6.4 Math Instructions
All the controllers of the MELSEC System Q can perform all four basic arithmetical operations
and can add, subtract, multiply and divide. MELSEC instructions are available for math opera
-
tions with binary values, binary block data, BCD values and character strings.
When you edit your program with GX IEC Developer in Ladder Diagram or IEC instruction list
additional IEC instructions can be used. In this chapter only these IEC instructions are
described. MELSEC instructions are covered in detail in the Programming Manual for the A/Q
series and the MELSEC System Q, art. no. 87431.
The IEC instructions for addition, subtraction, multiplication und division can be applied for the
data types INT (16-bit integer), DINT (32-bit integer) or REAL (floating decimal point values).
Please note that DINT and REAL devices can not assigned directly to these instructions and
must be defined as variables before (see chapter 4.6.2).
6.4.1 Addition
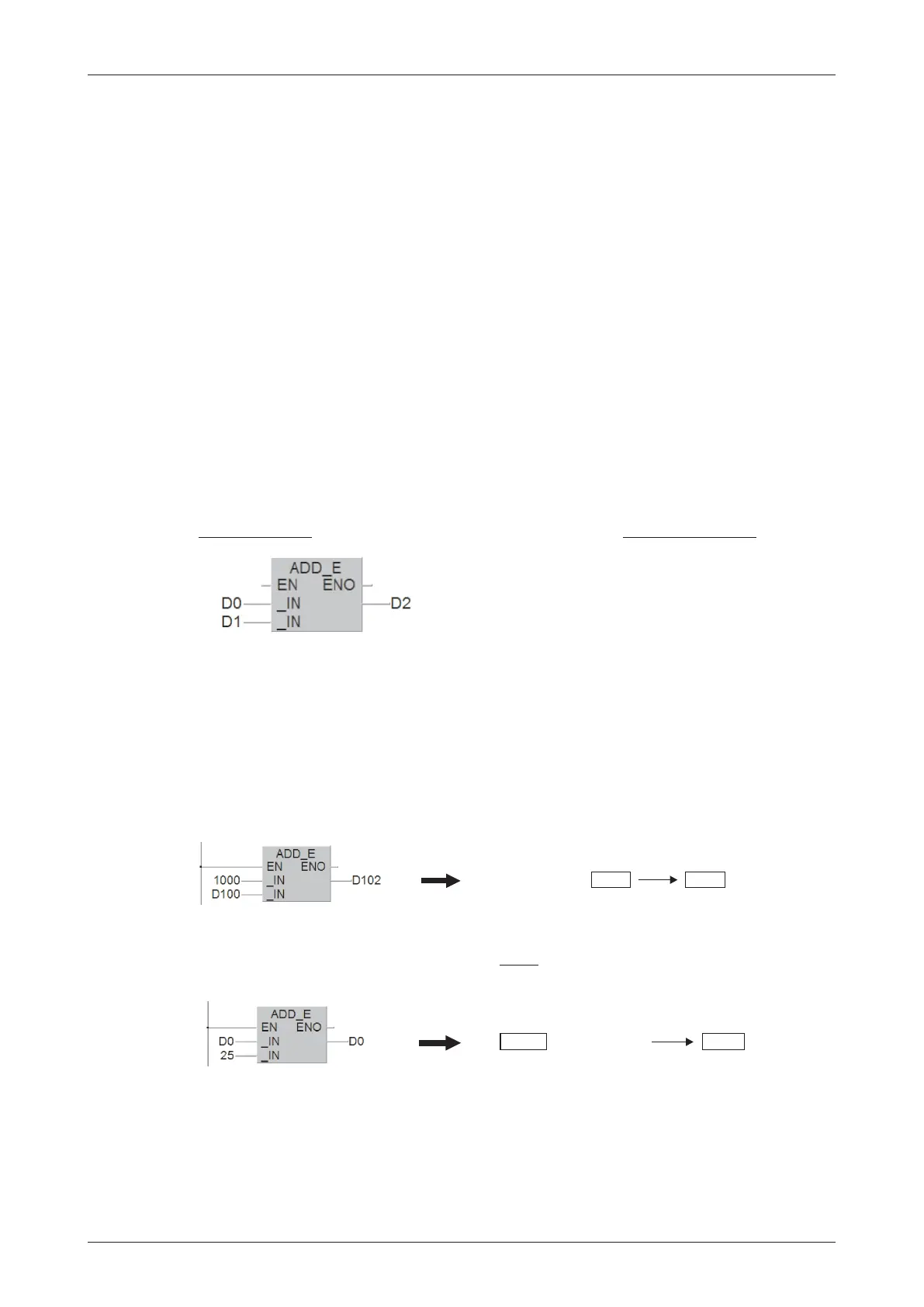
The ADD instruction calculates the sum of two values and writes the result to another device.
쐃
First source device or constant
쐇
Second source device or constant
쐋
Device in which the result of the addition is stored
The example above adds the contents of D0 and D1 and writes the result to D2.
Examples
Add 1,000 to the contents of data register D100:
If you want you can also write the result to one of the source devices. However, if you do this
remember that the result will then change in every
program cycle if the ADD instruction is exe
-
cuted cyclically!
The signs of the values are taken into account by the ADD instruction (e. g. 10 + (-5) = 5).
The data types of the input and output variable of the ADD instruction must be identical. This
can cause problems when the result of the addition exceeds the value range of the variables.
For example, when you add the two integer values (16 bit) "32700" and "100" the result stored
is not "32800" as expected but "-32736" since the maximum value of a 16 bit variable is
"32767". An overflow is interpreted as negative value and will lead to a wrong result.
MELSEC System Q Beginners Manual 6 – 25
More Advanced Programming Math Instructions
Ladder Diagram
IEC Instruction List
LD D0
ADD D1
ST D2
1000
53+
D 100
D 102
1053
18
25
D 0
+
D 0
43

 Loading...
Loading...











