4.9 Programming PLC Applications
Programmable logic controllers provide an almost unlimited number of ways to link inputs with
outputs. Your task is to choose the right instructions from the many supported by the control
-
lers of the MELSEC System Q to program a suitable solution for your application.
This chapter provides a simple example that demonstrate the development of a PLC applica
-
tion from the definition of the task to the finished program.
4.9.1 A rolling shutter gate
The first step is to have a clear concept of what you want to do. This means that you need to
take a “bottom-up” approach and write a clear description of what it is you want the PLC to do.
Task description
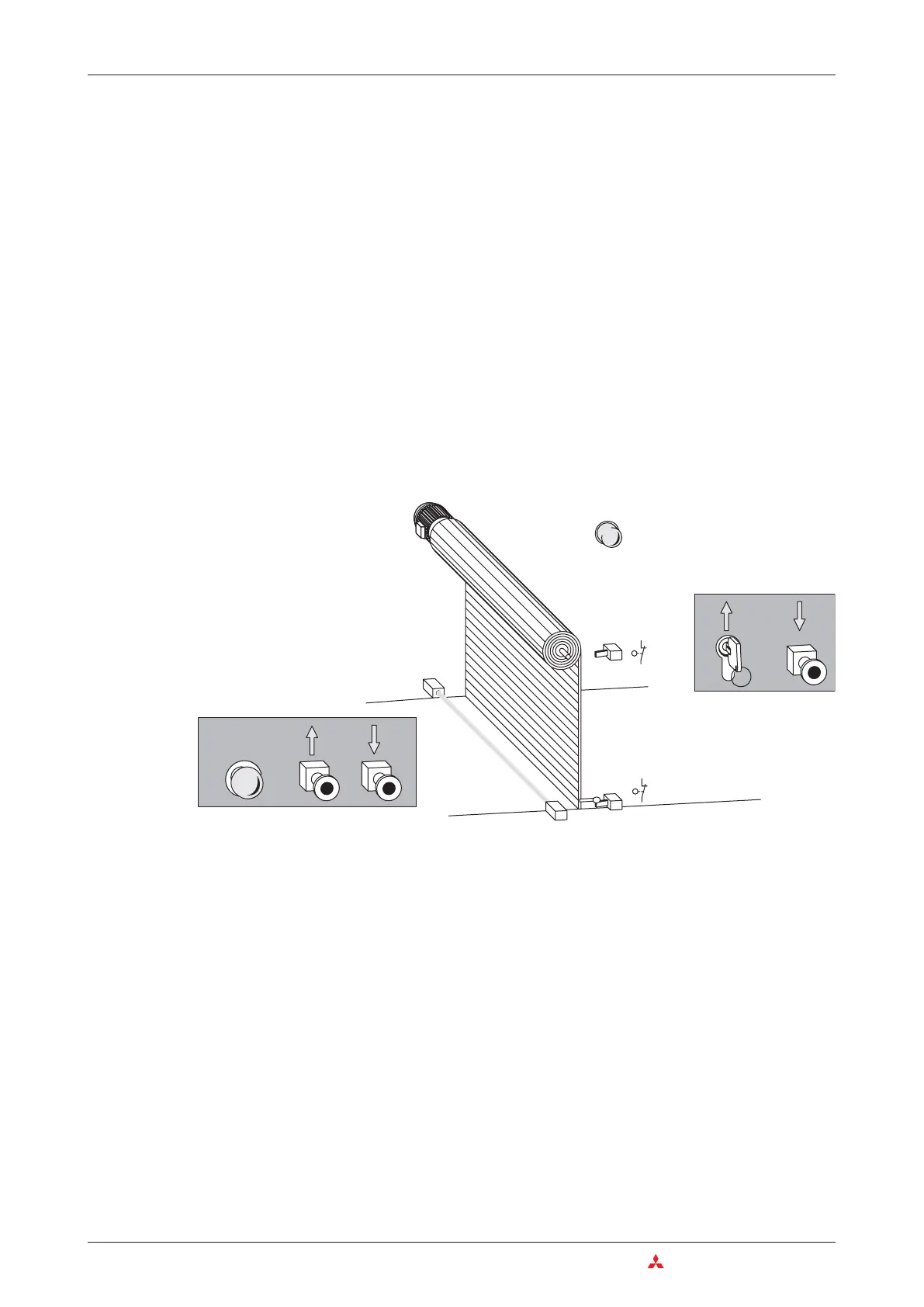
We want to implement a control system for a warehouse’s rolling shutter gate that will enable
easy operation from both outside and inside. Safety facilities must also be integrated in the
system.
쎲
Operation
–
It must be possible to open the gate from outside with the key-operated switch S1 and to
close it with pushbutton S5. Inside the hall it should be possible to open the gate with
pushbutton S2 and to close it with S4.
–
An additional time switch must close the gate automatically if it is open for longer than
20 s.
–
The states “gate in motion” and “gate in undefined position” must be indicated by a
blinking warning lamp.
쎲
Safety facilities
–
A stop button (S0) must be installed that can halt the motion of the gate immediately at any
time, stopping the gate in its current position. This Stop switch is not an Emergency OFF
function, however! The switch signal is only processed by the PLC and does not switch any
external power connections.
4–34 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Programming PLC Applications An Introduction to Programming
STOP
S1
WarninglampH1
S5
S3
S6
S7
S0 S2 S4

 Loading...
Loading...











