with the BMOV instruction
The MOV instruction described in section 6.2.1 can only write single 16 or 32 bit values to a
destination. If you want, you can program multiple sequences of MOV instructions to move
contiguous blocks of data. However, it is more efficient to use the BMOV (Block MOVe) instruc
-
tion, which is provided specifically for this purpose.
쐃
Data source (16-bit device, first device in source range)
쐇
Data destination (16-bit device, first device in destination range)
쐋
Number of elements to be moved
The example above works as follows:
BMOV also has a pulse-triggered version, BMOVP (see section 6.2.1 for details on pulse-trig-
gered execution).
Blocks of bit devices:When you move blocks of bit devices with BMOV the K factors of the data
source and the data destination must always be identical.
Example
–
Data source: K1M0
–
Data destination: K1Y0
–
Number of elements to be moved: 2
6–16 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Instructions for Moving Data More Advanced Programming
M0
M1
M2
M3
Y000
Y001
Y002
Y003
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
M4
M5
M6
M7
Y004
Y005
Y006
Y007
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
This copies 2 blocks with 4 bit
devices each.
Ladder Diagram
MELSEC Instruction List
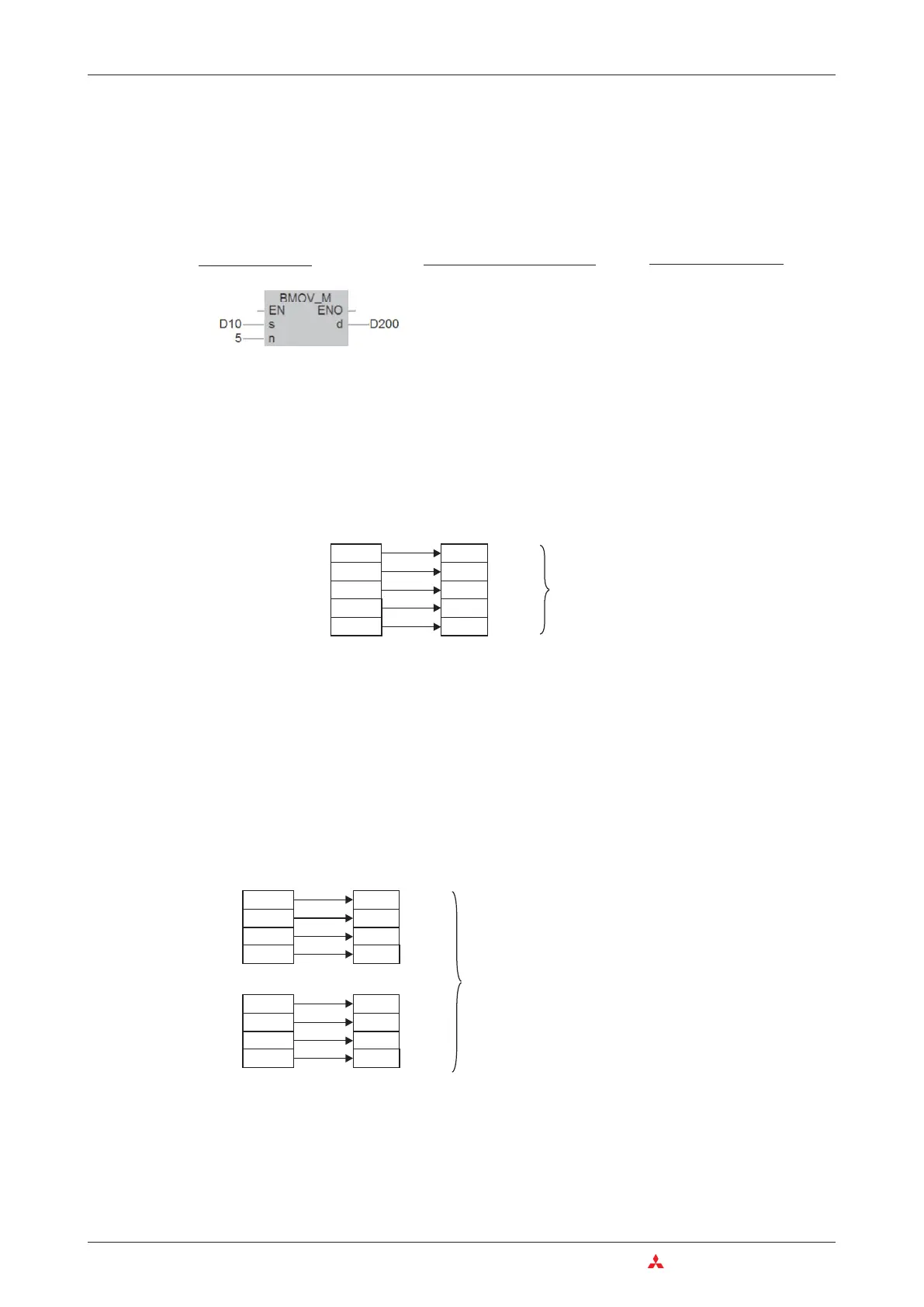
BMOV D10
D200
K5
IEC Instruction List
BMOV_M D10, 5, D200
D 10
D 11
D 12
D 13
D 200
D 201
D 202
D 203
D 14
D 204
1234
5678
-156
8765
4321
1234
5678
-156
8765
4321
5 Data registers
Data source (D10)
Data destination (D200)

 Loading...
Loading...











